SMS:Simulations: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Starting in version 11.1, SMS has the capacity to run certain models as a simulation. We refer to this approach as simulation based modeling. A simulation includes the domain (i.e. geometry in the form of a UGrid, 2D Mesh, Cartesian grid, etc.), boundary conditions, model parameters, event definition, and material set used for a single model run. Multiple simulations can exist within the same project in order to compare alternatives. These simulations don't need to use the same numeric model. | |||
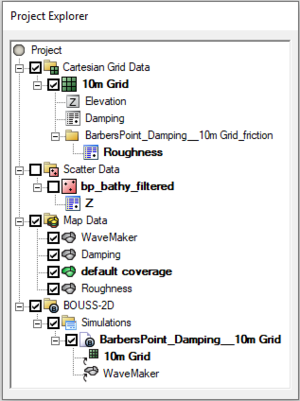
[[File:BOUSSsimulation.png|thumb|300 px|Example of the Project Explorer containing a simulation for the BOUSS-2D model.]] | |||
Starting in version 11.1, SMS has the capacity to run certain models as a simulation. A simulation includes the domain, boundary conditions, model parameters, event definition, and material set used for a single model run. Multiple simulations can exist within the same project in order to compare alternatives. | |||
==Simulation Based Modeling== | ==Simulation Based Modeling== | ||
A typical numerical simulation consists of the following components: | A typical numerical simulation consists of the following components: | ||
* A geometric domain – | * A geometric domain – This can be a structured or unstructured grid depending on the model being used. | ||
** Structured grids | ** Structured grids include multiple formats: | ||
*** Cartesian grids | *** Cartesian grids | ||
*** Rotated Cartesian grids | *** Rotated Cartesian grids | ||
*** Refined Cartesian grids | *** Refined Cartesian grids – Each row or column can have its own height or width | ||
*** | *** Quadtree grids – Each cell in the grid can be subdivided into two or more cells in each direction. These were previously referred to as telescoping grids. | ||
*** Curvilinear or Boundary fitted grids | *** Curvilinear or Boundary fitted grids – In this representation, the cells are still in a structured format meaning each cell has four neighbors and each corner point has four neighbors. However, the curvilinear of boundary fitted grid bends and stretches to match geometric features | ||
** Unstructured grids | ** Unstructured grids include multiple formats: | ||
* A set of | *** All Triangular mesh – All cells/elements are triangles. Supports nodal datasets (values at each node). Does not support cell-centered datasets. Some models require this format including ADCIRC and AdH. | ||
*** All quadrilateral mesh. – All cells/elements are quadrilaterals. Supports nodal datasets (values at each node). Does not support cell-centered datasets. | |||
*** Mixed mesh. – A combination of triangular and quadrilateral cells/elements. Supports nodal datasets (values at each node). Does not support cell-centered datasets. | |||
*** Voronoi Ugrid – Polygonal cells with edges between adjacent cells perpendicular to centroidal connection. Supports both nodal and cell-centered datasets. | |||
*** Unconstrained UGrid – Any number of edges in cells. Supports both nodal and cell-centered datasets. | |||
* A set of attributes assigned to specific locations in the domain. These locations could be at a single point, along a line or in a polygonal region. In SMS these types of components are stored as Map Module coverages with attributes on the geographic entities. The specific properties/attributes depend on the numeric model in use. Examples include: | |||
** Boundary conditions specified at a point or cell. | ** Boundary conditions specified at a point or cell. | ||
** Boundary conditions specified | ** Boundary conditions specified along a string of points or cells. | ||
** Boundary conditions specified at a cluster or group of points or cells. | ** Boundary conditions specified at a cluster or group of points or cells. | ||
** Spatial attributes assigned to each point or cell in the domain. Examples of this include: | ** Spatial attributes assigned to each point or cell in the domain. Examples of this include: | ||
| Line 22: | Line 26: | ||
* A set of model parameters. | * A set of model parameters. | ||
Traditionally the SMS has employed what is now referred to as grid based or mesh based modeling. | Traditionally the SMS has employed what is now referred to as grid based or mesh based modeling. This means that a numerical model simulation was inherently tied to a specific geometric domain or grid. This type of grid based modeling meant that all of the components of a simulation (the list above) would be specified explicitly for the domain. | ||
This approach meant that any change in a simulation, no matter how slight, | This approach meant that any change in a simulation, no matter how slight, required a completely independent copy of the entire set of components. | ||
