User:Mburton/HydroGeoSphere Polygon Properties Dialog: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
(Created page with "The Polygon Properties dialog in the HydroGeoSphere model is where the polygons associated with the boundary conditions are defined. There are four options for the polygon properties, which are listed on the left side of the dialog. The input parameters are shown on the right. thumb|400px|''Polygon Properties'' dialog ==Head or Flux== Head and Flux are two different Polygon boundary condition options, but they contain the same input parame...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
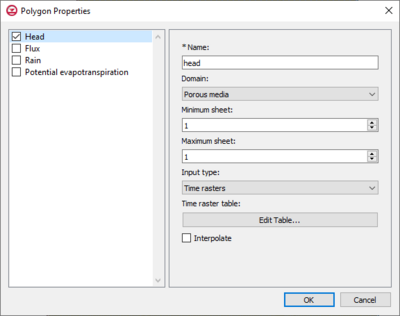
The Polygon Properties dialog in the HydroGeoSphere model is where the polygons associated with the boundary conditions are defined. There are four options for the polygon properties, which are listed on the left side of the dialog. The input parameters are shown on the right. | The Polygon Properties dialog in the HydroGeoSphere model is where the polygons associated with the boundary conditions are defined. There are four options for the polygon properties, which are listed on the left side of the dialog. The input parameters are shown on the right. Only one type of boundary condition can be assigned to a feature object on a Boundary Conditions coverage. | ||
[[File:HGS polygon prop.png|thumb|400px|''Polygon Properties'' dialog]] | [[File:HGS polygon prop.png|thumb|400px|''Polygon Properties'' dialog]] | ||
Revision as of 17:19, 7 August 2023
The Polygon Properties dialog in the HydroGeoSphere model is where the polygons associated with the boundary conditions are defined. There are four options for the polygon properties, which are listed on the left side of the dialog. The input parameters are shown on the right. Only one type of boundary condition can be assigned to a feature object on a Boundary Conditions coverage.
Head or Flux
Head and Flux are two different Polygon boundary condition options, but they contain the same input parameter options, which are listed below.
- Name: the name of the boundary condition. Names should be unique and contain no white space.
- Domain: the domain in which the boundary conditions are applied.
- Porous media
- Minimum sheet: the minimum node sheet; boundary conditions are applied between the minimum and maximum node sheets.
- Maximum sheet: the maximum node sheet; boundary conditions are applied between the minimum and maximum node sheets.
- Input type: how the boundary condition data is specified.
- Constant: constant value of the boundary condition.
- Time series: time-varying values of the boundary condition. A table is generated using the XY Series Editor dialog that is opened by clicking the Edit XY Series button by either manually entering the data, or importing the data.
- Interpolate
- Time rasters: the Edit Table... opens the Time raster table dialog where the data is entered by selecting a raster from outside GMS.
- Interpolate: causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function.
- Surface flow
- Input type: how the boundary condition data is specified.
- Constant: constant value of the boundary condition.
- Time series: time-varying values of the boundary condition. A table is generated using the XY Series Editor dialog that is opened by clicking the Edit XY Series button by either manually entering the data, or importing the data.
- Interpolate: causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function.
- Time rasters: the Edit Table... opens the Time raster table dialog where the data is entered by selecting a raster from outside GMS.
- Interpolate: causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function.
- Input type: how the boundary condition data is specified.
- Porous media
Rain or Potential evapotranspiration
Rain and Potential evapotranspiration are two different Polygon boundary condition options, but they contain the same input parameter options, which are listed below.
- Name: the name of the boundary condition. Names should be unique and contain no white space.
- Input type: how the boundary condition data is specified.
- Constant: constant value of the boundary condition.
- Time series: time-varying values of the boundary condition. A table is generated using the XY Series Editor dialog that is opened by clicking the Edit XY Series button by either manually entering the data, or importing the data.
- Interpolate: causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function.
- Time raster table: the Edit Table... opens the Time raster table dialog where the data is entered by selecting a raster from outside GMS.
- Interpolate: causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function.