User:Mburton/HydroGeoSphere Materials Dialog: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOINDEX__ | |||
{{Current development}} | |||
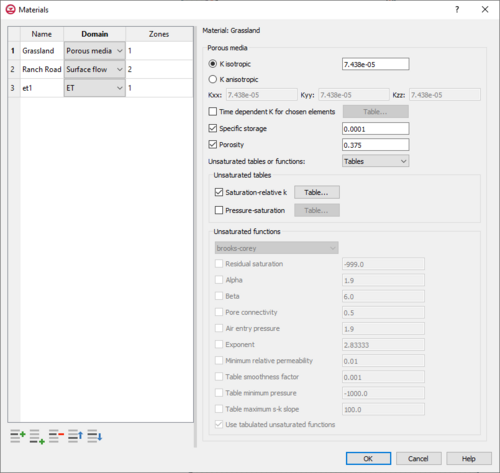
HydroGeoSphere's Materials dialog is accessed by right-clicking on the simulation in the Project Explorer and selecting Materials from the menu. The left side of the dialog contains a table with columns for the name, the domain, and the zone. Each domain contains various inputs to define parameters, which appear on the right side of the Materials dialog. | HydroGeoSphere's Materials dialog is accessed by right-clicking on the simulation in the Project Explorer and selecting Materials from the menu. The left side of the dialog contains a table with columns for the name, the domain, and the zone. Each domain contains various inputs to define parameters, which appear on the right side of the Materials dialog. | ||
[[File:HGS materials.png|thumb|500 px|HydroGeoSphere ''Materials'' dialog]] | [[File:HGS materials.png|thumb|500 px|HydroGeoSphere ''Materials'' dialog]] | ||
Revision as of 22:52, 14 August 2023
| This contains information currently under development. The content may change often. |
HydroGeoSphere's Materials dialog is accessed by right-clicking on the simulation in the Project Explorer and selecting Materials from the menu. The left side of the dialog contains a table with columns for the name, the domain, and the zone. Each domain contains various inputs to define parameters, which appear on the right side of the Materials dialog.
Domain: Porous Media
The following options appear on the right side of the Materials dialog when Porous media is selected under the Domain column in the table on the left side of the dialog.
- Porous media
- K isotropic: isotropic hydraulic conductivity
- K anisotropic: anisotropic hydraulic conductivity.
- Kxx: diagonal terms of the hydraulic conductivity tensor.
- Kyy: diagonal terms of the hydraulic conductivity tensor.
- Kzz: diagonal terms of the hydraulic conductivity tensor.
- Time dependent K for chosen elements: table defining time on and hydraulic conductivities in the x-, y-, and z- directions for each panel.
- Specific storage
- Porosity
- Unsaturated tables or functions: choose either tables or functions to enter the unsaturated values.
- Unsaturated tables
- Saturation-relative k: paired values of saturation and relative permeability entered in a table from lowest to highest saturation.
- Pressure-saturation: paired values of pressure and saturation entered in a table from lowest pressure to highest pressure, usually zero.
- Unsaturated tables
- Unsaturated functions: two functions methods are available, which are brooks-corey and van genuchten. These are selected from a dropdown menu.
- brooks-corey
- Residual saturation: residual water saturation.
- Alpha: for the brooks-corey function, this value is computed automatically from the air entry pressure.
- Beta: for the brooks-corey formulation
- Pore connectivity:
- Air entry pressure
- Exponent
- Minimum relative permeability: during a simulation, the model will choose the maximum value for relative permeability between the minimum value specified here, and the value computed from the active function. This option may improve convergence of the nonlinear solution.
- Table smoothness factor: smaller values cause more points to be generated for a smoother, more accurate table.
- Table minimum pressure: minimum pressure value in the pressure saturation table.
- Table maximum s-k slope: maximum slope of the saturation-relative permeability curve when nearing the full saturation.
- Use tabulated unsaturated functions: generate tables from the functional constitutive relationships and causes grok to use those tables instead of the functions.
- van genuchten
- Residual saturation: residual water saturation.
- Alpha
- Beta: for van genuchten this value must be greater than 1.0.
- Pore connectivity: the default value of pore connectivity recommended for the van genuchten formulation is 0.5
- Minimum relative permeability: during a simulation, the model will choose the maximum value for relative permeability between the minimum value specified here, and the value computed from the active function. This option may improve convergence of the nonlinear solution.
- Table smoothness factor: smaller values cause more points to be generated for a smoother, more accurate table.
- Table minimum pressure: minimum pressure value in the pressure saturation table.
- Table maximum s-k slope: maximum slope of the saturation-relative permeability curve when nearing the full saturation.
- Use tabulated unsaturated functions: generate tables from the functional constitutive relationships and causes grok to use those tables instead of the functions.
- brooks-corey
Domain: Surface Flow
The following options appear on the right side of the Materials dialog when Surface flow is selected under the Domain column in the table on the left side of the dialog.
- Surface flow
- X friction: friction factor in the X direction.
- Y friction: friction factor in the Y direciton.
- Time varying friction: import a table containing Time and Manning roughness coefficient.
- Rill storage height: sets the minimum water depth required for flow.
- Obstruction storage height: defines the parameters for interaction between the channel domain and the overland flow and subsurface domains.
- Coupling length
- Maximum flow depth:
- Read rill storage from raster: import a raster file that computes the rill storage height form elevation values for each element in the surface layer of the mesh.
- Scale factor: this option becomes available when Read rill storage from raster is selected.
Domain: ET
The following options appear on the right side of the Materials dialog when ET is selected under the Domain column in the table on the left side of the dialog.
- ET
- Evaporation depth
- Potential evaporation using transpiration
- EDF quadratic decay function: use the quadratic form of the evaporation function instead of the default, which is linear.
- Root depth: maximum root depth.
- RDF table: relative depth and root length density.
- Time-root depth table
- RDF quadratic decay function: use the quadratic form of the root-depth function instead of the default, which is linear.
- LAI tables: paired values of time and leaf area index entered from earliest to latest time.
- Time varying LAI from raster: allows for time varying leaf area index values from a time-file table.
- Transpiration fitting parameters
- C_1
- C_2
- C_3
- Transpiration limiting pressure head
- Hwp_et
- Hfc_et
- Ho_et
- Han_et
- Evaporation limiting pressure head
- He2_et
- He1_et
- Canopy storage parameter
- Canopy evaporation interval: controls the calculation of canopy evaporation by limiting the canopy evaporation rate over that time interval. The default value is zero.
- Initial interception storage: initial canopy interception storage value.