Beginning with SMS version 11.0 the SMS development team began a migration to simulation based modeling. | Beginning with SMS version 11.0 the SMS development team began a migration to simulation based modeling. This approach follows the concept that components of a simulation are constructed individually and then grouped together into a simulation. This allows a modeler to define multiple simulations with common building blocks (components). A domain (grid), set of boundary conditions, or set of initial conditions can be reused in multiple simulations. This approach makes the modeling process more inclusive and adaptable. | ||
In Version 12.0 of SMS, the simulation based modeling expanded to include the SRH-2D, CMS-Flow and BOUSS-2D | In Version 12.0 of SMS, the simulation based modeling expanded to include the SRH-2D, CMS-Flow and BOUSS-2D numeric models. | ||
In Version 13.2 of SMS, the simulation based modeling approach has expanded to ADCIRC, CMS-Wave, STWAVE and AdH. It is anticipated that all interfaces will be simulation based. | |||
==Working with Simulations== | ==Working with Simulations== | ||
A simulation can be created by right-clicking on a blank portion of the Project Explorer and choosing the ''New Simulation'' | A simulation can be created by right-clicking on a blank portion of the Project Explorer and choosing the ''New Simulation'' submenu. The ''New Simulation'' menu will have commands to create a new model simulation. Selecting a model will cause a simulation folder [[File:Simulation Folder Icon.svg|16 px]] for the chosen model to appear in the Project Explorer. | ||
After a simulation [[File:Simulation Icon.svg|16 px]] has been created, components may be added to the simulation. Components are often created as map coverages, meshes, grids, or | After a simulation [[File:Simulation Icon.svg|16 px]] has been created, components may be added to the simulation. Components are often created as map coverages, meshes, grids, or scatter sets. The individual map coverages, grids, or scatter sets can be linked to the simulation by clicking on the item in the Project Explorer and dragging it under the simulation item in the Project Explorer. Each simulation in the Project Explorer will show a list of all linked components [[File:Coverage Link.svg|16 px]]. This allows multiple simulations to make use of the same datasets. | ||
Components can also be added or removed from a simulation using the right-click ''Link To'' or ''Unlink From'' submenus. | Components can also be added or removed from a simulation using the right-click ''Link To'' or ''Unlink From'' submenus. | ||
Once a simulation exists future simulations are often similar to one already created. Often it is easier to make a copy of the simulation and make changes where appropriate. A simulation can be copied by right-clicking on the simulation and choosing '''Duplicate'''. All simulations for a model will be listed under the simulation [[File:Simulation Icon.svg|16 px]] for that model. Under the simulation data [[File:Simulation Data Icon.svg|16 px]] item all simulations for all models will be listed—SMS supports using more than one model for a project. | Once a simulation exists, future simulations are often similar to one already created. Often it is easier to make a copy of the simulation and make changes where appropriate. A simulation can be copied by right-clicking on the simulation and choosing '''Duplicate'''. All simulations for a model will be listed under the simulation [[File:Simulation Icon.svg|16 px]] for that model. Under the simulation data [[File:Simulation Data Icon.svg|16 px]] item all simulations for all models will be listed—SMS supports using more than one model for a project. | ||
:'''''Note:''''' When naming simulations, apostrophes are not allowed in the simulation name. Using an apostrophe in any simulation name may cause an error. | :'''''Note:''''' When naming simulations, apostrophes are not allowed in the simulation name. Using an apostrophe in any simulation name may cause an error. | ||
The right-click menu for a simulation includes menu commands specific to each model. | The right-click menu for a simulation includes menu commands specific to each model. | ||
=== Simulation Menu Preferences === | |||
[[File:SimulationMenuPreferencesMultiple.png|thumb|400 px|The ''Simulation Menu Preferences'' dialog]] | |||
In addition to some general commands, which are described below, the user has control over a set of simulation right-click menu options. These options are accessed by pressing the '''Edit''' button in the [[SMS:Preferences#Project Explorer|''Project Explorer'']] tab of the [[SMS:Preferences|''SMS Preferences'']] dialog. This dialog is accessed in the ''Edit'' menu using the '''Preferences''' command. | |||
<!--Update template--> | |||
The options in this dialog allow hiding or showing menu commands for the simulation right-click menus. The dialog has the following options: | |||
