GMS:UGrid Kriging Interpolation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
Kriging is a method of interpolation named after a South African mining engineer named D. G. Krige who developed the technique in an attempt to more accurately predict ore reserves. Over the past several decades kriging has become a fundamental tool in the field of geostatistics. | Kriging is a method of interpolation named after a South African mining engineer named D. G. Krige who developed the technique in an attempt to more accurately predict ore reserves. Over the past several decades kriging has become a fundamental tool in the field of geostatistics. | ||
| Line 120: | Line 118: | ||
:By default, the search space is a circle (sphere in 3D) centered at the point with a radius defined by the Maximum search radius item. For problems exhibiting anisotropy, the search space can be transformed to an ellipse (ellipsoid in 3D). The anis1 factor and the azimuth angle control the shape and orientation of the ellipse. The azimuth represents the rotation of the major principal axis clockwise from the +y axis. The anis1 factor represents the ratio of the search radius along the minor principal axis relative to the search radius (the maximum radius) in the major principal direction. In most cases, the anis1 factor and the azimuth angle should match the anis factor and azimuth angle defined in the [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | :By default, the search space is a circle (sphere in 3D) centered at the point with a radius defined by the Maximum search radius item. For problems exhibiting anisotropy, the search space can be transformed to an ellipse (ellipsoid in 3D). The anis1 factor and the azimuth angle control the shape and orientation of the ellipse. The azimuth represents the rotation of the major principal axis clockwise from the +y axis. The anis1 factor represents the ratio of the search radius along the minor principal axis relative to the search radius (the maximum radius) in the major principal direction. In most cases, the anis1 factor and the azimuth angle should match the anis factor and azimuth angle defined in the [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
*Experimental variogram | *''Experimental variogram'' – For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
**New | **''New'' – Brings up the ''Experimental Variogram'' dialog where new variogram can be defined. For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
**Delete | **''Delete'' – Removes the selected variogram. | ||
**Edit | **''Edit'' – Brings up the ''Experimental Variogram'' dialog where changes can be made to the existing variogram. | ||
**Standard Variogram | **''Standard Variogram'' – Generates a variogram automatically based on the existing data. | ||
*''Nested Structure'' – A model variogram is constructed using a combination of one or more model functions | *''Nested Structure'' – A model variogram is constructed using a combination of one or more model functions. | ||
**'''New''' – Creates a new nested structure in the list. | **'''New''' – Creates a new nested structure in the list. | ||
**''Delete'' – Removes the seleced nested structure. | **''Delete'' – Removes the seleced nested structure. | ||
* | *''Model function'' – Allows selecting on of four types of model functions: "Spherical", "Exponetial", "Gaussian", or "Power". For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
* | *''Azimuth angle'' – For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
* | *''Dip angle'' – For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
* | *''Plunge angle'' – For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
* | *''Nugget'' – Represents a minimum variance. For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
* | *''Contribution'' – For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
* | *''Range'' – For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
* | *''Anis1'' – For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
* | *''Anis2'' – For more information see the article [[GMS:Variogram Editor|''Variogram Editor'']]. | ||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:58, 12 November 2018
Kriging is a method of interpolation named after a South African mining engineer named D. G. Krige who developed the technique in an attempt to more accurately predict ore reserves. Over the past several decades kriging has become a fundamental tool in the field of geostatistics.
Kriging is based on the assumption that the parameter being interpolated can be treated as a regionalized variable. A regionalized variable is intermediate between a truly random variable and a completely deterministic variable in that it varies in a continuous manner from one location to the next and therefore points that are near each other have a certain degree of spatial correlation, but points that are widely separated are statistically independent (Davis, 1986). Kriging is a set of linear regression routines which minimize estimation variance from a predefined covariance model.
The kriging routines implemented in GMS are based on the Geostatistical Software Library (GSLIB) routines published by Deutsch and Journel (1992). Since kriging is a rather complex interpolation technique and includes numerous options, a complete description of kriging is beyond the scope of this reference manual. It is strongly encouraged to refer the GSLIB textbook for more information:
- Deutsch, C.V., & A.G. Journel. GSLIB: Geostatistical Software Library and User's Guide. Oxford University Press, New York, 1992.
Other good references on kriging include:
- Royle, A.G., F.L. Clausen, & P. Frederiksen. Practical Universal Kriging and Automatice Contouring. Geo-Processing, Vol. 1, No. 4, 1981.
