SMS:RMA4 Material Properties: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:RMA 4 MP. | [[Image:RMA 4 MP.png|thumb|450 px|''RMA4 Material Properties'' dialog]] | ||
The ''RMA4 Material Properties'' dialog is reached through the ''RMA4'' | '''Material Properties...''' menu command in the Mesh module. | The ''RMA4 Material Properties'' dialog is reached through the ''RMA4'' | '''Material Properties...''' menu command in the Mesh module. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[Category:RMA4|M]] | [[Category:RMA4|M]] | ||
[[Category:RMA4 Dialogs]] | [[Category:RMA4 Dialogs|mat]] | ||
[[Category:SMS Materials|R]] | [[Category:SMS Materials|R]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:39, 12 June 2020
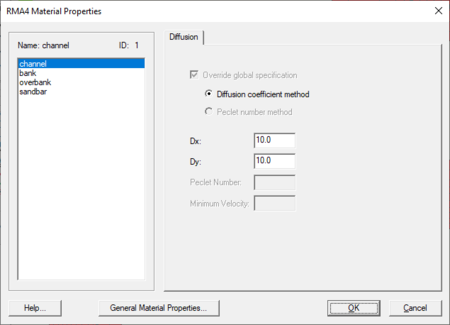
The RMA4 Material Properties dialog is reached through the RMA4 | Material Properties... menu command in the Mesh module.
The dialog has the following options:
- Material list – a list of available materials is populated on the left side of the dialog. Selecting a material allows the diffusion to be changed for the material.
- Overide global specification – When turned on the global diffusion will not be used for the material.
- Diffusion coefficient method – Specifies using diffusion coefficients to approximate turbulence.
- Peclet number method – Specifies the use of a Péclet number to determine diffusion.
- Dx – Specifies diffusion in the x direction.
- Dy – Specifies diffusion in the y direction.
- Peclet Number – Enter the Péclet number value.
- Minimum Velocity – The lowest velocity allowed for diffusion.
- General Material Properties – Brings up the Materials Data dialog.
Diffusion
Because RMA4 does not have the ability to model turbulence, diffusion coefficients may be used to approximate turbulence. By assigning a diffusion coefficient in the x and y directions for each material, the flow over that material will be altered somewhat to provide an approximation of turbulent flow over that region. A value of -1.0 may be applied to allow normal flow over the material. Positive values provide turbulence. The higher the value, the greater the effect is.
Related Topics
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||