GMS:GMG Package: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
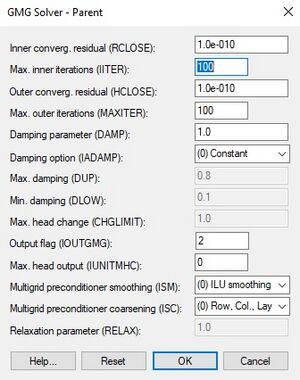
* ''Outer convergence residual (HCLOSE)'' – For nonlinear problems. After each linear solve (inner iteration), the maximum norm of the head change is compared against HCLOSE. Can be set to a large number for linear problems. Ignored if ''Maximum outer iterations'' is 1. | * ''Outer convergence residual (HCLOSE)'' – For nonlinear problems. After each linear solve (inner iteration), the maximum norm of the head change is compared against HCLOSE. Can be set to a large number for linear problems. Ignored if ''Maximum outer iterations'' is 1. | ||
* ''Maximum outer iterations (MAXITER)'' – Also referred to as MXITER. For linear problems, set to 1. For nonlinear problems, set to a higher number though it is usually unnecessary to go above 100. | * ''Maximum outer iterations (MAXITER)'' – Also referred to as MXITER. For linear problems, set to 1. For nonlinear problems, set to a higher number though it is usually unnecessary to go above 100. | ||
* ''Damping parameter (DAMP)'' – A value of 1.0 should be used for linear problems. For nonlinear problems, a value less than 1.0 but greater than | * ''Damping parameter (DAMP)'' – A value of 1.0 should be used for linear problems. For nonlinear problems, a value less than 1.0 but greater than 0.0 may be necessary to achieve convergence. | ||
0.0 may be necessary to achieve convergence. | |||
* Damping option (IADAMP) | * Damping option (IADAMP) | ||
* Maximum damping (DUP) | * Maximum damping (DUP) | ||