User:Mburton/HydroGeoSphere Point Properties Dialog: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOINDEX__ | |||
{{Current development}} | |||
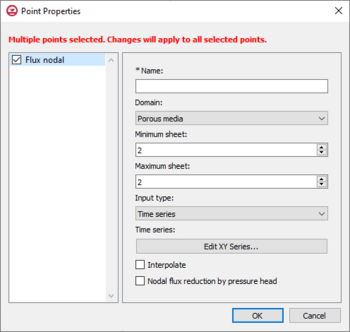
==Flux | The ''Point Properties'' dialog in the HydroGeoSphere model is where the input parameters for nodes associated with the relative coverage are set. The boundary conditions, observations, and hydrograph coverages each have their own individual parameters under the ''Point Properties'' dialog, depending on which coverage is active. Only one type of boundary condition can be assigned to a feature object on a boundary conditions coverage. For hydrograph or observation coverages, "Hydrograph" or "Observation" is the only option available to assign to a feature object, relative to the coverage type. | ||
*Name | [[File:HGS point prop.png|thumb|350 px|''Point Properties'' dialog for the boundary conditions coverage]] | ||
*Domain | |||
**Porous media | |||
***Minimum sheet | ==Flux Nodal, Boundary Conditions Coverage== | ||
***Maximum sheet | Flux nodal is a general specified flux boundary condition for a point on the boundary conditions coverage of a HydroGeoSphere model. The input options for a flux nodal designation are listed below. | ||
***Input type | * ''Name'' – The name of the boundary condition. Names should be unique and contain no white space. | ||
****Time series | * '''Domain''' – The domain in which the boundary conditions are applied. | ||
**Surface flow | ** ''Porous media'' | ||
***Input type | *** ''Minimum sheet'' – The minimum node sheet; boundary conditions are applied between the minimum and maximum node sheets. | ||
****Constant | *** ''Maximum sheet'' – The maximum node sheet; boundary conditions are applied between the minimum and maximum node sheets. | ||
****Time series | *** ''Input type'' – How the boundary condition data is specified. | ||
****Time raster table | **** ''Time series'' – Time-varying values of the boundary condition. A table is generated using the ''XY Series Editor'' dialog that is opened by clicking the '''Edit XY Series''' button by either manually entering the data, or importing the data. | ||
***Interpolate | ** ''Surface flow'' | ||
***Nodal flux reduction by pressure head | *** ''Input type'' – How the boundary condition data is specified. | ||
**** ''Constant'' – Constant value of the boundary condition. | |||
**** ''Time series'' – Time-varying values of the boundary condition. A table is generated using the ''XY Series Editor'' dialog that is opened by clicking the '''Edit XY Series''' button by either manually entering the data, or importing the data. | |||
**** ''Time raster table'' – The '''Edit Table...''' opens the ''Time raster table'' dialog where the data is entered by selecting a raster from outside GMS. | |||
*** ''Interpolate'' – Causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function. | |||
*** ''Nodal flux reduction by pressure head'' – Reduces flux as a function of the nodal pressure head to avoid pumping from the dry materials. | |||
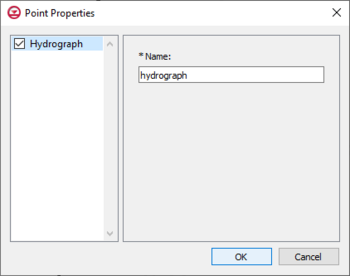
[[File:HGS point prop hydrograph.png|thumb|350px|''Point Properties'' dialog for the hydrograph coverage]] | |||
==Hydrograph, Hydrograph Coverage== | |||
GMS allows recording of hydrograph data on a point from the HydroGeoSphere model run. This requires that "Hydrograph" is set as the parameter for a point on a HydroGeoSphere hydrograph coverage, which is done inside the ''Point Properties'' dialog. The coverage then needs to be added to the simulation. Upon the simulation run, GMS will output detailed flow rate information at each time step for each point that has been assigned a hydrograph. The only input available in the ''Point Properties'' dialog on a hydrograph coverage is a name. The name should be something descriptive, and less than 80 characters. | |||
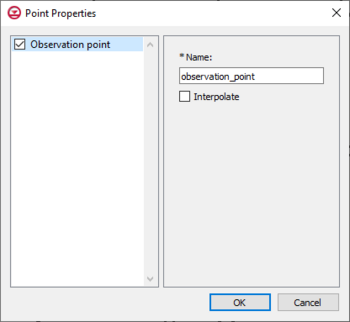
[[File:HGS point prop obs.png|thumb|350px|''Point Properties'' dialog for the observation coverage]] | |||
==Observation, Observation Coverage== | |||
GMS allows recording of observation data from the HydroGeoSphere model run through observation points on a HydroGeoSphere observations coverage. When an observation point is created, GMS outputs timeseries information specific to the observation point during the simulation run. To create an observation point, select a point to designate as an observation point and set the parameters inside the ''Point Properties'' dialog. The input options for an observation point are listed below. | |||
