SMS:BOUSS-2D Graphical Interface: Difference between revisions
| (83 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] graphical interface includes tools to assit with creating, editing, and debugging a [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] model | The [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] graphical interface includes tools to assit with creating, editing, and debugging a [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] model. | ||
== BOUSS-2D Menu == | == BOUSS-2D Menu == | ||
The following menu commands are available in the [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] | [[File:BOUSS GenerateArcs.png|thumb|250 px|Example of the BOUSS-2D ''Generate Arcs'' dialog.]] | ||
The following menu commands are available in the [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] simulation [[File:BOUSS2D Simulation Icon.svg|16 px]] right-click menu: | |||
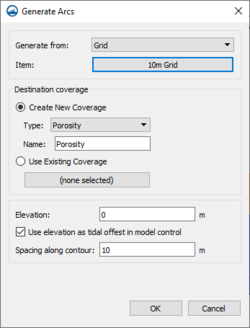
; '''Generating Arcs along land boundary''' : Opens a dialog that will create arcs in a damping or porosity coverage from an existing grid or scatterset. | |||
; '''Generating Arcs along open boundary''' : Opens a dialog that will create arcs in a damping or porosity coverage from an existing grid or scatterset. | |||
; [[SMS:BOUSS-2D Calculators|'''Calculators''']] : Brings up a pop up menu to access the''Wave Conditions Calculator'' (see appendix A) as well as the Run-up/Overtopping Estimator. | |||
; [[SMS:BOUSS-2D Probes|'''Probe Manager''']] : Brings up the ''Probe Manager'' to control time series output from the model. | |||
; '''Model Control…''' : | |||
Brings up a pop up menu to access the''Wave Conditions Calculator'' (see appendix A) as well as the Run-up/Overtopping Estimator. | |||
Brings up the ''Model Control'' dialog to specificy model parameters. | Brings up the ''Model Control'' dialog to specificy model parameters. | ||
; '''Model Check …''' : Launches the [[SMS:Model Check|Model Check]] to search for common problems. | |||
* '''Run BOUSS-2D''' | ; '''Export BOUSS-2D''' : When the BOUSS-2D files are exported a new directory under the project called “BOUSS-2D” is created. In this directory, the grids will be written to. Also a new directory under the “BOUSS-2D” will be created and it will be the name of the simulation. In this directory, the *.par file(link to Parameter file) can be found. | ||
; '''Run BOUSS-2D''' : Brings up a dialog that allows checking what executable of BOUSS-2D should be run and then runs the model with the currently loaded simulation. As the model runs, a dialog monitors progress of the model and gives the status messages. When the run is complete, the spatial solutions are read in for analysis and visualization. | |||
Brings up a dialog that allows | ; '''Save Project, Export, and Run BOUSS-2D''' : Performs the processes of saving the project, exporting BOUSS-2D files, and launching the BOUSS-2D model run. | ||
===Obsolete Commands=== | |||
The following commands are no long in use in current versions of SMS but may appear in older versions. | |||
; [[SMS:Spectral Energy|'''Spectral Energy''']] : Brings up the ''Spectral Energy'' dialog to define/view wave energy spectra. Generally, BOUSS-2D will generate wave conditions internally, but a spectrum may be input. This command also allows visualizing wave spectra that are generated inside of the model. | |||
; '''Assign BC''' : Used to assign damping, porosity, or wave maker conditions along a selected [[SMS:BOUSS-2D Graphical Interface#BC Cell Strings|cell string(s)]]. Using this command will open the ''BOUSS-2D Boundary Conditions'' dialog. | |||
; '''Assign Cell Attributes''' : Selected cells can be defined as land or water | |||
==Polygon Attributes== | |||
[[File:OceanPolygonAttributes.png|thumb|225 px|''Polygon Attributes'' dialog]] | |||
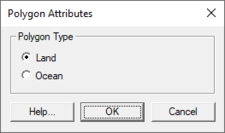
The ''Polygon Attributes'' dialog in BOUSS-2D is used to set the attributes for [[SMS:Feature Objects Types#Polygons|feature polygons]] before converting to a grid. It is reached by double-clicking on a polygon in an BOUSS-2D coverage. Attributes that can be specified for each polygon include: | |||
* Polygon Type | |||
** ''Land '' – Specifies the area as being land cells when the coverage is used to create a grid. | |||
** ''Ocean'' – Specifies the area as being ocean cells when the coverage is used to create a grid. | |||
==2D Grid Helps== | |||
[[File:BOUSS2D GridHelps.png|thumb|260 px|The ''BOUSS-2D Map → 2D Grid Helps'' dialog]] | |||
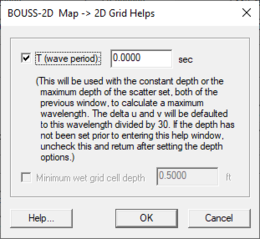
