SMS:AdH Materials
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
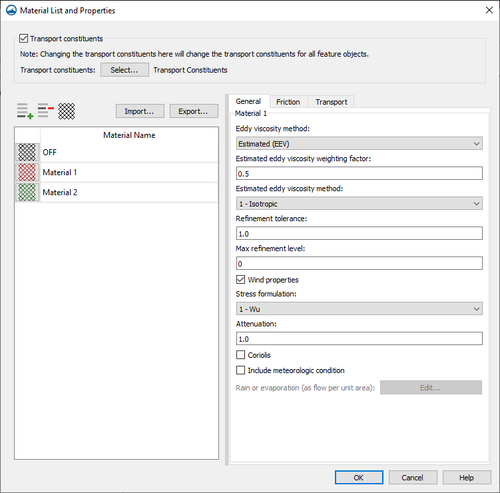
Material properties are set for AdH on an AdH materials coverage. In the Project Explorer, define the material attributes by right-clicking the materials coverage and selecting Material List and Properties to open the Material List and Properties dialog. The Material List and Properties dialog contains the following options:
- Transport constituents – Turning on this option will allow assigning transport constituents.
- Transport constituents – Clicking the Select button will open the Select Transport Constituent dialog where a transport component can be selected.
- Add Rows
 – Adds a material item to the list below this.
– Adds a material item to the list below this. - Delete Rows
 – Removes a selected material.
– Removes a selected material. - Change all material textures
 – Brings up the Texture Attributes dialog where the texture for all materials can be changed.
– Brings up the Texture Attributes dialog where the texture for all materials can be changed. - Import – Brings up an Open dialog where an AdH material file (*.adh_mat) can be imported into the dialog.
- Export – Brings up a Save dialog where an AdH materila file (*adh_mat) can be exported.
- Material list – The Materials list contains two columns (Color and Name) for the defined materials. The default "OFF" material cannot be edited (except the display pattern) and will always be at the top of the spreadsheet regardless of sorting. Each material is accompanied by a Color button in the Color column. To select a color and pattern, click on the button to open the Texture Attributes window. On the right side of the dialog, the numeric properties of the material are displayed and can be edited.
General
The General tab of the AdH Material List and Properties dialog contains the following options:
- Eddy viscosity method – Defines the eddy viscosity for the simulation using one of two methods. Both methods cannot be used for
one material, but both can be used in a single model.
- "Estimated (EEV)" – Defines eddy viscosity utilizing an equation to estimate the value.
- Estimated eddy viscosity weighing factor – Enter a value for the weighting factor.
- Estimated eddy viscosity method – Select one of the following methods:
- "1 – Isotropic"
- "2 – Anisotropic"
- "3 – Smagorinsky"
- "4 – Stansby"
- "Constant (EVS)" – Defines eddy viscosity through a user specified constant value.
- Vxx eddy viscosity
- Vxy eddy viscosity
- Vyy eddy viscosity
- "Estimated (EEV)" – Defines eddy viscosity utilizing an equation to estimate the value.
- Refinement tolerance – Enter a value to refine and relax the resolution of the model mesh during the simulation run.
- Max refinement level – Enter a value for the maximum level of mesh refinement.
- Wind properties – Check on to include wind stress calculations.
- Stress formulation – Select the method that will be used for wind stress.
- "0 – no transform"
- "1 – Wu"
- "2 – Teeter"
- Attenuation – Enter a scale factor to increase or decrease the wind shear stress magnitude.
- Stress formulation – Select the method that will be used for wind stress.
- Coriolis – Turn on to include the Coriolis force due to the earth’s rotation.
- Coriolis latitude – Enter a value for the latitude in decimal degrees.
- Include meteorologic condition – Turn on to include rain or evaporation for the material.
- Rain or evaporation – Click the Edit button to open an XY Series Editor dialog where rainfall or evaporation data can be entered.
Friction
- Friction
- "Off" – No friction will be applied to the model.
- "Manning's n (MNG)" – Friction will be applied using Manning's n.
- Manning's n – Specify the value of Manning's n.
- "Manning's Equation (MNC)" – Friction will be applied using the classic formulation Manning's n.
- Manning's n – Specify the value of Manning's n.
- "Equivalent roughness height (ERH)" – Friction will be applied using equivalent sand roughness height.
- Roughness height – Enter a value for the equivalent sand roughness height.
- "Submerged aquatic vegetation (SAV)" – Compute the drag coefficient associated with the bottom shear stress resulting from a steady current field over a bed consisting of submerged aquatic vegetation.
- Roughness height of canopy – Enter a value for the roughness height of the SAV canopy.
- Undeflected stem height – Enter a value for the undeflected stem height of the SAV.
- "Un-submerged rigid vegetation (URV)" – Compute a shear stress coefficient for use in computing the bottom shear stress resulting from a steady current through rigid, unsubmerged vegetation.
- Bed roughness height – Enter a value for the bed roughness height.
- Average stem diameter – Enter a value for the average stem diameter.
- Average stem density – Enter a value for the average stem density.
- "Equivalent drag obstructions (EDO)" – Computes a shear stress coefficient for use in computing the shear stress resulting from a steady current through or over an evenly distributed field of flow obstructions.
- Bed roughness height – Enter a value for the bed roughness height.
- Obstruction diameter – Enter a value for the average obstruction diameter.
- Obstruction height – Enter a value for the average obstruction height.
- "Ice friction (ICE, IRH, BRH)" – Applies as a pressure field on the water surface to account for the effects that stationary ice on the water surface has on the flow below.
- Ice thickness
- Ice density – Enter a value for the density of ice.
- Ice movement
- Ice roughness height – Enter a value for the equivalent ice roughness height.
- Bed roughness height – Enter a value for the equivalent bed roughness height.
- "Dune friction (DUN)" – Enter a value for the bedform roughness calibration coefficient.
- Dune Factor –
- Dune SEDLIB Inclusion – Turn on to use the sediment model for bedload
- Dune D50 – Enter a value for the d50 of the bed material.
- Dune D90 – Enter a value for the d90 of the bed material.
- Include Seasonal Roughness Adjustment
- Roughness adjustment factor
Transport
The Transport tab allows adjusting the tolerance for transport constituents going through the material. The tab requires that a transport constituent component to be selected.
Related Topics
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||