*''Simulation'' – This section is for turning on and off commands located in the simulation right-click menu for individual simulations. It includes the following commands: | |||
**Save Simulation | |||
**Run Simulation | |||
**Save Simulation and Run | |||
**Save Project and Simulation | |||
** Save Project, Simulation and Run | |||
*''Multiple Simulations for Model'' – This section is for turning on and off commands for the simulation data right-click menu that affects multiple simulations. This is accessed by right-clicking on the simulation folder [[File:Simulation Folder Icon.svg|16 px]] for each numerical model. It includes the following commands: | |||
**Save Multiple Simulations | |||
**Run Multiple Simulations | |||
**Save Multiple Simulations and Run | |||
**Save Project and Multiple Simulations | |||
** Save Project, Multiple Simulations and Run | |||
:'''''Note:''''' Saving a project does not save files used by the numeric model for the simulation run. The simulation must be saved for these files to be exported from the project. | |||
:'''''Note:''''' Some models do not support a Save and/or Run command. Menus selected in this dialog may not appear for those models. For example, if the '''Save Simulation and Run''' was the only menu item selected, but the model only supports the '''Save''' command, then the '''Save Simulation''' command would appear instead of the '''Save Simulation and Run''' command. | |||
===General Simulation Right-Click Menu Commands=== | ===General Simulation Right-Click Menu Commands=== | ||
{{Anchor|Simulation Menu}} | {{Anchor|Simulation Menu}} | ||
Right-clicking on any simulation object [[File:Simulation Icon.svg|16 px]] in the Project Explorer will bring up a menu for that simulation. | Right-clicking on any simulation object [[File:Simulation Icon.svg|16 px]] in the Project Explorer will bring up a menu for that simulation. Some of the commands are specific for the simulation model type. The simulation right-click menu has the following commands that are used by all simulations. | ||
* ''' | * '''Rename''' – Allows changing the simulation name. | ||
* '''Duplicate''' – Creates a copy of the selected simulation. All components linked to selected simulation will be linked to the duplicate simulation. Adding, or removing the components in the duplicate simulation will not change the original simulation. | * '''Duplicate''' – Creates a copy of the selected simulation. All components linked to selected simulation will be linked to the duplicate simulation. Adding, or removing the components in the duplicate simulation will not change the original simulation. | ||
* ''' | * '''Delete''' – Removes the selected simulation. This command does not delete or modify components linked to the simulation. | ||
* '''Properties''' – Brings up a ''Properties'' dialog that shows which model the simulation is using and what components have been applied. | * '''Properties''' – Brings up a ''Properties'' dialog that shows which model the simulation is using and what components have been applied. | ||
Right-clicking on the simulation folder [[File:Simulation Folder Icon.svg|16 px]] | Right-clicking on the simulation folder [[File:Simulation Folder Icon.svg|16 px]] always includes the following commands: | ||
* '''New Simulation''' – This command will create a new simulation of the same model type as the simulation folder. | * '''New Simulation''' – This command will create a new simulation of the same model type as the simulation folder. | ||
* '''Simulation Run Queue''' – Opens the [[SMS:Simulations#Simulation_Run_Queue|''Simulation Run Queue'']] dialog. | * '''Simulation Run Queue''' – Opens the [[SMS:Simulations#Simulation_Run_Queue|''Simulation Run Queue'']] dialog. | ||
* ''' | |||
Additional commands appear in the simulation right-click menu depend on the settings in the ''Simulation Menu Preferences'' dialog as described above. | |||
If any of the ''Multiple'' simulation commands are invoked, a dialog appears listing the simulations in this folder with toggle box next to each as shown. The user may then select which simulations should be included in this command. | |||
[[File:MultipleSimulations.png|thumb|250px|The ''Simulations'' dialog for multiple simulations]] | |||
These optional commands should be self explanatory based on their name. In general, their function can be described as: | |||
*A command that says '''Save Simulation''' generates the files for the numeric model simulation run, but does not save the project files. | |||
*A command that says '''Save Project''' saves the project such as mesh and map data, but doesn't generate the files needed for the simulation run. This command is typically used with the ''Save Simulation'' command. | |||
*A command that says '''Run Simulation''' runs the simulation. It is necessary to save the simulation files as part of or before using a run command. | |||
