SMS:SRH-2D Boundary Conditions: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
*"Exit-EX" – A supercritical exit boundary condition. | *"Exit-EX" – A supercritical exit boundary condition. | ||
*"Symmetry" – Defined as a boundary where all dependent variables are extrapolated assuming the gradient of the variable in a direction normal to the boundary is zero except the velocity component normal to the boundary. | *"Symmetry" – Defined as a boundary where all dependent variables are extrapolated assuming the gradient of the variable in a direction normal to the boundary is zero except the velocity component normal to the boundary. | ||
*"Monitor-Line" – Not a real boundary at all; it is an internal polyline which may be used to monitor the total flow discharge through it. | *"Monitor-Line" – Not a real boundary at all; it is an internal polyline which may be used to monitor the total flow discharge through it. Monitor lines are applied the model to determine the flow and sediment flux across the lines at specified locations in the model. SRH-2D creates a *_LN#.DAT file (where * indicates the run name and # is the monitor line number) for each monitor line that details the bed and water-surface elevations, the flow, and the sediment flux across the lines. The monitor lines can be used to determine when the model reaches steady state conditions. For example, by comparing the predicted water-surface elevations over time and at various locations along the reach, the user can determine when the water-surface elevation reaches a steady state condition. | ||
===Structure Boundary Conditions=== | ===Structure Boundary Conditions=== | ||
Revision as of 22:03, 12 December 2016
SRH-2D supports a variety of boundary conditions for hydraulic computation. The boundary conditions for the model are specified through the SRH-2D Boundary Conditions coverage by selecting an arc or by selecting a nodestring in the mesh. Once the arc or nodestring has been selected, double-clicking, or right-clicking and using the Assign Linear BC... command, will bring up a dialog where the boundaries can be assigned.
All currently supported boundary types are exterior boundaries with the exception of a monitor line. Other boundary types include the following: Inlet-Q, Inlet-SC, Exit-EX, Exit-H, Exit-Q, Wall, and Symmetry.
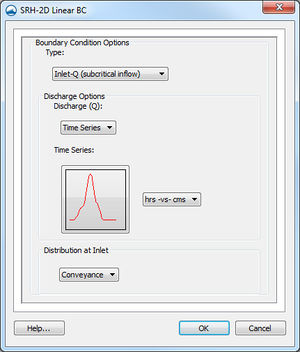
SRH-2D Linear BC Dialog
The SRH-2D Linear BC dialog contains multiple boundary condition types. Selecting a type for an arc will determine what boundary conditions can be assigned to the arc.
Inflow and Outflow Boundary Conditions Options
SMS provides options for the following boundary conditions:
Inlet-Q
A subcritical inlet boundary that may be given as a constant discharge or as a variable discharge hydrograph. The velocity distribution type may be selected from the boundary condition menu.
- Discharge (Q) – Specify as either a "Constant" or a "Time Series".
- "Constant" – Use for a steady state simulation.
- Constant Q – Enter a real positive value along with the units as either "cfs" or "cms".
- "Time Series" – Use for unsteady flow.
- Time Series Files – Clicking the button will bring up the XY Series Editor. Units must be specified as either "cfs" or "cms".
- Distribution at Inlet – The lateral distribution of the velocity. Options include:
- "Conveyance" – Calculates the conveyance parameter first then the velocity. The flow direction is assumed to be normal.
- "Profile" – Uses a depth average velocity profile.
- "Q" – A constant unit discharge, q=vh, is assumed with flow direction normal to the inlet boundary.
- "Velocity" – A constant velocity magnitude is imposed at the inlet with flow direction normal to the inlet boundary.
Inlet-SC
A supercritical inlet boundary that may be given as a constant discharge or as a variable discharge hydrograph. Inlet-SC also requires information about depth. Within the boundary condition menu, the velocity distribution type may be specified.
- Supercritical Inflow Options – Specify the discharge type and water surface elevation units.
- Discharge (Q) – Set as one of the following:
- "Constant" – Use for a steady state simulation.
- "Time Series" – Use for unsteady flow.
