WMS:What's new in WMS version 10.0
The WMS software development team is excited about the release of WMS 10.0! This page lists the exciting new features that have been added to WMS 10.0.
What's new in WMS 10.0
GSSHA Interface and Model Updates
Model Calibration Updates
The newest version of GSSHA supports PEST-style automated calibration methods. WMS 10.0 has an interface to these automated calibration methods in GSSHA. WMS 10.0 allows you to have multiple calibration points and allows you to calibrate to observations other than outlet flow values such as depths, snow water equivalent, and other parameters. More information about automated calibration in GSSHA using WMS 10.0 is located here and here.
Depth Varying Overland Flow Roughness
The newest version of GSSHA has a mapping table that supports a depth-varying overland flow roughness exponent. This parameter is used in addition to the roughness mapping table. Without the addition of this table, a default exponent of 0.0 is used, which means the roughness does not change with overland flow depth.
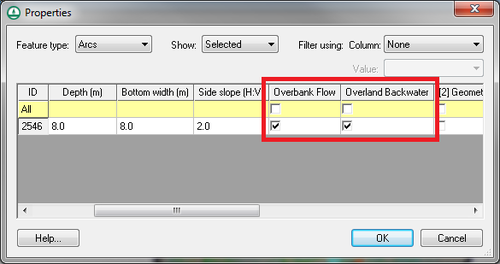
Link/Node-Specific Overbank and Backwater Options
GSSHA previously had two options that could be defined globally. The first option, the overbank flow option (OVERBANK_FLOW), increases the level of connection between the overland flow and the channel in the 1D hydraulic model by allowing water to spill from the channel back onto the overland flow plane. If the second option, the overland backwater option (OVERLAND_BACKWATER), is turned on, flow from the overland flow model to the channel in the 1D hydraulic model is restricted if the elevation of the water in the channel exceeds the overland cell elevation. This option can now be defined at each of the arcs (links) in your GSSHA model in the GSSHA arc properties dialog. If this option is defined for one of the arcs, the global option is turned off.
Storm and Tile Drain Interface Tools
WMS 10.0 contains many new GSSHA storm and tile drain interface tools. A detailed description of all the tools is available here.
New GSSHA Tutorial
Several of the GSSHA tutorials have been updated to reflect changes to GSSHA and its interface, especially the storm and tile drain tutorial and the calibration tutorial.
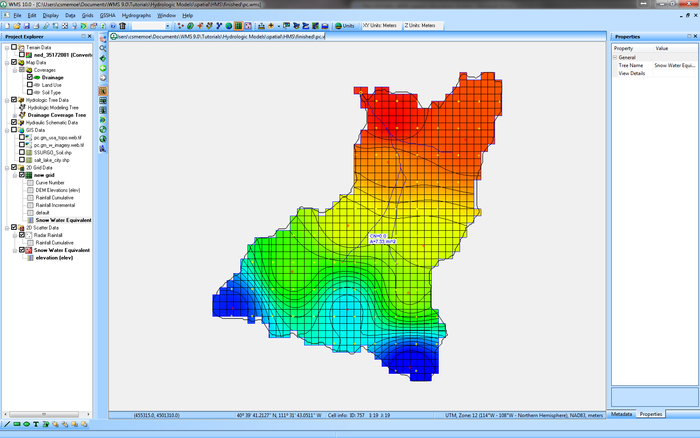
Also, a new tutorial has been added to the list of WMS tutorials under the Spatial modeling section. This tutorial describes how to convert an HMS model to a GSSHA model using simple, easy-to-follow steps from the WMS interface.
Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS)
Support for HMS 4.0
WMS 10.0 supports HMS 4.0. This new version of the HMS model is included with the WMS installation.
DSS Grid Parameters
The capability of computing several gridded DSS parameters and exporting them to a DSS file for use in HMS has been added to the HMS ModClark interface. In addition, several types HMS grids can be computed and exported with your HMS model. A grid can be defined at any resolution and Green Ampt, SMA, and Curve Number parameters can be computed using land use and soil maps. In addition, snowmelt parameters, evapotranspiration parameters, infiltration parameters, and other hydrologic parameters can be interpolated to your grid from scattered data and then exported to your HMS ModClark model.