All of the above applies equally to multiple simulations commands and single simulations commands. | |||
==Simulation Run Queue== | ==Simulation Run Queue== | ||
| Line 63: | Line 99: | ||
*''Maximum Number of Concurrent Processes Allowed'' – Determines how many processes can be active in SMS at the same time. A simulation may contain multiple processes. | *''Maximum Number of Concurrent Processes Allowed'' – Determines how many processes can be active in SMS at the same time. A simulation may contain multiple processes. | ||
The run queue will show all simulations that are either currently running or have not yet been removed from the run queue. Each simulation will be listed in the order the simulation runs were started. Each simulation can be expanded to show what happened during the model run. If the model has a pre-processor and/or a post-processor, these will be displayed separately from the main model run. Process bars display how much of the process | The run queue will show all simulations that are either currently running or have not yet been removed from the run queue. Each simulation will be listed in the order the simulation runs were started. Each simulation can be expanded to show what happened during the model run. If the model has a pre-processor and/or a post-processor, these will be displayed separately from the main model run. Process bars display how much of the process has been completed. | ||
The following actions can be taken for each simulation: | The following actions can be taken for each simulation: | ||
| Line 72: | Line 108: | ||
===Monitoring Data=== | ===Monitoring Data=== | ||
The '''Simulation Run Queue''' contains an option for ''Monitoring Data''. Turning on this option activates the tabs underneath for the selected simulation. The tabs are: | The '''Simulation Run Queue''' contains an option for ''Monitoring Data''. Turning on this option activates the tabs underneath for the selected simulation. The tabs are: | ||
* ''Command Line'' – Shows the command line entries for the selected process. | * ''Command Line'' – Shows the command line entries for the selected process. Reports errors encountered during the simulation run. | ||
* ''Residual Plot'' – Shows the residual plot for the selected simulation. | * ''Residual Plot'' – Shows the residual plot for the selected simulation. | ||
* ''Monitor Point Plot'' – If monitor points are included in the simulation, this | * ''Monitor Point Plot'' – If monitor points are included in the simulation, this shows a plot for the point location once the simulation has included the point in the simulation run. | ||
* ''Monitor Line Plot'' – If monitor lines are included in the simulation, this | * ''Monitor Line Plot'' – If monitor lines are included in the simulation, this shows a plot for the line location once the simulation has included the line in the simulation run. | ||
==Simulation Properties== | ==Simulation Properties== | ||
Right-clicking on a simulation and selecting the '''Properties''' command will bring up a ''Simulation Properties'' dialog. This dialog will list the name of simulation, the simulation model type, and all coverages and geometries applied to the simulation. It also has ''Notes'' tab where notes about the simulation can be entered. | Right-clicking on a simulation and selecting the '''Properties''' command will bring up a ''Simulation Properties'' dialog. This dialog will list the name of simulation, the simulation model type, and all coverages and geometries applied to the simulation. It also has a ''Notes'' tab where notes about the simulation can be entered. | ||
==Models That Use | ==Models That Use Simulation Based Modeling== | ||
Not all models usable in SMS can be created in the simulation format. Models that currently make use of the simulation format are: | Not all models usable in SMS can be created in the simulation format. Models that currently make use of the simulation format are: | ||
{|class="wikitable" | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 123: | Line 159: | ||
|align="center"|11.1 | |align="center"|11.1 | ||
|See [[SMS:TUFLOW Simulation|TUFLOW Simulation]] | |See [[SMS:TUFLOW Simulation|TUFLOW Simulation]] | ||
|- | |||
|[[SMS:TUFLOW|TUFLOW FV]] | |||
|align="center"|13.2 | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[SMS:WAM|WAM]] | |[[SMS:WAM|WAM]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:55, 11 September 2023
Starting in version 11.1, SMS has the capacity to run certain models as a simulation. We refer to this approach as simulation based modeling. A simulation includes the domain (i.e. geometry in the form of a UGrid, 2D Mesh, Cartesian grid, etc.), boundary conditions, model parameters, event definition, and material set used for a single model run. Multiple simulations can exist within the same project in order to compare alternatives. These simulations don't need to use the same numeric model.
