GMS:Linear: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
:<math>z = f(x,y) = -\frac{A}{C}x-\frac{B}{C}y-\frac{D}{C}</math> | :<math>z = f(x,y) = -\frac{A}{C}x-\frac{B}{C}y-\frac{D}{C}</math> | ||
which is the form of the plane equation used to compute the elevation at any point on the triangle. | :which is the form of the plane equation used to compute the elevation at any point on the triangle. | ||
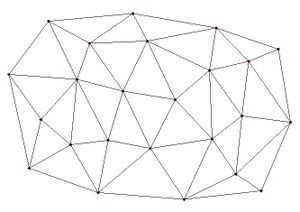
Since the network of triangles only covers the convex hull of the point data, extrapolation beyond the convex hull is not possible with the linear interpolation scheme. Any points outside the convex hull of the point data are assigned the default extrapolation value entered | Since the network of triangles only covers the convex hull of the point data, extrapolation beyond the convex hull is not possible with the linear interpolation scheme. Any points outside the convex hull of the point data are assigned the default extrapolation value entered in the ''Interpolation Options'' dialog. The figure below shows a network of triangles created from point data. | ||
:{{hide in print|[[File:convex_hull.jpg|thumb|none|left|300 px|Network of triangles]]}} | :{{hide in print|[[File:convex_hull.jpg|thumb|none|left|300 px|Network of triangles]]}} | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{{Navbox GMS}} | {{Navbox GMS}} | ||
[[Category:Equations|L]] | [[Category:Equations|L]] | ||
[[Category:Interpolation|L]] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:50, 9 June 2022
If the linear interpolation scheme is selected, the data points are first triangulated to form a network of triangles. The equation of the plane defined by the three vertices of a triangle is as follows:
- where A, B, C, and D are computed from the coordinates of the three vertices (x1,y1,z1), (x2,y2,z2), and (x3,y3,z3):
The plane equation can also be written as:
- which is the form of the plane equation used to compute the elevation at any point on the triangle.
Since the network of triangles only covers the convex hull of the point data, extrapolation beyond the convex hull is not possible with the linear interpolation scheme. Any points outside the convex hull of the point data are assigned the default extrapolation value entered in the Interpolation Options dialog. The figure below shows a network of triangles created from point data.
See also
GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||