HY8:Outlet Control Computations: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
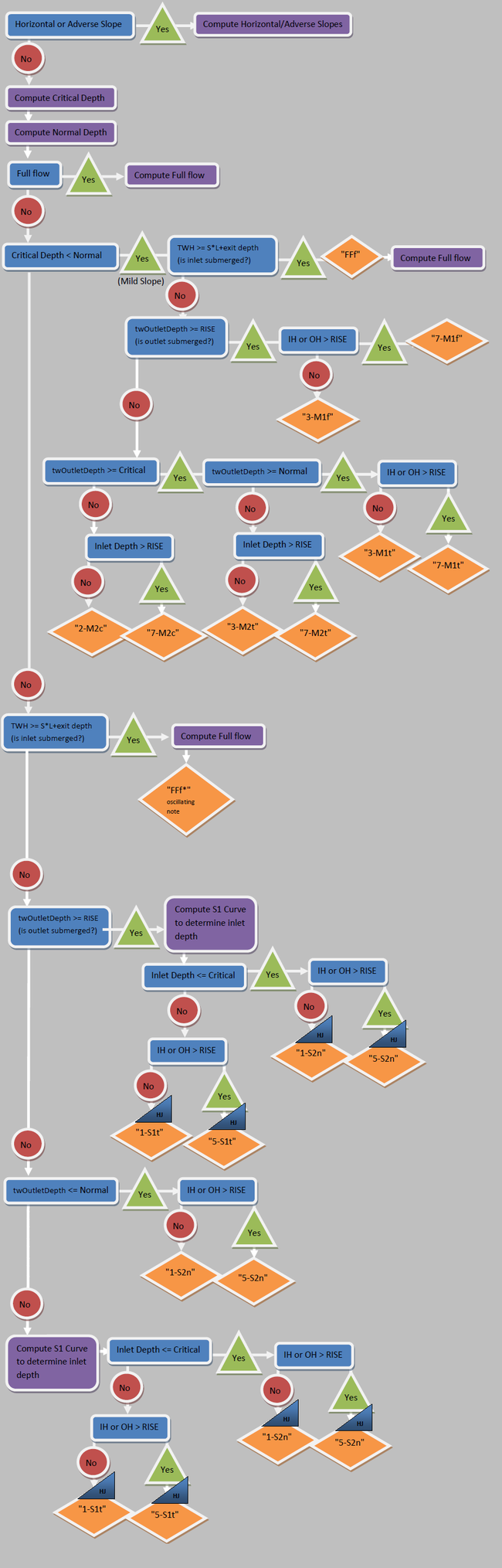
This flowchart uses the following terms: | This flowchart uses the following terms: | ||
'''HJ''' = Check for Hydraulic Jumps | '''HJ''' = Check for [[WMS:HY-8_Hydraulic_Jump_Calculations|Hydraulic Jumps]] | ||
'''Full flow''' = Check if the culvert is flowing full | '''Full flow''' = Check if the culvert is flowing full | ||
Revision as of 17:57, 5 October 2011
Outlet control means that the amount of water the culvert barrel can carry is limited by the barrel and/or tailwater conditions downstream. As a result, the flow in the barrel is subcritical, and the energy equation may be used to find the upstream headwater depth. Several flow profiles are possible and are shown below and on page 32 of HDS-5. The following correlations apply to HY-8: Type A in HDS-5 is Type 4 in HY-8, Type B in HDS-5 is Type 3 in HY-8; Type C in HDS-5 is Type 6 in HY-8, Type D in HDS-5 is Type 7 in HY-8, and Type E in HDS-5 is Type 2 in HY-8. Descriptions of these flow types may be found in HY-8 by selecting the “Flow Types” button from the Culvert Summary Table.
The logic for determining flow type due to outlet control is shown in the figure below:
This flowchart uses the following terms:
HJ = Check for Hydraulic Jumps
Full flow = Check if the culvert is flowing full
TWH = Depth of the tailwater from the invert of the tailwater channel at the culvert outlet
twOutletDepth = Depth of the tailwater from the invert of the culvert at the culvert outlet. If the culvert is buried, this value is taken from the top of the embedment material.
IH = Inlet control headwater depth measured at the inlet invert of the culvert
OH = Outlet control headwater depth measured at the inlet invert of the culvert
RISE = Height of the culvert. If the culvert is buried, this value is taken from the top of the embedment material.
Inlet Depth = The depth computed at the entrance to the culvert using the direct step profile computation method
Critical = The critical depth in the culvert
Normal = The normal depth in the culvert
The following table describes the various flow types defined in the above flow chart:
| Flow Type | Flow Control | Submerged Inlet | Submerged Outlet | Length Full | Flow Regime | Outlet Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Inlet |
No |
No |
NONE |
S2n |
Normal |
|
1 |
Inlet |
No |
No |
NONE |
S1t |
Tailwater |
|
1 |
Inlet |
No |
Yes |
Part |
S1f |
Full |
|
1 |
Inlet |
No |
No |
NONE |
JS1t |
Jump to Tailwater |
|
1 |
Inlet |
No |
Yes |
Most |
JS1f |
Jump to Full |
|
5 |
Inlet |
Yes |
No |
NONE |
S2n |
Normal |
|
5 |
Inlet |
Yes |
No |
NONE |
S1t |
Tailwater |
|
5 |
Inlet |
Yes |
Yes |
Part |
S1f |
Full |
|
5 |
Inlet |
Yes |
No |
NONE |
JS1t |
Jump to Tailwater |
|
5 |
Inlet |
Yes |
Yes |
Part |
JS1f |
Jump to Full |
|
2 |
Outlet |
No |
No |
NONE |
M2c |
Critical |
|
3 |
Outlet |
No |
No |
NONE |
M1t |
Tailwater |
|
3 |
Outlet |
No |
No |
NONE |
M2t |
Tailwater |
|
3 |
Outlet |
No |
Yes |
Part |
M1f |
Full |
|
4 |
Outlet |
Yes |
Yes |
All |
FFf |
Full |
|
6 |
Outlet |
Yes |
No |
Most |
FFt |
Tailwater |
|
6 |
Outlet |
Yes |
No |
Most |
FFc |
Critical |
|
7 |
Outlet |
Yes |
No |
Part |
M1t |
Tailwater |
|
7 |
Outlet |
Yes |
No |
Part |
M2t |
Tailwater |
|
7 |
Outlet |
Yes |
No |
Part |
M2c |
Critical |