Simulation Based Modeling
A typical numerical simulation consists of the following components:
- A geometric domain – This can be a structured or unstructured grid depending on the model being used.
- Structured grids include multiple formats:
- Cartesian grids
- Rotated Cartesian grids
- Refined Cartesian grids – Each row or column can have its own height or width
- Quadtree grids – Each cell in the grid can be subdivided into two or more cells in each direction. These were previously referred to as telescoping grids.
- Curvilinear or Boundary fitted grids – In this representation, the cells are still in a structured format meaning each cell has four neighbors and each corner point has four neighbors. However, the curvilinear of boundary fitted grid bends and stretches to match geometric features
- Unstructured grids include multiple formats:
- All Triangular mesh – All cells/elements are triangles. Supports nodal datasets (values at each node). Does not support cell-centered datasets. Some models require this format including ADCIRC and AdH.
- All quadrilateral mesh. – All cells/elements are quadrilaterals. Supports nodal datasets (values at each node). Does not support cell-centered datasets.
- Mixed mesh. – A combination of triangular and quadrilateral cells/elements. Supports nodal datasets (values at each node). Does not support cell-centered datasets.
- Voronoi Ugrid – Polygonal cells with edges between adjacent cells perpendicular to centroidal connection. Supports both nodal and cell-centered datasets.
- Unconstrained UGrid – Any number of edges in cells. Supports both nodal and cell-centered datasets.
- Structured grids include multiple formats:
- A set of attributes assigned to specific locations in the domain. These locations could be at a single point, along a line or in a polygonal region. In SMS these types of components are stored as Map Module coverages with attributes on the geographic entities. The specific properties/attributes depend on the numeric model in use. Examples include:
- Boundary conditions specified at a point or cell.
- Boundary conditions specified along a string of points or cells.
- Boundary conditions specified at a cluster or group of points or cells.
- Spatial attributes assigned to each point or cell in the domain. Examples of this include:
- Material types for each cell to define a roughness value.
- A dataset to define an initial water level.
- A set of model parameters.
Traditionally the SMS has employed what is now referred to as grid based or mesh based modeling. This means that a numerical model simulation was inherently tied to a specific geometric domain or grid. This type of grid based modeling meant that all of the components of a simulation (the list above) would be specified explicitly for the domain.
This approach meant that any change in a simulation, no matter how slight, required a completely independent copy of the entire set of components.
Beginning with SMS version 11.0 the SMS development team began a migration to simulation based modeling. This approach follows the concept that components of a simulation are constructed individually and then grouped together into a simulation. This allows a modeler to define multiple simulations with common building blocks (components). A domain (grid), set of boundary conditions, or set of initial conditions can be reused in multiple simulations. This approach makes the modeling process more inclusive and adaptable.
In Version 12.0 of SMS, the simulation based modeling expanded to include the SRH-2D, CMS-Flow and BOUSS-2D numeric models.
In Version 13.2 of SMS, the simulation based modeling approach has expanded to ADCIRC, CMS-Wave, STWAVE and AdH. It is anticipated that all interfaces will be simulation based.
Working with Simulations
A simulation can be created by right-clicking on a blank portion of the Project Explorer and choosing the New Simulation submenu. The New Simulation menu will have commands to create a new model simulation. Selecting a model will cause a simulation folder ![]() for the chosen model to appear in the Project Explorer.
for the chosen model to appear in the Project Explorer.
After a simulation ![]() has been created, components may be added to the simulation. Components are often created as map coverages, meshes, grids, or scatter sets. The individual map coverages, grids, or scatter sets can be linked to the simulation by clicking on the item in the Project Explorer and dragging it under the simulation item in the Project Explorer. Each simulation in the Project Explorer will show a list of all linked components
has been created, components may be added to the simulation. Components are often created as map coverages, meshes, grids, or scatter sets. The individual map coverages, grids, or scatter sets can be linked to the simulation by clicking on the item in the Project Explorer and dragging it under the simulation item in the Project Explorer. Each simulation in the Project Explorer will show a list of all linked components ![]() . This allows multiple simulations to make use of the same datasets.