- Davis, J.C. Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1986.
- Lam, N.S. Spatial Interpolation Methods: A Review. The American Cartographer. Vol. 10, No. 2, 1983.
- Heine, G.W., A Controlled Study of Some Two-Dimensional Interpolation Methods, COGS Computer Contributions, Vol. 2, No. 2.
- Olea, T.A., Optimal Contour Mapping using Universal Kriging. J. Geophys. Research, Vol. 79, No. 5, 1974.
- Journel, A.G., & Huijbregts, C.J. Mining Geostatistics. Academic Press, New York, NY, 1978.
Kriging Techniques
A powerful set of kriging techniques with varying degrees of sophistication have been implemented in GMS. The selection of the Kriging method and the definition of the variograms are accomplished using the Kriging Options dialog. There are several differences between 2D and 3D Kriging. The supported techniques include:
Ordinary Kriging
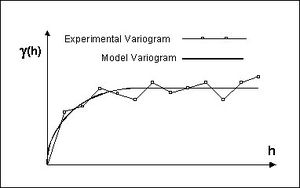
The first step in ordinary kriging is to construct a variogram from the scatter point set to be interpolated. A variogram consists of two parts: an experimental variogram and a model variogram. Suppose that the value to be interpolated is referred to as f. The experimental variogram is found by calculating the variance (g) of each point in the set with respect to each of the other points and plotting the variances versus distance (h) between the points. Several formulas can be used to compute the variance, but it is typically computed as one half the difference in f squared.
Once the experimental variogram is computed, the next step is to define a model variogram. A model variogram is a simple mathematical function that models the trend in the experimental variogram.
As can be seen in the above figure, the shape of the variogram indicates that at small separation distances, the variance in f is small. In other words, points that are close together have similar f values. After a certain level of separation, the variance in the f values becomes somewhat random and the model variogram flattens out to a value corresponding to the average variance.
Once the model variogram is constructed, it is used to compute the weights used in kriging. The basic equation used in ordinary kriging is as follows:
Where n is the number of scatter points in the set, fi are the values of the scatter points, and wi are weights assigned to each scatter point.
This equation is essentially the same as the equation used for inverse distance weighted interpolation (equation 9.8) except that rather than using weights based on an arbitrary function of distance, the weights used in kriging are based on the model variogram. For example, to interpolate at a point P based on the surrounding points P1, P2, and P3, the weights w1, w2, and w3 must be found. The weights are found through the solution of the simultaneous equations:
where S(dij) is the model variogram evaluated at a distance equal to the distance between points i and j. For example, S(d1p) is the model variogram evaluated at a distance equal to the separation of points P1 and P. Since it is necessary that the weights sum to unity, a fourth equation is added:
Since there are now four equations and three unknowns, a slack variable, l, is added to the equation set. The final set of equations is as follows:
The equations are then solved for the weights w1, w2, and w3. The f value of the interpolation point is then calculated as:
By using the variogram in this fashion to compute the weights, the expected estimation error is minimized in a least squares sense. For this reason, kriging is sometimes said to produce the best linear unbiased estimate. However, minimizing the expected error in a least squared sense is not always the most important criteria and in some cases, other interpolation schemes give more appropriate results (Philip & Watson, 1986).
An important feature of kriging is that the variogram can be used to calculate the expected error of estimation at each interpolation point since the estimation error is a function of the distance to surrounding scatter points. The estimation variance can be calculated as:
When interpolating to an object using the kriging method, an estimation variance dataset is always produced along with the interpolated dataset. As a result, a contour or isosurface plot of estimation variance can be generated on the target mesh or grid.
Simple Kriging
Simple kriging is similar to ordinary kriging except that the following equation is not added to the set of equations:
and the weights do not sum to unity. Simple kriging uses the average of the entire data set while ordinary kriging uses a local average (the average of the scatter points in the kriging subset for a particular interpolation point). As a result, simple kriging can be less accurate than ordinary kriging, but it generally produces a result that is "smoother" and more aesthetically pleasing.
Universal Kriging
One of the assumptions made in kriging is that the data being estimated are stationary. That is, when moving from one region to the next in the scatter point set, the average value of the scatter points is relatively constant. Whenever there is a significant spatial trend in the data values such as a sloping surface or a localized flat region, this assumption is violated. In such cases, the stationary condition can be temporarily imposed on the data by use of a drift term. The drift is a simple polynomial function that models the average value of the scatter points. The residual is the difference between the drift and the actual values of the scatter points. Since the residuals should be stationary, kriging is performed on the residuals and the interpolated residuals are added to the drift to compute the estimated values. Using a drift in this fashion is often called "universal kriging."
