GMS:Horizons Wizard: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
(→Step 1) |
(→Step 1) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
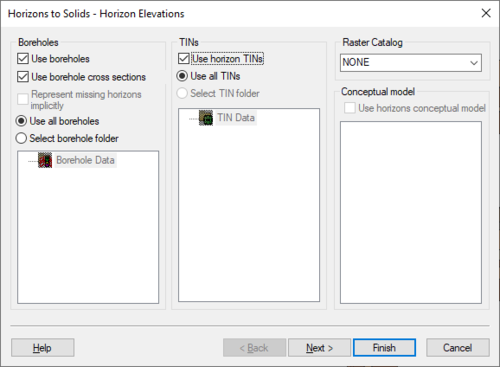
[[File:HorizonsWizard1.png|thumb|none|500 px|The ''Horizon Elevation'' step of the ''Horizons'' wizard]] | [[File:HorizonsWizard1.png|thumb|none|500 px|The ''Horizon Elevation'' step of the ''Horizons'' wizard]] | ||
===Including Borehole Cross Sections=== | |||
If the Horizon process using horizons on borehole contacts does not produce the desired results, the borehole data can be supplemented with [[GMS:Borehole Cross Sections|user-defined cross sections]] using the [[GMS:Borehole Cross Sections|''Cross Section Editor'']]. | |||
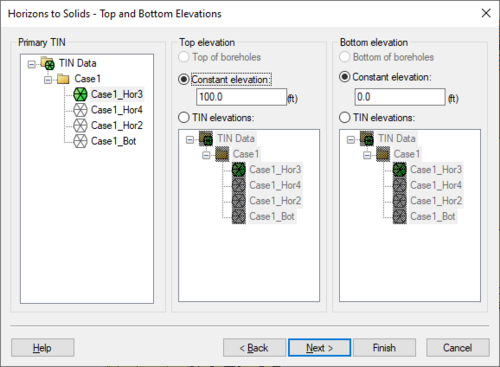
For example, when the '''Horizons → Solids''' command is executed, the user can choose to include cross section data. If this option is selected, the material boundaries (arcs) on the cross sections inherit the horizon ID assigned to the adjacent borehole contact and the points along the material boundary are added to the contacts when interpolating the horizon surfaces. The resulting solids match the user-defined cross sections as closely as possible. In other words, by creating a few simple cross section, the user has complete control over the shape of the solids created by the horizons technique. | |||
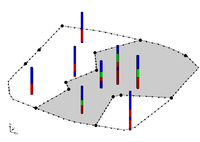
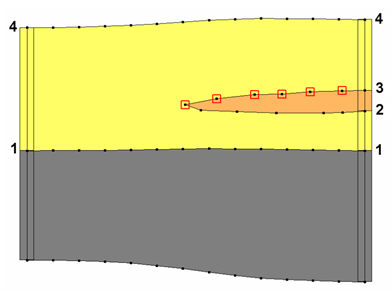
The match between the resulting solid and the user defined cross section is a function of two things: first, the density of the points on the user defined cross section, and second the triangle density of the primary TIN. As mentioned, the arcs on the cross sections inherit the horizon ID from the borehole contact as shown below. | |||
[[Image:xsect_hor.jpg|none|frame|Example of how cross section data inherits horizon id from boreholes]] | |||
In this case the marked points on the cross section inherit horizon ID 3. If wanting more control over the interpolation of horizon 3, then add more points to the arc. This can be done by selecting the '''Select Arc''' tool's right-click '''Redistribute Virtices''' command in the ''Cross Section Editor''. The triangle density of the primary TIN also controls how well the resulting solid matches the user-defined cross section. Since the points on the cross section are interpolated to the primary TIN, if the TIN does not have a significant number of triangles in the vicinity of the cross section then there is no way the TIN surface can match the cross section. | |||
==Step 2== | ==Step 2== | ||