. This allows multiple simulations to make use of the same datasets.
Components can also be added or removed from a simulation using the right-click Link To or Unlink From submenus.
Once a simulation exists, future simulations are often similar to one already created. Often it is easier to make a copy of the simulation and make changes where appropriate. A simulation can be copied by right-clicking on the simulation and choosing Duplicate. All simulations for a model will be listed under the simulation ![]() for that model. Under the simulation data
for that model. Under the simulation data ![]() item all simulations for all models will be listed—SMS supports using more than one model for a project.
item all simulations for all models will be listed—SMS supports using more than one model for a project.
- Note: When naming simulations, apostrophes are not allowed in the simulation name. Using an apostrophe in any simulation name may cause an error.
The right-click menu for a simulation includes menu commands specific to each model.
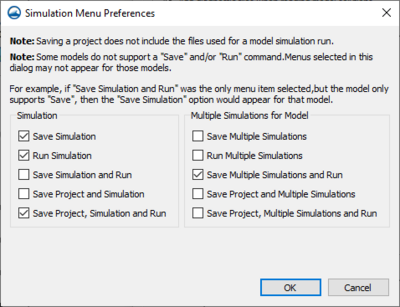
Simulation Menu Preferences
In addition to some general commands, which are described below, the user has control over a set of simulation right-click menu options. These options are accessed by pressing the Edit button in the Project Explorer tab of the SMS Preferences dialog. This dialog is accessed in the Edit menu using the Preferences command. The options in this dialog allow hiding or showing menu commands for the simulation right-click menus. The dialog has the following options:
- Simulation – This section is for turning on and off commands located in the simulation right-click menu for individual simulations. It includes the following commands:
- Save Simulation
- Run Simulation
- Save Simulation and Run
- Save Project and Simulation
- Save Project, Simulation and Run
- Multiple Simulations for Model – This section is for turning on and off commands for the simulation data right-click menu that affects multiple simulations. This is accessed by right-clicking on the simulation folder
 for each numerical model. It includes the following commands:
for each numerical model. It includes the following commands:
- Save Multiple Simulations
- Run Multiple Simulations
- Save Multiple Simulations and Run
- Save Project and Multiple Simulations
- Save Project, Multiple Simulations and Run
- Note: Saving a project does not save files used by the numeric model for the simulation run. The simulation must be saved for these files to be exported from the project.
- Note: Some models do not support a Save and/or Run command. Menus selected in this dialog may not appear for those models. For example, if the Save Simulation and Run was the only menu item selected, but the model only supports the Save command, then the Save Simulation command would appear instead of the Save Simulation and Run command.
General Simulation Right-Click Menu Commands
Right-clicking on any simulation object ![]() in the Project Explorer will bring up a menu for that simulation. Some of the commands are specific for the simulation model type. The simulation right-click menu has the following commands that are used by all simulations.
in the Project Explorer will bring up a menu for that simulation. Some of the commands are specific for the simulation model type. The simulation right-click menu has the following commands that are used by all simulations.
- Rename – Allows changing the simulation name.
- Duplicate – Creates a copy of the selected simulation. All components linked to selected simulation will be linked to the duplicate simulation. Adding, or removing the components in the duplicate simulation will not change the original simulation.
- Delete – Removes the selected simulation. This command does not delete or modify components linked to the simulation.
- Properties – Brings up a Properties dialog that shows which model the simulation is using and what components have been applied.
Right-clicking on the simulation folder ![]() always includes the following commands:
always includes the following commands:
- New Simulation – This command will create a new simulation of the same model type as the simulation folder.
- Simulation Run Queue – Opens the Simulation Run Queue dialog.
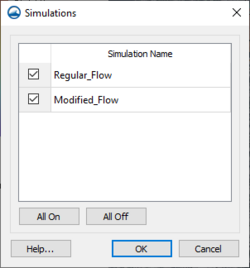
Additional commands appear in the simulation right-click menu depend on the settings in the Simulation Menu Preferences dialog as described above. If any of the Multiple simulation commands are invoked, a dialog appears listing the simulations in this folder with toggle box next to each as shown. The user may then select which simulations should be included in this command.
