|
|
| Line 8: |
Line 8: |
|
| |
|
| ==Interpolation== | | ==Interpolation== |
| A raster catalog can be interpolated to other GMS objects (TINs, meshes etc) by right-clicking on the raster catalog and selecting the desired interpolation command. Unlike interpolating from multiple selected rasters, when interpolating from a raster catalog, only one data set will be created. | | A raster catalog can be interpolated to other GMS objects (TINs, meshes etc) by right-clicking on the raster catalog and selecting the desired interpolation command. Unlike interpolating from multiple selected rasters, when interpolating from a raster catalog, only one dataset will be created. |
|
| |
|
| ==Horizons -> Solids== | | ==Horizons → Solids== |
| Raster catalogs are used to create solids using the Horizons -> Solids method. Each raster represents the top of a horizon. The figure below shows a sample raster catalog. | | Raster catalogs are used to create solids using the Horizons → Solids method. Each raster represents the top of a horizon. The figure below shows a sample raster catalog. |
|
| |
|
| [[Image:raster_catalog_table.png|Example raster catalog.]] | | [[Image:raster_catalog_table.png|Example raster catalog.]] |
A raster catalog is an attribute table that references rasters that are currently loaded into the GMS project. Raster catalogs are used for interpolation and to create solids from horizons.
Creation
To create a raster catalog simply select some rasters from the Project Explorer, right-click and select the New Raster Catalog command.
Interpolation
A raster catalog can be interpolated to other GMS objects (TINs, meshes etc) by right-clicking on the raster catalog and selecting the desired interpolation command. Unlike interpolating from multiple selected rasters, when interpolating from a raster catalog, only one dataset will be created.
Horizons → Solids
Raster catalogs are used to create solids using the Horizons → Solids method. Each raster represents the top of a horizon. The figure below shows a sample raster catalog.
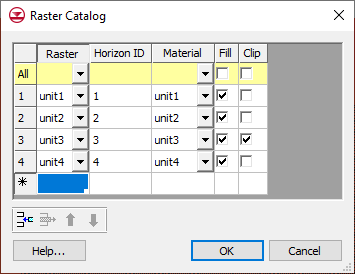
In the first column of the table the user selects the raster. Then the user can enter a Horizon ID and the associated material. There are two additional fields: Fill and Clip. If the Fill field is turned on then the raster will be used in the interpolation process for the associated horizon. If the Clip field is turned on then any horizon surface with a horizon id less than the associated horizon id will be clipped to this surface. The following images show examples of the effect of the Clip field.
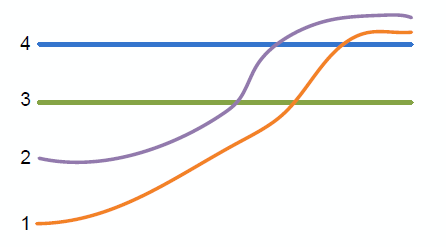
Raster surfaces.
The above figure shows a slice through raster surfaces that have been indexed with horizon ids. Below we see the resulting stratigraphy if the clip field is off (zero) for each raster.
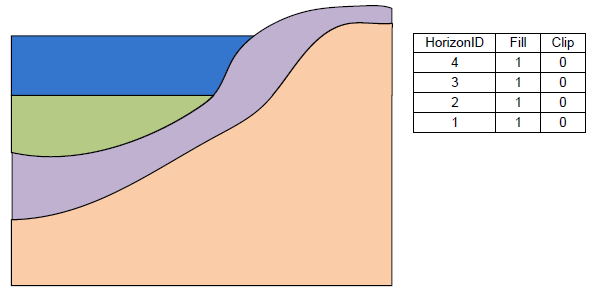
Stratigraphy with the Clip field turned off.
The next 2 examples show how the stratigraphy changes when the Clip field is turned on.
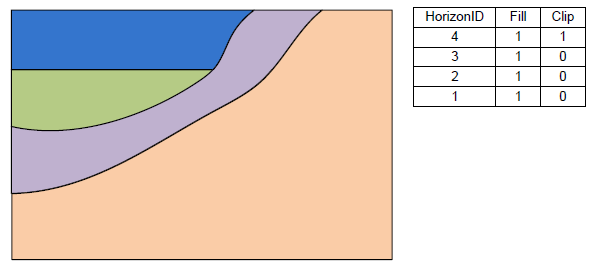
Stratigraphy with the Clip field on for horizon 4.
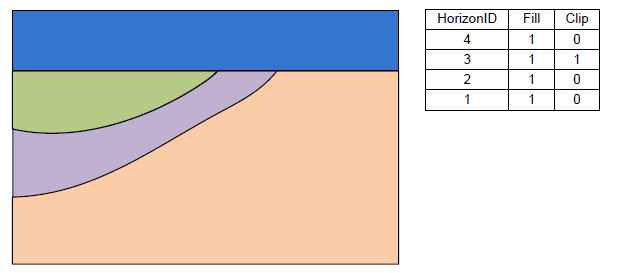
Stratigraphy with the Clip field on for horizon 3.
The final example shows a case where the Fill field is off and the Clip field is on.
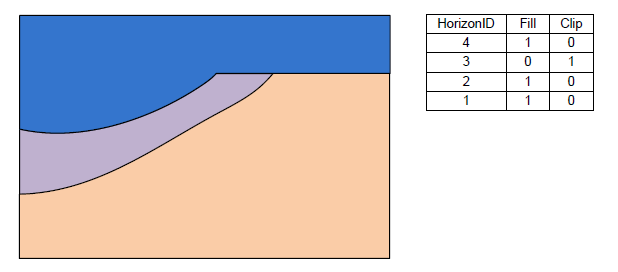
Stratigraphy with the Fill-off and Clip-on for horizon 3.