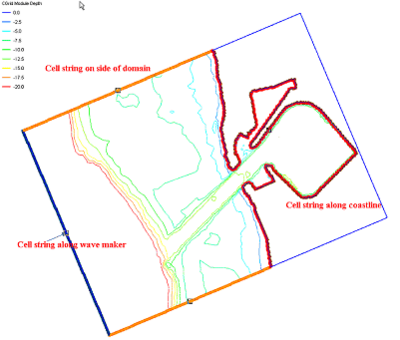
SMS:BOUSS-2D BC Cell Strings
When the BOUSS-2D grid is created, SMS creates cell strings around the computational boundaries of the domain. A cell string is a list of contiguous node locations in the grid. The image to the right shows a grid with four cell strings that were automatically created. The cell string on the left includes the cells along the open ocean. This one has been assigned to be a wave-maker. The one on the right defines the interface between ocean and land along the coastline, and the top and bottom define the portion of the grid that are open to the ocean on those sides.
Cell strings can also be created manually to specify the location of structures, wave-makers, and areas where damping and/or porosity layers may be necessary.
Boundary conditions are specified along cell strings in the BOUSS-2D Boundary Conditions dialog, which is accessed by selecting one or more cell strings using the select cell string tool, and then selecting the Assign BC menu item from the BOUSS-2D menu. Normally, the user will select a single cell string and assign a boundary condition. If a boundary condition has already exists for the selected cell string, the attributes are displayed. The different options for a cell string include:
- Unassigned BC. When a cell string is created in BOUSS-2D its default boundary condition type is Unassigned. Unassigned cell strings do not influence the model. In fact, unassigned cell strings are not saved as part of the BOUSS-2D input files.
- Damping BC. Waves propagating out of the computational domain are absorbed in damping regions (or damping layers) placed around the perimeter of the computational domain. Damping layers can also be used to model the partial reflection from harbor structures inside the computational area. The user must enter a physical width into the “Width” edit field to specify the size of the damping layer. The damping region extends the width on either side of the cell string. The damping value is a non-dimensional damping coefficient that is allowed to vary from 0.0 to 1.0. No damping will occur when a value of 0.0 is used. Waves will be damped when a value of 1.0 is used along the side boundaries. A typical value for shoreline is 0.1. The default damping value is 1.0. SMS will assign the value specified at the cell string and ramp down to 0.0 at a distance of “width” from the cell string.
- Porosity BC. Porosity boundary conditions are used to simulate partial wave reflection and transmission through surface-piercing porous structures such as breakwaters. Enter a physical width into the “Width” edit field to specify the size of the porous structure. Like with the damping regions, this width is extended on both sides of the cell string. The porosity value is a non-dimensional porosity coefficient that is allowed to vary from 0.0 to 1.0. A value of 0.0 corresponds to an impervious structure, while a value of near 1.0 would correspond to a highly porous structure. Typical porosity for stone type breakwaters is 0.4. The default porosity value is 1.0.
- Wave-maker BC. The wave-maker option is only available when a single cell string is selected and that cell string lies in a single column or row (straight line). Legal cell strings can be created using the SHIFT key when creating cell strings, using automatically created cell strings along a grid boundary, or by creating short cell strings. The extent and position of the wave maker can be modified using I,J indices in the dialog. BOUSS-2D generates waves emanating from this cell string. The properties of the waves are defined using the Wave Generator Properties dialog (described below) that is accessed through the Options button. The edit fields are used to position and size the wave maker in the computational domain. The first two values are the Start and End cells of the wave maker along the column or row that is specified by the third value, which is the Offset value. The Start and End values are limited to the number of cells in either the I- or J-direction, and the Offset value is limited to the number of rows or columns.
When the OK button is clicked, a check is done to see if the wave maker cell string is at a constant depth. If the depth varies by more than 20% and the wave maker is on the edge of the grid (not internal), the user is asked whether they want to force constant depth along the wave maker cell string or not. If so, the grid is extended to allow the wave maker to be at the deepest elevation along the string, with a maximum slope of 1:10 from the existing grid to the new wave-maker position. A Wave Calculator is provided as part of BOUSS-2D interface in SMS (see Appendix B) to assist users in the preparation of wave input parameters required by the model. Note that the BOUSS-2D | Assign BC menu item is disabled any time multiple wave makers are selected or if a wave maker and one or more other cell strings are selected.
Modules: Mesh Module · Cartesian Grid Module · Scatter Module · Map Module · GIS Module · Particle Module
Models: ADCIRC · BOUSS-2D · CGWAVE · CMS-Flow · CMS-Wave · FESWMS · FVCOM · Generic Mesh Model · GENESIS · HYDRO AS-2D · PTM · SRH-2D · Steering · STWAVE · TABS · TUFLOW