These optional commands should be self explanatory based on their name. In general, their function can be described as:
- A command that says Save Simulation generates the files for the numeric model simulation run, but does not save the project files.
- A command that says Save Project saves the project such as mesh and map data, but doesn't generate the files needed for the simulation run. This command is typically used with the Save Simulation command.
- A command that says Run Simulation runs the simulation. It is necessary to save the simulation files as part of or before using a run command.
All of the above applies equally to multiple simulations commands and single simulations commands.
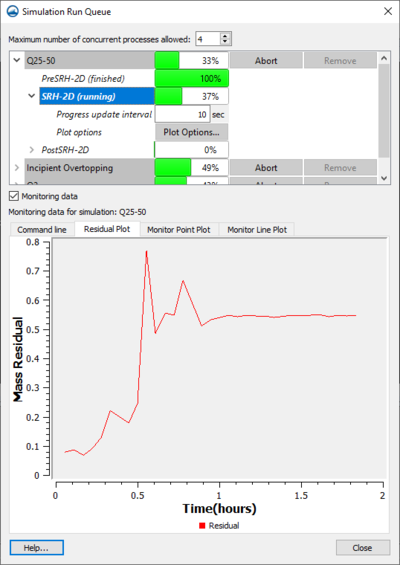
Simulation Run Queue
The Simulation Run Queue is used to manage multiple simulations. Once a simulation is started, the Simulation Run Queue appears. The dialog can also be reached by right-clicking on a simulation item in the Project Explorer and selecting the Simulation Run Queue command.
The number of processes allowed in the run queue is determined by the following option:
- Maximum Number of Concurrent Processes Allowed – Determines how many processes can be active in SMS at the same time. A simulation may contain multiple processes.
The run queue will show all simulations that are either currently running or have not yet been removed from the run queue. Each simulation will be listed in the order the simulation runs were started. Each simulation can be expanded to show what happened during the model run. If the model has a pre-processor and/or a post-processor, these will be displayed separately from the main model run. Process bars display how much of the process has been completed.
The following actions can be taken for each simulation:
- Load – Loads the solution files into SMS from a completed simulation run.
- Abort – Ends a simulation run before it has completed.
- Remove – Deletes a completed or aborted simulation from the run queue.
- Plot Options – Opens the Plot Options dialog. If the Monitoring Data option is turned on, the display of the plot line color, width, and style can be adjusted in this dialog.
Monitoring Data
The Simulation Run Queue contains an option for Monitoring Data. Turning on this option activates the tabs underneath for the selected simulation. The tabs are:
- Command Line – Shows the command line entries for the selected process. Reports errors encountered during the simulation run.
- Residual Plot – Shows the residual plot for the selected simulation.
- Monitor Point Plot – If monitor points are included in the simulation, this shows a plot for the point location once the simulation has included the point in the simulation run.
- Monitor Line Plot – If monitor lines are included in the simulation, this shows a plot for the line location once the simulation has included the line in the simulation run.
Simulation Properties
Right-clicking on a simulation and selecting the Properties command will bring up a Simulation Properties dialog. This dialog will list the name of simulation, the simulation model type, and all coverages and geometries applied to the simulation. It also has a Notes tab where notes about the simulation can be entered.
Models That Use Simulation Based Modeling
Not all models usable in SMS can be created in the simulation format. Models that currently make use of the simulation format are:
| Model | Initial Version | Model Simulation Specifics |
|---|---|---|
| ADCIRC | 13.0 | See ADCIRC Graphical Interface |
| BOUSS-2D | 11.2 | See BOUSS-2D Simulations |
| BOUSS Runup/Overtopping | 11.1 | |
| CMS-Flow | 12.1 | See CMS-Flow Simulation |
| EFDC | 11.1 | |
| HEC-RAS | 12.2 | See HEC-RAS Simulation |
| SRH-2D | 12.0 | See SRH-2D Simulation |
| STWAVE | 13.0 | See STWAVE Graphical Interface |
| TUFLOW | 11.1 | See TUFLOW Simulation |
| TUFLOW FV | 13.2 | |
| WAM | 11.1 | See WAM Simulation Model Control |
Related Topics
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||