New HMS Tutorial
A new tutorial titled Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model describes how to use solely online data sources available from the WMS interface to collect all the data required and build an HMS model for any part of the United States.
National Streamflow Statistics (NSS) 6.0 Support
WMS 10.0 supports NSS version 6.0 with the updated database, which contains all the latest regression equations for the United States as of May 2014.
EPA SWMM Updates
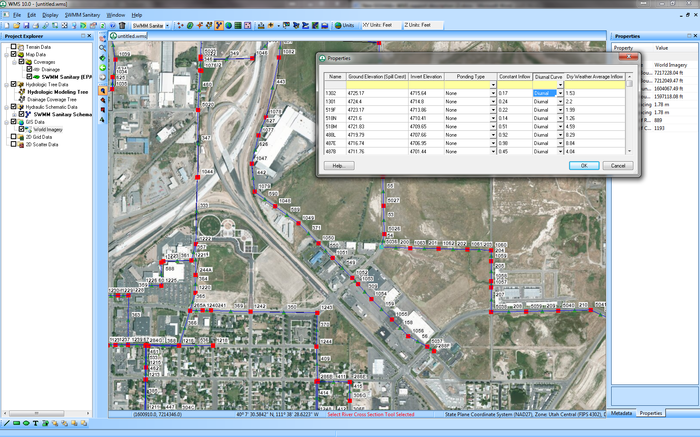
Sanitary Sewer Modeling Options
Sanitary sewer modeling tools have been added to the EPA SWMM interface in WMS. The following tools have been added to the WMS interface that allow you to define sanitary sewer models and read existing sanitary sewer models:
- A sanitary sewer coverage.
- An option to define diurnal curves and assign curves to nodes/manholes.
- An option to import infiltration and domestic flows from ESRI shapefiles and to export these values to EPA SWMM.
- An option to import a peaking factor for the domestic flows and export these values to EPA SWMM
- An option to import SWMM 5 models with sanitary sewer options and export these models to ESRI shapefiles
SWMM 5.1 Support
WMS 10.0 Supports the most recent version of SWMM, version 5.1.
Additional Web Services
FEMA Flood Maps
The capability to read FEMA Flood Maps using web services has been added to WMS 10.0. Options to import both raster flood images and vector floodplain boundary maps are available.
Flood Map Legend
The FEMA flood map legend for FEMA flood images downloaded to WMS 10.0 is shown below:
Precipitation Web Services
NOAA Atlas 14 Data
Getting a precipitation value has never been easier with the option to get NOAA Atlas 14 data for a delineated watershed in WMS. Options are available to get the mean, upper confidence interval value, and lower value for most watersheds delineated within the United States. The button to get NOAA atlas 14 precipitation values data is available for the commonly used watershed models in WMS, including HMS, HEC-1, and GSSHA. Just select the rainfall hyetograph option for any of these models and a button will appear that allows you to get the precipitation from the web.
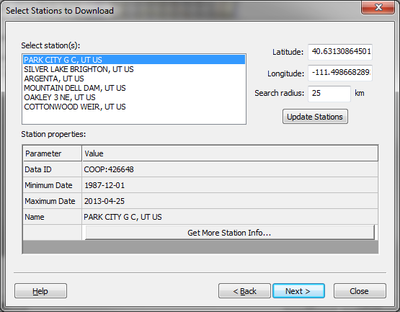
NCDC Station Wizard
The NCDC Station Wizard allows you to view rainfall gage stations surrounding your watershed, analyze the data associated with these stations, and download the rainfall data. When the data is downloaded, WMS creates creates a rain gage coverage and assigns the rainfall data to gages in this coverage. These gages can then be used in the GSSHA, HMS, or HEC-1 hydrologic models. This exciting tool makes it possible to download historic rainfall data for many areas directly from WMS and then use this historic data in your watershed model.
Release Notes
To view the list of bugs fixed in WMS 10.0, visit the WMS release notes page.
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||