GMS:Horizons Applications: Difference between revisions
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
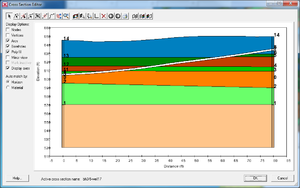
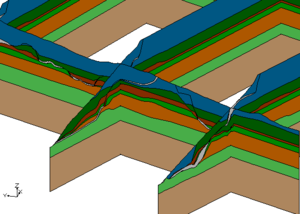
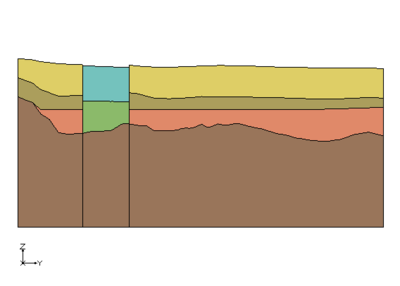
In this application the user wanted to create a set of solids where there would be distinct materials below a river bed compared to the other materials in the study area. The following cross section shows what the user wanted to create. | In this application the user wanted to create a set of solids where there would be distinct materials below a river bed compared to the other materials in the study area. The following cross section shows what the user wanted to create. | ||
[[Image:Xsect_hor_application.png|400px|border]] | {{hide in print|[[Image:Xsect_hor_application.png|400px|border]]}} | ||
{{only in print|[[Image:Xsect_hor_application.png|250px|border]]}} | |||
=== Primary TINs === | === Primary TINs === | ||
Revision as of 17:49, 23 June 2011
The horizons method has been applied at a variety of sites to construct solid models of the subsurface. This page highlights example applications of the Horizons Method.
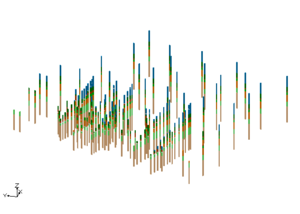
Modeling a Slope Failure
In this example a combination of boreholes, user defined cross sections, and TINs were used to create solids at a site with a slope failure.
Vertical Boundary Between Solids
In this application the user wanted to create a set of solids where there would be distinct materials below a river bed compared to the other materials in the study area. The following cross section shows what the user wanted to create.
Primary TINs
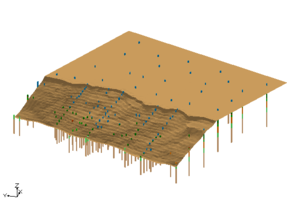
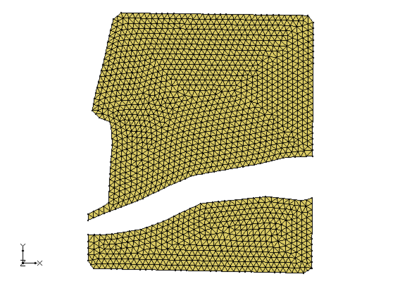
To create solids that would match this cross section, the user created 2 different primary tins and executed the Horizons->Solids command for each primary TIN. The first TIN covered the area of the river and the second TIN covered the remainder of the study area as show in the images below.

|
|
Solids
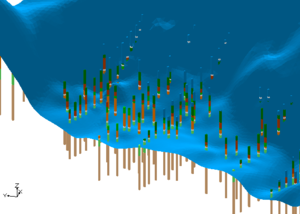
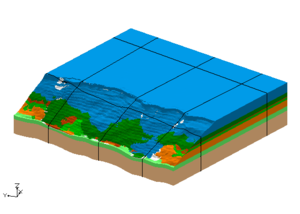
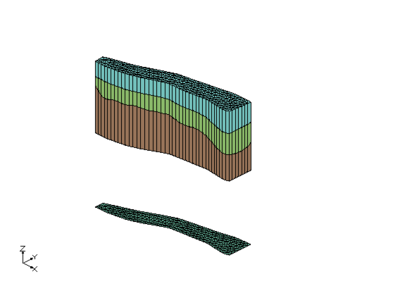
The user had TINs that defined the top elevations of the horizon surfaces. There were 3 TINs used in the area around the river and there were 4 TINs used the remainder of the study area. Solids were created for the river area using the first TIN as the primary TIN. Solids were also created in remainder of the study area by using the second TIN as the primary TIN. Notice the the bottom most material matches in both sets of solids. This is because the same TIN with that horizon was used when creating both sets of solids.
|
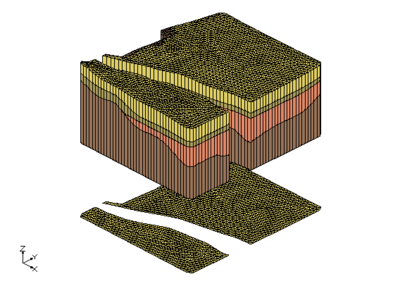
|
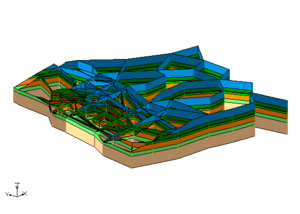
Cross Sections from Solids
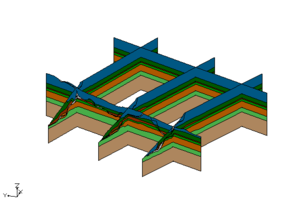
These images show the solids together and cross section cut through the solids. Again notice how the bottom most material matches across both sets of solids.
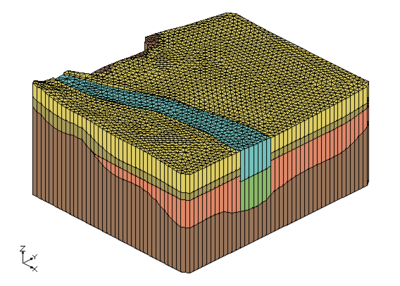
|
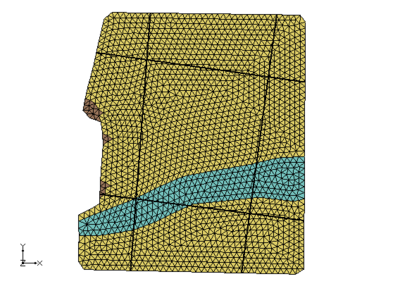
|
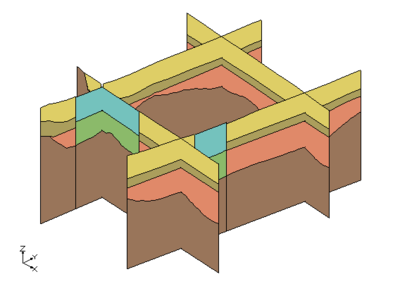
|
GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||