When creating a Cartesian grid from a BOUSS-2D map coverage, the ''Map → 2D Grid'' dialog contains and addition option: the '''Grid Helps''' button at the bottom of the dialog. Clicking the '''Grid Helps''' button will open the ''BOUSS-2D Map → 2D Grid Helps'' dialog. An appropriate cell size depends on the wavelength of the waves being modeled. Use the ''BOUSS-2D Map → 2D Grid Helps'' dialog to get help with determining a cell size. | |||
== Model Control == | == Model Control == | ||
The [[SMS:BOUSS-2D Model Control|BOUSS-2D Model Control | The [[SMS:BOUSS-2D Model Control|''BOUSS-2D Model Control'']] dialog is used to setup the options that apply to the simulation as a whole. These options include time controls, run types, output options, global parameters, print options and other global settings. | ||
==Wave Maker== | |||
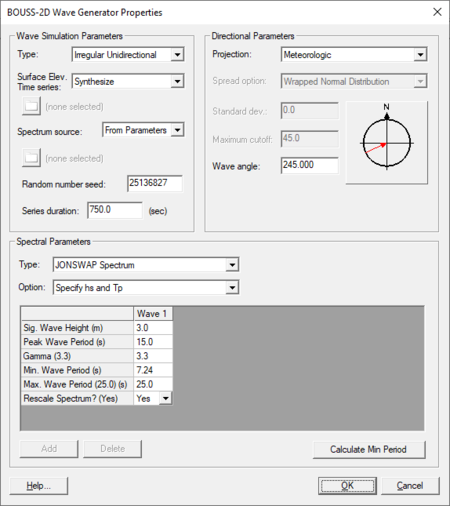
[[File:BOUSS WaveGeneratorProp.png|thumb|450 px|The ''BOUSS-2D Wave Generator Properties'' dialog.]] A wave maker is created be position a point in a wave maker coverage in the Map module. BOUSS-2D generates waves emanating from this point. Right-clicking on the point and selecting the '''Attributes''' will open the ''BOUSS-2D Wave Generator Properties'' dialog where the properties of the wave are defined. The dialog contains the following three sections: | |||
'''''Wave Simulation Parameters''''' | |||
* ''Type'' – Options include "Regular", "Irregular Unidirectional", and "Irregular Multidimensional". Selecting "Irregular Multidimensional" will activate the ''Spread option'', ''Standard dev.'', and ''Maximum cutoff'' fields under ''Directional Parameters''. | |||
* ''Surface Elev. Time Series'' – Can be "Synthesize" or "From File". | |||
* ''Spectrum source'' – Can be "From Parameters" or "From File". | |||
* ''Random number seed'' – | |||
* ''Series Duration'' – | |||
'''''Spectral Parameters''''' | |||
* ''Type'' – Available when the "Irregular Unidirectional" or "Irregular Multidimensional" type has been selected. Options include: | |||
** "TMA Spectrum (Shallow Water)" | |||
** "JONSWAP Spectrum" | |||
** "Bretschneider (ITTC) Spectrum" | |||
** "Pierson-Moskowitz Spectrum" | |||
** "Ochi-Hubble Double Peak Spectrum" | |||
* ''Option'' – Contains specific options for the "JONSWAP Spectrum" and "Pierson-Moskowitz Spectrum" types. | |||
** "Specify hs and Tp" | |||
** "Specify wind speed and fetch distance" | |||
** "Specify wind speed 19.5 m above sea level" | |||
** "Specify significant wave height" | |||
** "Specify spectral peak period" | |||
*Wave parameters – This spreadsheet allows setting parameters for each wave run. Available parameters depend on the selected type. These options can include: | |||
:{| | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* ''Wave Height'' | |||
* ''Wave Period'' | |||
* ''Number of Wave Cycles'' | |||
* ''Sig. Wave Height'' | |||
* ''Peak Wave Period'' | |||
| | |||
* ''hs. Low/High Freq.'' | |||
* ''Tp. Low/High Freq.'' | |||
* ''Gamma'' | |||
* ''Wind Speed @ 19.5 m'' | |||
* ''Spectral Peak Period'' | |||
| | |||
* ''Min. Wave Period'' | |||
* ''Max. Wave Period'' | |||
* ''Tidal Offset'' | |||
* ''Storm Duration'' | |||
* ''Rescale Spectrum'' | |||
|} | |||
* '''Add''' – Create an additional wave column in the spreadsheet. | |||
* '''Delete''' – Remove a selected wave column from the spreadsheet. | |||
* '''Calculate Min Period''' – Opens a data selection window where a dataset can be specified. | |||
'''''Directional Parameters''''' | |||
* ''Projection'' – Can be set to "Oceanographic", "Meteorologic", "Shore Normal", or "Cartesian". | |||
* ''Spread option'' – Options include "Wrapped Normal Distributions" and "Cosine Power Function". This field is only active when the wave simulation ''Type'' is set for "Irregular Multidirectional". | |||
* ''Standard dev.'' – Active when the wave simulation ''Type'' is set for "Irregular Multidirectional". | |||
* ''Maximum cutoff'' – Active when the wave simulation ''Type'' is set for "Irregular Multidirectional". | |||
* ''Wave angle'' – This is the angle the wave will move from the wave point. | |||
<!--This information is obsolete | |||
== Boundary Conditions == | == Boundary Conditions == | ||
[[Category:SMS Boundary Conditions| | [[Category:SMS Boundary Conditions|BOUSS-2D]] | ||
All numeric models require boundary condition data. In [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]], boundary conditions are defined on cell strings. The default boundary condition is a closed boundary (no flow). | All numeric models require boundary condition data. In [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]], boundary conditions are defined on cell strings. The default boundary condition is a closed boundary (no flow). | ||
