HY8:Increased Resistance in Culverts: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
m (Jcreer moved page HY8 Increased Resistance in Culverts to HY8:Increased Resistance in Culverts) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Increased Resistance in Box Culverts== | |||
The input variables required for this calculation are the following: | |||
* h/r<sub>i</sub>—Ratio of roughness element height divided by hydraulic radius taken about the top of the roughness element. | |||
* Height of the roughened section (h) | |||
==Increased Resistance in Circular Culverts== | ==Increased Resistance in Circular Culverts== | ||
The input variables required for this calculation is the following: | The input variables required for this calculation is the following: | ||
Revision as of 16:36, 30 November 2016
Increased Resistance in Box Culverts
The input variables required for this calculation are the following:
- h/ri—Ratio of roughness element height divided by hydraulic radius taken about the top of the roughness element.
- Height of the roughened section (h)
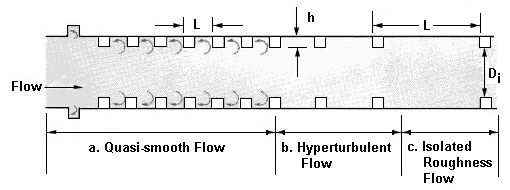
Increased Resistance in Circular Culverts
The input variables required for this calculation is the following:
- L/Di — Ratio of roughness element spacing divided by the diameter of the culvert opening at the roughness element. (Range = .05 to 1.5)
- h/Di — Ratio of roughness element height divided by the diameter of the culvert opening at the roughness element. (Range = .005 to .1).
- Lr/Pi — Ratio of the roughness length to inside perimeter (Range = 0.0 to 1.0)
- Diameter of roughened section (Opening, Di)
The following figure shows the flow regimes and variables for an increased resistance energy dissipator implemented in a circular culvert.
Variables from the figure
- L — Length from beginning of one roughness element to the beginning of the next roughness element.
- h — height of roughness element
- Di — diameter of roughened section (opening)