- Units – Can be set as "U.S. Customary" or "Metric".
- Supercritical Constant Inflow Options – Enter values for a steady state simulation.
- Discharge (Q) – Enter a real positive value for the flow.
- Water Elevation (WSE) – Enter a real positive value for the water surface elevation.
- Supercritical Varied Inflow Options – Use for unsteady flow.
- Time Series Discharge File – Clicking the button will bring up the XY Series Editor for entering the varied discharge values.
- Water Elevation (WSE) – Can be entered as either a "Time Series" or a "Rating Curve"
- Time Series vs. WSE File – Clicking the button will bring up the XY Series Editor for entering the time versus elevation values.
- Q vs. WSE Files – Clicking the button will bring up the XY Series Editor for entering the flow versus elevation rating curve values.
- Distribution at Inlet – The lateral distribution of the velocity. Options include:
- "Conveyance" – Calculates the conveyance parameter first then the velocity. The flow direction is assumed to be normal.
- "Profile" – Uses a depth average velocity profile.
- "Q" – A constant unit discharge, q=vh, is assumed with flow direction normal to the inlet boundary.
- "Velocity" – A constant velocity magnitude is imposed at the inlet with flow direction normal to the inlet boundary.
Exit-H
A stage type exit boundary where water surface elevation may be given as a constant number or as a stage-discharge or rating curve.
- Water Elevation(WSE) – Set as either a constant, a time series, or a rating curve.
- "Constant" – Use for a steady state simulation.
- Constant WSE – Enter a positive value for the water surface elevation.
- Populate – Launches the Populate dialog to automatically generate an estimated constant.
- "Time Series" – Use for unsteady flow.
- Time Series vs. WSE file – Clicking the button will bring up the XY Series Editor for entering the time versus elevation values.
- "Rating Curve" – Use for unsteady flow.
- Q vs. WSE file – Clicking the button will bring up the XY Series Editor for entering the discharge versus elevation rating curve values. The Populate dialog can be accessed from the XY Series Editor to automatically generate an estimated rating curve.
Exit-Q
An exit boundary with a discharge given as a constant number or as a hydrograph.
- Discharge (Q) – Specify as either a "Constant" or a "Time Series".
- "Constant" – Use for a steady state simulation.
- Constant Q – Enter a real positive value along with the units as either "cfs" or "cms".
- "Time Series" – Use for unsteady flow.
- Time Series Files – Clicking the button will bring up the XY Series Editor. Units must be specified as either "hrs-vs-cfs" or "hrs-vs-cms".
Wall
Solid wall boundaries may represent banks and islands. No-slip condition is assumed at solid walls for the dynamic wave solver.
- Add Extra Roughness at Wall Boundary – Can be turn "On" or "Off".
- Roughness Height in mm – Only available with the "On" option.
Boundary Conditions Without Additional Options
The following boundary conditions do not have additional options.
- "Exit-EX" – A supercritical exit boundary condition.
- "Symmetry" – Defined as a boundary where all dependent variables are extrapolated assuming the gradient of the variable in a direction normal to the boundary is zero except the velocity component normal to the boundary.
- "Monitor-Line" – Not a real boundary at all; it is an internal polyline which may be used to monitor the total flow discharge through it. Monitor lines are applied the model to determine the flow and sediment flux across the lines at specified locations in the model. SRH-2D creates a *_LN#.DAT file (where * indicates the run name and # is the monitor line number) for each monitor line that details the bed and water-surface elevations, the flow, and the sediment flux across the lines. The monitor lines can be used to determine when the model reaches steady state conditions. For example, by comparing the predicted water-surface elevations over time and at various locations along the reach, the user can determine when the water-surface elevation reaches a steady state condition.
Structure Boundary Conditions
In general, two arcs must be selected before assigning arcs a structure boundary condition.
- Weir – See the SRH-2D Structures article for more information.
- Culvert – See the SRH-2D Structures article for more information.
- Pressure zone – See the SRH-2D Structures article for more information.
- Gate – See the SRH-2D Structures article for more information.
Related Topics
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||