User:Jcreer/SMS:Toolbox: Difference between revisions
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
**"Meteorologic" – Sets that the output dataset will use a Meteorological angle convention. | **"Meteorologic" – Sets that the output dataset will use a Meteorological angle convention. | ||
**"Oceanographic" – Sets that the output dataset will use an Oceanographic angle convention. | **"Oceanographic" – Sets that the output dataset will use an Oceanographic angle convention. | ||
*''Output | *''Output dataset name'' – Select the name for the output dataset. | ||
{{-}} | {{-}} | ||
Revision as of 18:28, 25 June 2021
Starting with version 13.2 , SMS includes a general purpose toolbox that allows the SMS process to interact with external python scripts. In SMS 13.2 this is a beta feature. For this version, the user accesses the toolbox by right clicking on the "Project" item at the top of the tree in the "Project Explorer" and selecting "Toolbox". This bring up the SMS toolbox dialog.
SMS Toolbox
Tools in the toolbox allow the user to operate on data in an SMS interactive session as well as data in external files. Each tool in the toolbox links to a python script that produces a specific output. Example output from a tool could include, but are not limited to:
- a graphic or plot.
- a report (document or spreadsheet) for a specified analytical process.
- a new geometry item in SMS.
- a new dataset in SMS.
- a new data file.
Tools Tab
Available tools in the SMS Tool dialog are divided into categories, typically based on the type of output or the type of arguments used in the tool. Currently these categories include:
- Datasets – Contains tools for manipulating datasets attached meshes, scatters sets, or Ugrids.
- Rasters – Contains tools for manipulating raster files in the GIS module.
- UGrids – Contains tools for manipulating UGrids, scatter sets, and meshes.
History Tab
The toolbox maintains a history of all tools invoked for a session of SMS. Eventually this history will be recorded so that it includes all tools invoked for this project.
The history section includes the tool and the date/time the tool was invoked. Double-clicking on an entry in the history tab launches the listed tool. The input fields are populated with the arguments that were used in the previous invocation of the tool. These inputs can be changed for the new invocation of the tool.
Dataset Tools
Angle Convention
This tool converts between angle conventions, converting an angle convention to another angle convention dataset. The tool has the following options:
- Input scalar dataset – Select the scalar dataset that will be the input.
- Input angle convention – Select the type of angle convention used in the input scalar dataset.
- "Cartesian" – Specifies that the input dataset uses a Cartesian angle convention.
- "Meteorologic" – Specifies that the input dataset uses a Meteorological angle convention.
- "Oceanographic" – Specifies that the input dataset uses an Oceanographic angle convention.
- Output angle convention – Select the angle convention for the new dataset.
- "Cartesian" – Sets that the output dataset will use a Cartesian angle convention.
- "Meteorologic" – Sets that the output dataset will use a Meteorological angle convention.
- "Oceanographic" – Sets that the output dataset will use an Oceanographic angle convention.
- Output dataset name – Select the name for the output dataset.
Canopy Coefficient
This tool computes a canopy coefficient from a landuse raster. The tool has the following options:
- Input landuse raster – Select which landuse raster in the project will be the input.
- Interpolation option – Select which of the following options will be used for interpolation.
- "Node location" – Interpolation based around node location.
- "Area around node" – Interpolation based around the area around a node. This adds an option to the dialog.
- Minimum percent blocked which ignores wind stress – Set the minimum potential percent blocked that will ignore the wind stress.
- Target grid – Select the grid which will be the target.
- Landuse raster type – Select the type of the landuse raster.
- "NLCD" – Sets the landuse raster type to National Land Cover Dataset (NLCD).
- "C-CAP" – Sets the landuse raster type to C-CAP.
- "Other" – Sets the landuse raster type to Other. This adds an option to the dialog.
- Landuse to canopy coefficient mapping table – The Select File... button will allow a table file to be selected. The entire file name will be displayed in the text box to its right.
- Output canopy coefficient dataset – Type out the name for the canopy coefficient dataset that will be output.
Compare Datasets
This tool compares two datasets by creating a new dataset of the differences. The tool has the following options:
- Dataset 1 – Select the first dataset to compare.
- Inactive values option – From the drop-down menu, select the desired approach for handling inactive values in the dataset.
