GMS:HydroGeoSphere Polygon Properties: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOC bottom}} | {{TOC bottom}} | ||
{{HGS Links}} | {{HGS Links}} | ||
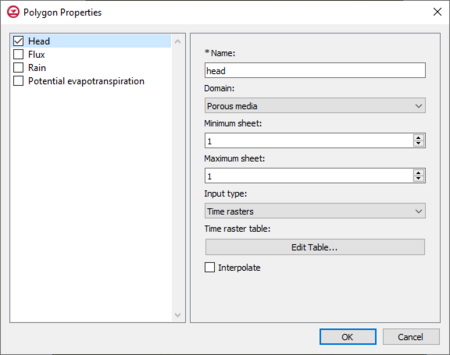
The ''Polygon Properties'' dialog is where | The ''Polygon Properties'' dialog in the HydroGeoSphere model is where a polygon or polygons can be assigned a boundary condition. There are four options for the polygon properties, which are listed on the left side of the dialog: head, flux, rain, and potential evapotranspiration. The input parameters are shown on the right when one of the four boundary conditions is selected. Only one type of boundary condition can be assigned to a feature object on a boundary conditions coverage. | ||
==Head or Flux | [[File:HGS polygon prop.png|thumb|450px|''Polygon Properties'' dialog for the boundary conditions coverage]] | ||
==Head or Flux== | |||
Head and flux are two separate available arc property types on a boundary conditions coverage, but the input options available are the same. Head is a general specified head boundary condition, and flux is a general specified flux boundary condition. The input options for head and flux are listed below. | Head and flux are two separate available arc property types on a boundary conditions coverage, but the input options available are the same. Head is a general specified head boundary condition, and flux is a general specified flux boundary condition. The input options for head and flux are listed below. | ||
* ''Name'' – | * ''Name'' – The name of the boundary condition. Names should be unique and contain no white space. | ||
* ''Domain'' – The domain in which the boundary | * '''Domain''' – The domain in which the boundary conditions are applied. | ||
** | ** ''Porous media'' | ||
*** ''Minimum sheet'' – | *** ''Minimum sheet'' – The minimum node sheet; boundary conditions are applied between the minimum and maximum node sheets. | ||
*** ''Maximum sheet'' – | *** ''Maximum sheet'' – The maximum node sheet; boundary conditions are applied between the minimum and maximum node sheets. | ||
*** ''Input type'' – How the boundary condition data is specified. | *** ''Input type'' – How the boundary condition data is specified. | ||
**** ''Constant'' – Constant value of the boundary condition. | |||
**** ''Time series'' – Time-varying values of the boundary condition. A table is generated using the ''XY Series Editor'' dialog that is opened by clicking the '''Edit XY Series''' button by either manually entering the data, or importing the data. | |||
***** ''Interpolate'' | |||
**** | **** ''Time rasters'' – The '''Edit Table...''' button opens the ''Time raster table'' dialog where the data is entered by selecting a raster from outside GMS. | ||
***** ''Interpolate'' – Causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function. | ***** ''Interpolate'' – Causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function. | ||
** ''Surface flow'' | |||
*** ''Input type'' – How the boundary condition data is specified. | *** ''Input type'' – How the boundary condition data is specified. | ||
**** ''Constant'' – Constant value of the boundary condition. | |||
**** ''Time series'' – Time-varying values of the boundary condition. A table is generated using the ''XY Series Editor'' dialog that is opened by clicking the '''Edit XY Series''' button by either manually entering the data, or importing the data. | |||
***** ''Interpolate'' – Causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function. | |||
**** ''Time rasters'' – The '''Edit Table...''' opens the ''Time raster table'' dialog where the data is entered by selecting a raster from outside GMS. | |||
***** '' | |||
***** ''Interpolate'' – Causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function. | ***** ''Interpolate'' – Causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function. | ||
== | ==Rain or Potential Evapotranspiration== | ||
Rain is a general specified flux boundary condition that converts fluxes to nodal volumetric fluxes. Potential evapotranspiration is a specified flux which is used in conjunction with evapotranspiration properties and is applied as a second-type boundary condition. Rain and potential evapotranspiration are two different polygon boundary condition options, but they contain the same input parameter options, which are listed below. | |||
* ''Name'' – | * ''Name'' – The name of the boundary condition. Names should be unique and contain no white space. | ||
* ''Input type'' – How the boundary condition data is specified. | * '''Input type''' – How the boundary condition data is specified. | ||
** ''Constant'' – Constant value of the boundary condition. | |||
** ''Time series'' – Time-varying values of the boundary condition. A table is generated using the ''XY Series Editor'' dialog that is opened by clicking the '''Edit XY Series''' button by either manually entering the data, or importing the data. | |||
*** ''Interpolate'' – Causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function. | |||
** ''Time raster table'' – The '''Edit Table...''' opens the ''Time raster table'' dialog where the data is entered by selecting a raster from outside GMS. | |||
*** '' | |||
*** ''Interpolate'' – Causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function. | *** ''Interpolate'' – Causes time-varying values to be interpolated, resulting in a smoother application of the time-varying function. | ||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
Revision as of 15:26, 2 May 2024