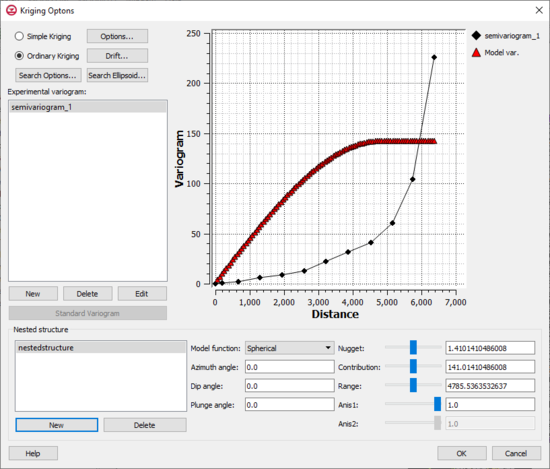
Kriging Options Dialog
The kriging options can be edited with the Kriging Options dialog. This dialog is reached through the Interpolate UGrid to Ugrid dialog. The options in the Kriging Options dialog are as follows:
- Simple Kriging – Use the simple Kriging method.
- Ordinary Kriging – Use the ordinary Kriging method.
- Options – Opens the Interpolate – Advanced dialog with options to truncate the data and set anistropy options.
- Drift – Brings up the Drift Coefficients dialog. When performing universal kriging a drift function should be defined. Each of the toggles in the dialog represents a single component of the polynomial equation defining the drift. Initially, all of the toggles off by default. Turning on coefficients enables universal kriging and defines the drift polynomial. For example, to use a planar drift function, only the linear terms should be used.
- Search Options – Brings up the Search Options dialog. The Minimum and Maximum values in the Number of points to use for kriging controls how many of the points found in the search radius are actually used in the kriging calculations. If fewer than the minimum value are found, a default value (-999) is assigned to the interpolation point. If greater than the maximum value is found, the closest points are used.
- The input data cutoff values are used to screen out data values outside the specified range. Points with values outside this range are ignored.
- If the Octant option is selected in the search type section, a maximum of N points in each of the eight octants (for 2D a quadrant is used) surrounding the interpolation point are used in the calculations. This method results in better performance with clustered data. If the Normal method is selected, the octant approach is not used.
- Search Ellipsoid – Brings up the Search Ellipsoid dialog. When a value is interpolated to an interpolation point, only a subset of the scatter points in the vicinity of the interpolation point are used in the calculations. The items in the Search Ellipsoid dialog control the shape of a "search space" surrounding the interpolation point. Only points in this search space are considered candidates for use in the kriging calculations.
- By default, the search space is a circle (sphere in 3D) centered at the point with a radius defined by the Maximum search radius item. For problems exhibiting anisotropy, the search space can be transformed to an ellipse (ellipsoid in 3D). The anis1 factor and the azimuth angle control the shape and orientation of the ellipse. The azimuth represents the rotation of the major principal axis clockwise from the +y axis. The anis1 factor represents the ratio of the search radius along the minor principal axis relative to the search radius (the maximum radius) in the major principal direction. In most cases, the anis1 factor and the azimuth angle should match the anis factor and azimuth angle defined in the Variogram Editor.
- Experimental variogram – For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
- New – Brings up the Experimental Variogram dialog where new variogram can be defined. For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
- Delete – Removes the selected variogram.
- Edit – Brings up the Experimental Variogram dialog where changes can be made to the existing variogram.
- Standard Variogram – Generates a variogram automatically based on the existing data.
- Nested Structure – A model variogram is constructed using a combination of one or more model functions.
- New – Creates a new nested structure in the list.
- Delete – Removes the seleced nested structure.
- Model function – Allows selecting on of four types of model functions: "Spherical", "Exponetial", "Gaussian", or "Power". For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
- Azimuth angle – For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
- Dip angle – For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
- Plunge angle – For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
- Nugget – Represents a minimum variance. For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
- Contribution – For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
- Range – For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
- Anis1 – For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
- Anis2 – For more information see the article Variogram Editor.
Related Topics
GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||