- "Use specified value for inactive value" – A specified value will replace inactive values.
- "Inactive values result in an inactive value" – Inactive values will be left as inactive in the comparison dataset.
- Specified value – Enter a value that will be used for inactive values.
- Dataset 2 – Select the second dataset to compare. This has the same options available for dealing with inactive dataset.
- Output dataset name – Enter the name of the new comparison dataset.
Directional Roughness
The Landuse Raster to Directional Roughness tool converts a landuse raster (NLCD, C-CAP, etc.) to a coastal directional roughness dataset. The tool has the following options:
- Input landuse raster – Select the landuse raster that will be the input.
- Method – Select which method will be used for computation.
- "Linear" – Selects the Linear method.
- "Sector" – Selects the Sector method.
- Total distance – Sets the total distance in meters.
- Weighted distance – Sets the weighted distance in meters.
- Target grid – Select which grid will be the target.
- Landuse raster type – Select which type the landuse raster is.
- "NLCD" – Sets the landuse raster type to NLCD.
- "C-CAP" – Sets the landuse raster type to C-CAP.
- "Other" – Sets the landuse raster type to Other. This selection adds an option to the dialog.
- Landuse to directional roughness mapping table – The Select File... button allows a table file to be selected. Its full file name will appear on the box to its right.
- Default wind reduction value – Set the default wind reduction value.
- Output wind reduction data set – Type out the name for the wind reduction dataset that will be output.
Geometry Gradient
This tool computes geometry gradient datasets. The tool has the following options:
- Input dataset – Select the dataset to use in the gradient computations.
- Gradient vector – Select to create a gradient vector dataset.
- Gradient magnitude – Select to create a gradient magnitude dataset.
- Gradient direction – Select to create a gradient direction dataset.
- Output gradient vector dataset name – Enter the name for the new gradient vector dataset.
- Output gradient magnitude dataset name – Enter the name for the new gradient magnitude dataset.
- Output gradient direction dataset name – Enter the name for the new gradient direction dataset.
Landuse Raster to Mannings N
This tool converts a landuse raster (NLCD, C-CAP, etc.) to a Mannings N dataset. The tool has the following options:
- Input landuse raster – Select the landuse raster that will be the input.
- Landuse raster type – Select the type for the landuse raster.
- "NLCD" – Set the landuse raster type to NLCD.
- "C-CAP" – Set the landuse raster type to C-CAP.
- "Other" – Set the landuse raster type to Other.
- Target grid – Select the grid that will be the target.
- Landuse to Mannings N mapping table Use the Select File... button to get the table file, and the full file name will be displayed in the box to its right.
- Select File... – The button to click to get the table file.
- Default Mannings N option – Select which of the following will be used for the default Mannings N. The option that is selected will populate an option in the dialog.
- "Constant" – Sets the default Mannings N to be a constant.
- Default Mannings N value – Sets a constant value to the default Mannings N.
- "Dataset" – Sets the default Mannings N to be a dataset.
- Default Mannings N data set – Select a data set to be used for the default Mannings N.
- "Constant" – Sets the default Mannings N to be a constant.
- Subset mask data set (optional) – Select a data set to be used for the subset mask, which is optional.
- Output Mannings N data set – Type out the name for the Mannings N data set that will be output.
Map Activity
This tool builds a dataset with values copied from one dataset and activity mapped from another. The tool has the following options:
- Value dataset– Select the dataset that will define the values for the new dataset.
- Activity dataset – Select the dataset that will define the activity for the new dataset.
- Output dataset – Enter the name for the new activity dataset.
Scalar to Vector
This tool converts a pair of scalar datasets to a vector dataset. The tool has the following options:
- Input type – In order to convert the scalar dataset, the tool needs to know input to use.
- "Vx and Vy" – This option will designate the input dataset values as Vx and Vy.
- "Magnitude and Direction" This option will designate the input dataset values as magnitude and direction.
- Input Vx or magnitude scalar dataset – Select the scalar dataset to use for the Vx or magnitude input.
- Input Vy or direction scalar dataset – Select the scalar dataset to use for the Vy or direction input.
- Output vector dataset name – Enter the name for the new vector dataset.
Smooth Datasets
This tool smooths datasets by limiting slope or area. The tool has the following options:
- Input elevation data set – Set the elevation dataset that will be the input.
