HY8:Inlet Depression: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The | The depression of a culvert is the vertical drop of the inlet control section below the stream bed. An inlet depression is defined by entering a value for each of the following items (see drawing below): | ||
*Depression | *Depression | ||
* | *Depression Slope | ||
*Crest Width | *Crest Width | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
=== | ===DEPRESSION SLOPE=== | ||
Slope between the stream bed and the face invert. The | Slope between the stream bed and the face invert. The depression slope must be set between 2:1 and 3:1. | ||
===CREST WIDTH=== | ===CREST WIDTH=== | ||
Length of weir crest at the top of the | Length of weir crest at the top of the depression slope. Designing the crest width becomes an iterative process in HY-8 as the user must select a crest width wide enough so that it does not control the headwater calculations. If the selected crest width is not wide enough the crest section will produce a higher headwater elevation than the culvert throat. The user must continue to increase the crest width and run the analysis until the headwater depth ceases to change with increasing crest width. Once this occurs the crest section no longer controls and may be used in analysis and construction. | ||
[[Image:HY8Inlet%20Depression.gif]] | [[Image:HY8Inlet%20Depression.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 19:21, 6 October 2011
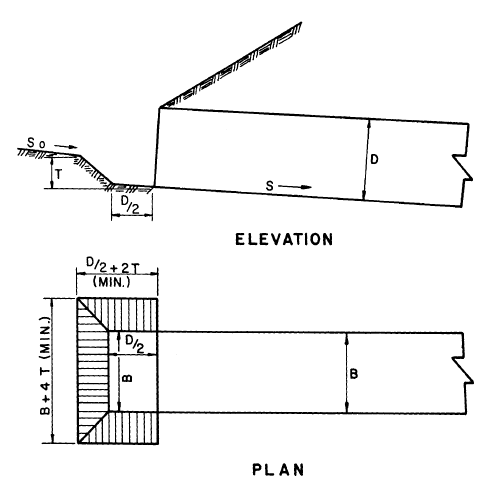
The depression of a culvert is the vertical drop of the inlet control section below the stream bed. An inlet depression is defined by entering a value for each of the following items (see drawing below):
- Depression
- Depression Slope
- Crest Width
DEPRESSION
The vertical drop of inlet control section below the stream bed.
DEPRESSION SLOPE
Slope between the stream bed and the face invert. The depression slope must be set between 2:1 and 3:1.
CREST WIDTH
Length of weir crest at the top of the depression slope. Designing the crest width becomes an iterative process in HY-8 as the user must select a crest width wide enough so that it does not control the headwater calculations. If the selected crest width is not wide enough the crest section will produce a higher headwater elevation than the culvert throat. The user must continue to increase the crest width and run the analysis until the headwater depth ceases to change with increasing crest width. Once this occurs the crest section no longer controls and may be used in analysis and construction.