* ''Name'' – This should be a descriptive name for the observation point, and less than 40 characters. | |||
* ''Interpolate'' – Output values are linearly interpolated from the nodal values at the vertices at the element that contains the observation point. | |||
{{noindex}} | {{noindex}} | ||
[[Category:HydroGeoSphere]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:00, 26 September 2023
| This contains information currently under development. The content may change often. |
The Point Properties dialog in the HydroGeoSphere model is where the input parameters for nodes associated with the relative coverage are set. The boundary conditions, observations, and hydrograph coverages each have their own individual parameters under the Point Properties dialog, depending on which coverage is active. Only one type of boundary condition can be assigned to a feature object on a boundary conditions coverage. For hydrograph or observation coverages, "Hydrograph" or "Observation" is the only option available to assign to a feature object, relative to the coverage type.
Flux Nodal, Boundary Conditions Coverage
Flux nodal is a general specified flux boundary condition for a point on the boundary conditions coverage of a HydroGeoSphere model. The input options for a flux nodal designation are listed below.
- Name – The name of the boundary condition. Names should be unique and contain no white space.
- Domain – The domain in which the boundary conditions are applied.
- Porous media
- Minimum sheet – The minimum node sheet; boundary conditions are applied between the minimum and maximum node sheets.
- Maximum sheet – The maximum node sheet; boundary conditions are applied between the minimum and maximum node sheets.
- Input type – How the boundary condition data is specified.
- Time series – Time-varying values of the boundary condition. A table is generated using the XY Series Editor dialog that is opened by clicking the Edit XY Series button by either manually entering the data, or importing the data.
- Surface flow
- Input type – How the boundary condition data is specified.
- Constant – Constant value of the boundary condition.
- Time series – Time-varying values of the boundary condition. A table is generated using the XY Series Editor dialog that is opened by clicking the Edit XY Series button by either manually entering the data, or importing the data.
- Time raster table – The Edit Table... opens the Time raster table dialog where the data is entered by selecting a raster from outside GMS.
- Interpolate – Causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function.
- Nodal flux reduction by pressure head – Reduces flux as a function of the nodal pressure head to avoid pumping from the dry materials.
- Input type – How the boundary condition data is specified.
- Porous media
Hydrograph, Hydrograph Coverage
GMS allows recording of hydrograph data on a point from the HydroGeoSphere model run. This requires that "Hydrograph" is set as the parameter for a point on a HydroGeoSphere hydrograph coverage, which is done inside the Point Properties dialog. The coverage then needs to be added to the simulation. Upon the simulation run, GMS will output detailed flow rate information at each time step for each point that has been assigned a hydrograph. The only input available in the Point Properties dialog on a hydrograph coverage is a name. The name should be something descriptive, and less than 80 characters.
Observation, Observation Coverage
GMS allows recording of observation data from the HydroGeoSphere model run through observation points on a HydroGeoSphere observations coverage. When an observation point is created, GMS outputs timeseries information specific to the observation point during the simulation run. To create an observation point, select a point to designate as an observation point and set the parameters inside the Point Properties dialog. The input options for an observation point are listed below.
- Name – This should be a descriptive name for the observation point, and less than 40 characters.
- Interpolate – Output values are linearly interpolated from the nodal values at the vertices at the element that contains the observation point.