- Anchor – Select which type of anchor.
- "Minimum value" – Sets the anchor to minimum value.
- "Maximum value" – Sets the anchor to maximum value.
- Smoothing option – Select which type of smoothing option. The option selected will add options to the dialog.
- "Elemental area change" – Sets the smoothing option to elemental area change.
- Smoothing area change limit – Sets a limit to the smoothing area change.
- Smoothing minimum cell size – Sets the minimum cell size to the smoothing.
- "Maximum slope" – Sets the smoothing option to maximum slope.
- Smoothing maximum slope – Sets the maximum slope to the smoothing.
- "Elemental area change" – Sets the smoothing option to elemental area change.
- Subset mask data set (optional) – Select a data set for the subset mask (which is optional).
- Output dataset – Type out a name for the dataset that will be output.
Smooth Datasets by Neighbor
This tool smooths datasets by averaging nodal neighbors. The tool has the following options:
- Input data set – Set the dataset that will be the input.
- Number of levels – The amount of levels to the dataset.
- "1"
- "2"
- Interpolation method – Set the interpolation method for the smoothing. The option selected may add options to the dialog.
- "Average" – Sets the interpolation method to average.
- Weight of nodal neighbors – Set the value for the weight of the nodal neighbors.
- "IDW" – Sets the interpolation method to IDW.
- "Average" – Sets the interpolation method to average.
- Subset mask data set (optional) – Select a data set for the subset mask (which is optional).
- Output dataset – Type out a name for the dataset that will be output.
Vector to Scalar
This tool converts vector datasets to scalar datasets. The tool has the following options:
- Input vector data set – Select the vector dataset located in the project.
- Data set name prefix – Enter a prefix that will be affixed to the converted datasets.
- Magnitude – Enter the magnitude for the dataset.
- Direction – Enter the direction for the dataset.
- Vx – Enter the Vx for the dataset.
- Vy – Enter the Vy for the dataset.
Raster Tools
Blend Raster to Edges
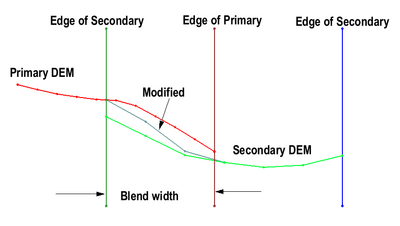
The Blend Raster to Edges tool is intended to facilitate the use of multiple topo/bathy DEMs (potentially from multiple sources) as a source for elevation data on a surface and avoid discontinuities that may exist between the DEMs.
The tool creates a new raster that is a modified version of the raster that is the second argument to the tool. The modified version transition along its active edges from the values in the raster to the values in the primary raster (the first argument).
This tool is intended to be used to pre-condition topo/bathy sources for use in the Interpolate Priority Rasters tool.
Input parameters
- Primary raster – Use the drop-down to select the raster that will be designated as the primary raster.
- Secondary raster – Use the drop-down to select the raster that will be designated as the secondary raster.
- Blend width along edge – Where the edges of the primary and secondary rasters meet, the edges will be blended to the width specified with this option.
Output parameters
- Output raster – Provide a name for the new blended raster.
Current Location in toolbox
Rasters/Blend Raster to Edges
Related Tools
Clip Raster from Elevations
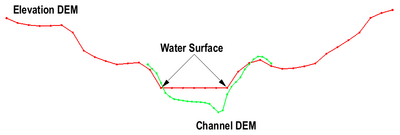
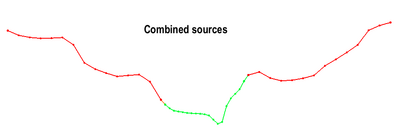
The Clip Raster from Elevations tool creates a new raster (DEM) from a source raster creating invalid data regions in areas where the source raster data are determined to be invalid. To be invalid, the data from the source raster would be either above, or below a provide elevation raster. The side that is invalid is specified as an input parameter.
The Clip Raster from Elevations tool is intended to facilitate the use of multiple topo/bathy DEMs (potentially from multiple sources).
