SMS:CMS-Flow Hard Bottom: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
CMS-Flow includes a Hard Bottom morphologic constraint that "provides the capability to simulate mixed bottom types within a single simulation," (ERDC/CHL TR-06-9 Two-Dimensional Depth-Averaged Circulation Model CMS-M2D: Version 3.0, Report 2, Sediment Transport and Morphology Change [ | __NOINDEX__ | ||
{{SMS Deprecated Feature}} | |||
CMS-Flow includes a Hard Bottom morphologic constraint that "provides the capability to simulate mixed bottom types within a single simulation," (ERDC/CHL TR-06-9 Two-Dimensional Depth-Averaged Circulation Model CMS-M2D: Version 3.0, Report 2, Sediment Transport and Morphology Change [https://erdc-library.erdc.dren.mil/jspui/bitstream/11681/7613/1/CHL-TR-06-9.pdf], p. 33). Hard bottom is a cell depth constraint applied to areas of the grid which represent exposed or covered non-erodible material such as bedrock. This specification limits the erosion of sediment to the hard bottom depth and therefore constrains water depth. During sediment transport calculations, exposed hard bottom cells may become covered through deposition. | |||
By default, CMS-Flow cells are fully-erodible cells with no specified hard bottom depth (inactive cells; denoted by the | By default, CMS-Flow cells are fully-erodible cells with no specified hard bottom depth (inactive cells; denoted by the | ||
| Line 8: | Line 10: | ||
Hard bottom should be specified only for computational (ocean) cells. | Hard bottom should be specified only for computational (ocean) cells. | ||
The hard bottom dataset can created, edited, viewed and verified using the following SMS interface features. | The hard bottom dataset can be created, edited, viewed and verified using the following SMS interface features. | ||
== Model Control == | == Model Control == | ||
| Line 53: | Line 55: | ||
[[Category:CMS-Flow|H]] | [[Category:CMS-Flow|H]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:CMS Dialogs|hard]] | ||
[[Category:Archived CMS-Flow|hard]] | |||
[[Category:External Links]] | [[Category:External Links]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:19, 27 April 2023
| This contains information about features no longer in use for the current release of SMS. The content may not apply to current versions. |
CMS-Flow includes a Hard Bottom morphologic constraint that "provides the capability to simulate mixed bottom types within a single simulation," (ERDC/CHL TR-06-9 Two-Dimensional Depth-Averaged Circulation Model CMS-M2D: Version 3.0, Report 2, Sediment Transport and Morphology Change [1], p. 33). Hard bottom is a cell depth constraint applied to areas of the grid which represent exposed or covered non-erodible material such as bedrock. This specification limits the erosion of sediment to the hard bottom depth and therefore constrains water depth. During sediment transport calculations, exposed hard bottom cells may become covered through deposition.
By default, CMS-Flow cells are fully-erodible cells with no specified hard bottom depth (inactive cells; denoted by the CMS-Flow null value of -999.0).
When specified, cell hard bottom depths will appear in the Project Explorer as a scalar dataset beneath the CMS-Flow grid. This dataset can not be deleted, though it can be edited like any other dataset. A CMS-Flow simulation must contain the hard bottom dataset (even if it is not specified) so SMS will create a defaulted (inactive cells) dataset if it does not already exist when saving the simulation.
Hard bottom should be specified only for computational (ocean) cells.
The hard bottom dataset can be created, edited, viewed and verified using the following SMS interface features.
Model Control
Within the CMS-Flow Model Control window, the hard bottom dataset can be created from the Sediment tab. If the dataset does not exist, it can be created using the Create Dataset button. If a dataset exists (created using the Data Calculator) which represents the intended hard bottom specifications, the Select Dataset... button can be used to select such dataset and copy the values to the hard bottom dataset.
Hard Bottom Specification
Although the hard bottom dataset can be edited (when its the active dataset) by selecting a cell (or group of cells) and changing the scalar (S) value in the Edit Window, an user-friendly window exists which provides specification options. With the Select Grid Cell tool active, make a selection, right-click to bring up the tool menu and choose the Specify Hard Bottom... option.
