GMS:FEMWATER Conceptual Model Approach: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{FEMWATER Links}} | {{FEMWATER Links}} | ||
The preferred method for setting up a FEMWATER simulation is to use the feature object tools in the [[GMS:Map Module|Map module]] to define a FEMWATER conceptual model of a site being studied. The conceptual model is a high-level description of the site including sources/sinks, the boundary of the domain to be modeled, rainfall and seepage zones, and material zones within each of the layers. The conceptual model is defined with [[GMS:Feature Objects|feature objects]], including points, arcs, and polygons, and is constructed independently of a numerical grid. Once the conceptual model is complete, a mesh is automatically constructed to fit the conceptual model, and the FEMWATER data are converted from the conceptual model to the nodes, elements, and element faces. The dialogs and interactive editing tools in the FEMWATER menu can then be used to edit or review the data if desired. | The preferred method for setting up a FEMWATER simulation is to use the feature object tools in the [[GMS:Map Module|Map module]] to define a FEMWATER conceptual model of a site being studied. The conceptual model is a high-level description of the site including sources/sinks, the boundary of the domain to be modeled, rainfall and seepage zones, and material zones within each of the layers. The conceptual model is defined with [[GMS:Feature Objects|feature objects]], including points, arcs, and polygons, and is constructed independently of a numerical grid. Once the conceptual model is complete, a mesh is automatically constructed to fit the conceptual model, and the FEMWATER data are converted from the conceptual model to the nodes, elements, and element faces. The dialogs and interactive editing tools in the ''FEMWATER'' menu can then be used to edit or review the data if desired. | ||
A FEMWATER model can be created in GMS using one of two methods: assigning and editing values directly to the nodes and elements of a mesh (the direct approach), or by constructing a grid-independent representation of the model using feature objects and allowing GMS to automatically assign the values to the nodes and elements (the conceptual model approach). Except for simple problems, the conceptual model approach is typically the most effective. | A FEMWATER model can be created in GMS using one of two methods: assigning and editing values directly to the nodes and elements of a mesh (the direct approach), or by constructing a grid-independent representation of the model using feature objects and allowing GMS to automatically assign the values to the nodes and elements (the conceptual model approach). Except for simple problems, the conceptual model approach is typically the most effective. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
===Two Step Process=== | ===Two Step Process=== | ||
A FEMWATER conceptual model is used to build a numerical model using a two step process. In the first step, a 3D mesh is created. This can be done by using the feature objects in conjunction [[#Building the 3D Mesh from the FEMWATER Conceptual Model|with a set of TINs to build a 3D Mesh]] or a solid can be converted to a layered 3D Mesh using the [[GMS:Solids to Layered Mesh|'''''Solids -> Layered Mesh''''']] command. In the second step, the boundary conditions and recharge values assigned to the feature objects are automatically assigned to the appropriate nodes and element faces of the 3D mesh using the Feature Objects | Map -> FEMWATER command. | A FEMWATER conceptual model is used to build a numerical model using a two step process. In the first step, a 3D mesh is created. This can be done by using the feature objects in conjunction [[#Building the 3D Mesh from the FEMWATER Conceptual Model|with a set of TINs to build a 3D Mesh]] or a solid can be converted to a layered 3D Mesh using the [[GMS:Solids to Layered Mesh|'''''Solids -> Layered Mesh''''']] command. In the second step, the boundary conditions and recharge values assigned to the feature objects are automatically assigned to the appropriate nodes and element faces of the 3D mesh using the '''''Feature Objects | Map -> FEMWATER''''' command. | ||
To create a FEMWATER conceptual model right click on the Map Data folder in the [[GMS:The GMS Screen|Project Explorer]] and select the '''''New Conceptual Model''''' command. In the Conceptual Model Properties dialog change the model type to FEMWATER in the pull-down list. In the dialog the simulation options of flow and transport can also be toggled on or off. Next create a [[GMS:Coverages|coverage]] by right clicking on the FEMWATER conceptual model in the data tree and selecting '''''New Coverage'''''. The coverage attributes can then be setup in the '''Coverage Setup''' dialog. | To create a FEMWATER conceptual model right click on the Map Data folder in the [[GMS:The GMS Screen|Project Explorer]] and select the '''''New Conceptual Model''''' command. In the Conceptual Model Properties dialog change the model type to FEMWATER in the pull-down list. In the dialog the simulation options of flow and transport can also be toggled on or off. Next create a [[GMS:Coverages|coverage]] by right clicking on the FEMWATER conceptual model in the data tree and selecting '''''New Coverage'''''. The coverage attributes can then be setup in the '''Coverage Setup''' dialog. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
=====Map -> 2D Mesh===== | =====Map -> 2D Mesh===== | ||
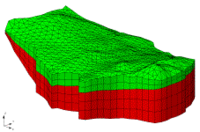
[[Image:meshgenc.gif|right|frame|Converting a FEMWATER Conceptual Model (a) Conceptual Model (b) 2D Mesh Created with Map -> 2D Mesh Command (c) 3D Mesh Created by Extruding 2D Mesh (d) 3D Mesh after Map -> FEMWATER Command.]] | [[Image:meshgenc.gif|right|frame|Converting a FEMWATER Conceptual Model (a) Conceptual Model (b) 2D Mesh Created with '''''Map -> 2D Mesh''''' Command (c) 3D Mesh Created by Extruding 2D Mesh (d) 3D Mesh after Map -> FEMWATER Command.]] | ||
The first step in building the 3D mesh is to select the Feature Objects | Map -> 2D Mesh command. This command creates a 2D mesh by automatically filling in the interior of the conceptual model with nodes and elements. The size and spacing of the elements is controlled by the spacing of the vertices on the arcs and by the refine point attribute assigned to any wells in the interior of the conceptual model. | The first step in building the 3D mesh is to select the '''''Feature Objects | Map -> 2D Mesh''''' command. This command creates a 2D mesh by automatically filling in the interior of the conceptual model with nodes and elements. The size and spacing of the elements is controlled by the spacing of the vertices on the arcs and by the refine point attribute assigned to any wells in the interior of the conceptual model. | ||
An example of the '''''Map -> 2D Mesh''''' command is shown in the following figure. A sample FEMWATER conceptual model is shown in part a. The 2D mesh resulting from execution of the '''''Map -> 2D Mesh''''' command is shown in part b. | An example of the '''''Map -> 2D Mesh''''' command is shown in the following figure. A sample FEMWATER conceptual model is shown in part a. The 2D mesh resulting from execution of the '''''Map -> 2D Mesh''''' command is shown in part b. | ||