GMS:Raster Catalog: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[[Image:raster_catalog4.png|Raster surfaces.]] | [[Image:raster_catalog4.png|Raster surfaces.]] | ||
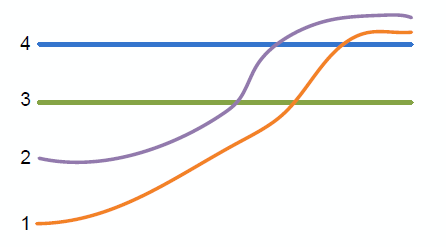
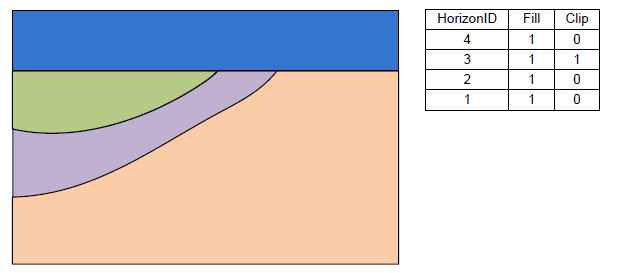
The above figure shows a slice through raster surfaces that have been indexed with horizon ids. | The above figure shows a slice through raster surfaces that have been indexed with horizon ids. | ||
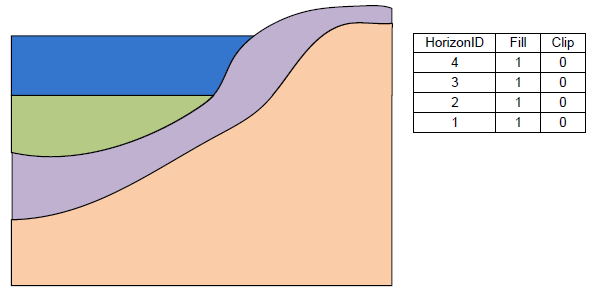
[[Image:raster_catalog3.png|Example 1 of the effect of the Clip field.]] | [[Image:raster_catalog3.png|Example 1 of the effect of the Clip field.]] | ||
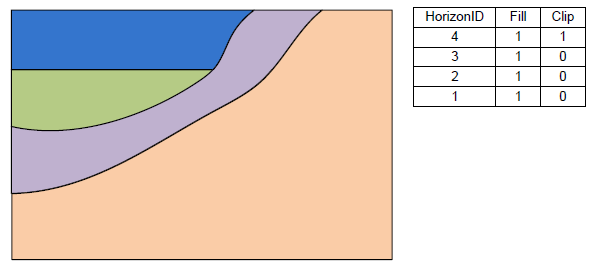
[[Image:raster_catalog1.png|Example 2 of the effect of the Clip field.]] | [[Image:raster_catalog1.png|Example 2 of the effect of the Clip field.]] | ||
[[Image:raster_catalog2.png|Example 3 of the effect of the Clip field.]] | [[Image:raster_catalog2.png|Example 3 of the effect of the Clip field.]] | ||
Revision as of 21:25, 21 August 2012
| This contains information about functionality available starting at GMS version 9.0. The content may not apply to other versions. |
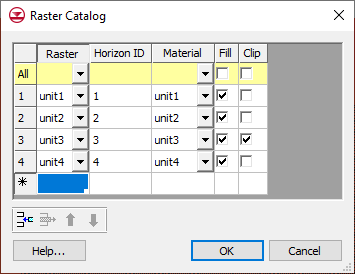
A raster catalog is an attribute table that references rasters that are currently loaded into the GMS project. Each raster represents the top of a horizon. The figure below shows a sample raster catalog.
In the first column of the table the user selects the raster. Then the user can enter a Horizon ID and the associated material. There are two additional fields: Fill and Clip. If the Fill field is turned on then the raster will be used in the interpolation process for the associated horizon. If the Clip field is turned on then any horizon surface with a horizon id less than the associated horizon id will be clipped to this surface. The following images show examples of the effect of the Clip field.
The above figure shows a slice through raster surfaces that have been indexed with horizon ids.