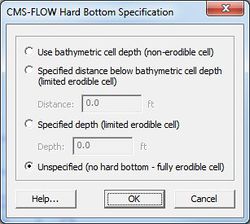
This will open the CMS-Flow Hard Bottom Specification window.
The following options are provided in the Hard Bottom Specification window:
- Use bathymetric cell depth – Sets the cell hard bottom depth to be the cell geometry value thereby creating an exposed non-erodible condition. If multiple cells were selected, then each cell will use its respective bathymetric depth.
- Specified distance below bathymetric cell depth – Sets the cell hard bottom depth to be the cell geometry value plus the specified distance thereby creating a sediment-covered non-erodible condition. The distance is limited to positive values to ensure the hard bottom depth is greater than the geometry value. The cell can provide sediment for transportation, however, the amount of erosion is limited. If multiple cells were selected, then each cell will use its respective bathymetric depth.
- Specified depth – Sets the cell hard bottom depth to the specified depth thereby creating a sediment-covered non-erodible condition similar to specified distance. The depth is limited to greater than the geometry value. If multiple cells were selected, then the depth is limited to greater than the largest geometry value and all cells will have the same value.
- Unspecified – Resets to an inactive hard bottom condition. The cell hard bottom depth is set to the CMS-Flow null value. If multiple cells were selected, then all cells will be reset.
If no cells are selected when opening the Hard Bottom Specification window, then all computational (ocean) cells will be used. If a selection of only non-computational cells, then specification cannot occur. If a selection contains computational and non-computational cells, then the specification will only apply to the computational cells.
If multiple computational cells with differing specifications are selected, the window will not display a selected specification type and the OK button will be disabled. This is to protect the previous specifications from being overwritten by mistake. The OK button will be enabled when an option is selected. The minimum hard bottom depth of the multiple computational cells selected will be displayed in the Depth edit field and the minimum hard bottom depth minus the maximum geometry depth of the multiple computational cells selected will be displayed in the Distance edit field.
Display Options
The hard bottom dataset (when its the active dataset) will only display the cells with hard bottom specified if the Ocean cell display option is turned on. Inactive hard bottom cells are not displayed.
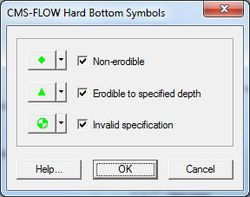
CMS-Flow includes hard bottom symbols to differentiate specifications. On the Cartesian Grid page of the Display Options window (when CMS-Flow is the active model), the Hard bottom symbols check box controls the display of symbols that will appear in hard bottom cells (even if the hard bottom dataset is not active). If this is turned on, then the user must be aware of the individual symbol settings accessed by clicking on the Options... button. The Options... button displays the CMS-Flow Hard Bottom Symbols window.
Hard bottom symbols can be selected for three hard bottom specification types:
- Non-erodible – Displayed in exposed hard bottom cells (cell hard bottom depth is equal to cell bathymetric depth).
- Erodible to specified depth – Displayed in sediment-covered hard bottom cells (cell hard bottom depth is greater than cell bathymetric depth).
- Invalid specification – Displayed in hard bottom cells where the hard bottom depth is less than cell bathymetric depth (the geometry is below the erosion limit).
If the Hard bottom symbols check box is turned off, no symbols will be displayed and the individual settings cannot be accessed, however, the individual settings will not be changed.
Model Check
The CMS-Flow Model Checker, accessed from the CMS-Flow | Model Check... menu item, includes a check to ensure that no invalid hard bottom specifications exist in the grid. An invalid specification may be created, for example, by setting an infeasible hard bottom scalar value in the Edit Window or adjusted the grid's geometry without updating the hard bottom. It is suggested that the model checker be used prior to running CMS-Flow.
Related Topics
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||