The example of forcing a low flow channel into a DEM illustrates one example of an application of this tool. In this case, it is common for the DEM to have the water surface elevation in regions where the low flow channel exists. These water surface elevation values should not be used in a hydraulic simulation of the area. Instead, channel bed elevations should be supplied. Local survey cross sections are often composed into a channel surface for this purpose. However, due to datum adjustments, time, and roundoff error, the surfaces may have discontinuities. Depending on the situation, the modeler may choose to invalidate the portion of the channel surface that is above the DEM to prevent numerical levees along the edge of the channel.
This tool is intended to be used to pre-condition topo/bathy sources for use in the Interpolate Priority Rasters tool.
Input parameters
- Raster to clip – This option designates the raster which will have elevation values clipped by the elevation raster.
- Elevation raster – This option selects the elevation raster to use.
- Clip elevations above or below elevations raster – Once the raster to clip and elevation raster have been specified, the tool can either clip elevation values either above or below the elevation raster's values.
- "Clip elevations above" – This option removes values that are above the elevation values of the elevation raster.
- "Clip elevations below" – This option removes values that are below the elevation values of the elevation raster.
Output parameters
- Output raster – Enter the name for the new clipped raster.
Current Location in toolbox
Rasters/Blend Raster to Edges
Related Tools
Interpolate Priority Rasters
This tool interpolates multiple rasters to a UGrid with priority. Each source is added to the list in priority order. If a value is not obtained when interpolating from the highest priority source, the tool looks for a value in the next source until either a value is found or all sources are exhausted. The tool has the following options:
- Grid – This option allows you to select the geometry that will receive the interpolated rasters.
- Default value option – This option will allow you to select the default value. Depending on the selection, the options may be added to the dialog.
- "Constant" – The default value option is Constant. This selection adds the Default constant value option.
- Default constant value – This option allows you to set a constant value which will be default.
- "Dataset" – The default value option is Dataset. This selection adds the Default dataset option.
- Default dataset – This option allows you to select which dataset will be default.
- "Raster data" – The default value option is Raster data. There will be no extra options for this selection.
- "Constant" – The default value option is Constant. This selection adds the Default constant value option.
- Output data set name – Allows setting the name of the new interpolated raster.
- Raster 1 (highest priority) – Select the raster that will be given highest priority during the interpolation process.
- Raster 2 – Select the raster that will be given the next highest priority during the interpolation process.
- Raster n – Additional rasters may be selected and given priority in the order they are selected.
Merge Elevation Rasters
This tool merges two or more elevation rasters with priority into a new raster. The tool has the following options:
- Raster 1 – Select the first elevation raster to be merged. This raster will be given the highest priority during the merge.
- Blend distance – Enter a distance for the edges of the raster to be blended when merged with another raster. This option can be set for each raster being merged.
- Raster 2 – Select second raster to be merged. This raster will have the next highest priority.
- Raster n – Additional rasters can be added to the merge with lowering priority.
- Merged raster – Enter a name for the new merged raster.
UGrid to Raster
This tool converts a UGrid into a raster. The tool has the following options:
- Dataset – From the drop-down menu, select the dataset to convert to a raster.
- Pixel size – Enter the pixel resolution size for the new raster.
- Null value – Enter the null value.
- Extrapolation width – Set the extrapolation width.
- Output raster – Enter the name for the new raster.
UGrid Tools
Convert to Voronoi UGrid
This tool converts an existing UGrid to a Voronoi UGrid. The tool has the following options:
- Input grid – Select the geometry that will be converted to a Voronoi UGrid.
- Output grid name – Enter the name for the new Voronoi UGrid.
Merge Ugrids
The tool merges two 2D UGrids into a new 2D grid. The tool has the following options:
- Primary grid – Select the grid that will act as the primary grid. If there are conflicts during the merge, this grid will receive priority to resolve the conflict.
- Secondary grid – Select the grid that will act as the secondary grid during the merge.
- Merged grid – Enter the name of the new merged UGrid.
Smooth UGrid
This tool smooths a UGrid. The tool has the following options:
- Input grid – Select the UGrid to use.
- Maximum slope – Set the maximum potential slope.
- Anchor type – Select which of the following options will be the anchor type.
- "Minimum value" – Sets the anchor type to minimum value.
- "Maximum value" – Sets the anchor type to maximum value.
- Smoothed grid – Enter the name of the new smoothed UGrid.