:[[Image:SMS BOUSS 2D BC.jpg|thumb|none|left|325 px|''BOUSS-2D Boundary Conditions'' dialog]] | :[[Image:SMS BOUSS 2D BC.jpg|thumb|none|left|325 px|''BOUSS-2D Boundary Conditions'' dialog]] | ||
| Line 51: | Line 106: | ||
Cell strings can also be created manually to specify the location of structures, wave-makers, and areas where damping and/or porosity layers may be necessary. | Cell strings can also be created manually to specify the location of structures, wave-makers, and areas where damping and/or porosity layers may be necessary. | ||
Boundary conditions are specified along cell strings in the BOUSS-2D Boundary Conditions dialog, which is accessed by selecting one or more cell strings using the select cell string tool, and then selecting the Assign BC menu item from the BOUSS-2D menu. Normally, | Boundary conditions are specified along cell strings in the BOUSS-2D ''Boundary Conditions'' dialog, which is accessed by selecting one or more cell strings using the select cell string tool, and then selecting the '''Assign BC''' menu item from the ''BOUSS-2D'' menu. Normally, select a single cell string and assign a boundary condition. If a boundary condition has already exists for the selected cell string, the attributes are displayed. The different options for a cell string include: | ||
# ''Unassigned BC'' – When a cell string is created in BOUSS-2D its default boundary condition type is Unassigned. Unassigned cell strings do not influence the model. In fact, unassigned cell strings are not saved as part of the BOUSS-2D input files. | # ''Unassigned BC'' – When a cell string is created in BOUSS-2D its default boundary condition type is Unassigned. Unassigned cell strings do not influence the model. In fact, unassigned cell strings are not saved as part of the BOUSS-2D input files. | ||
# ''Damping BC'' – Waves propagating out of the computational domain are absorbed in damping regions (or damping layers) placed around the perimeter of the computational domain. Damping layers can also be used to model the partial reflection from harbor structures inside the computational area. | # ''Damping BC'' – Waves propagating out of the computational domain are absorbed in damping regions (or damping layers) placed around the perimeter of the computational domain. Damping layers can also be used to model the partial reflection from harbor structures inside the computational area. Enter a physical width into the ''Width'' edit field to specify the size of the damping layer. The damping region extends the width on either side of the cell string. The damping value is a non-dimensional damping coefficient that is allowed to vary from 0.0 to 1.0. No damping will occur when a value of 0.0 is used. Waves will be damped when a value of 1.0 is used along the side boundaries. A typical value for shoreline is 0.1. The default damping value is 1.0. SMS will assign the value specified at the cell string and ramp down to 0.0 at a distance of “width” from the cell string. | ||
# ''Porosity BC'' – Porosity boundary conditions are used to simulate partial wave reflection and transmission through surface-piercing porous structures such as breakwaters. Enter a physical width into the “Width” edit field to specify the size of the porous structure. Like with the damping regions, this width is extended on both sides of the cell string. The porosity value is a non-dimensional porosity coefficient that is allowed to vary from 0.0 to 1.0. A value of 0.0 corresponds to an impervious structure, while a value of near 1.0 would correspond to a highly porous structure. Typical porosity for stone type breakwaters is 0.4. The default porosity value is 1.0. | # ''Porosity BC'' – Porosity boundary conditions are used to simulate partial wave reflection and transmission through surface-piercing porous structures such as breakwaters. Enter a physical width into the “Width” edit field to specify the size of the porous structure. Like with the damping regions, this width is extended on both sides of the cell string. The porosity value is a non-dimensional porosity coefficient that is allowed to vary from 0.0 to 1.0. A value of 0.0 corresponds to an impervious structure, while a value of near 1.0 would correspond to a highly porous structure. Typical porosity for stone type breakwaters is 0.4. The default porosity value is 1.0. | ||
# ''Wave-maker BC'' – The wave-maker option is only available when a single cell string is selected and that cell string lies in a single column or row (straight line). Legal cell strings can be created using the ''SHIFT'' key when creating cell strings, using automatically created cell strings along a grid boundary, or by creating short cell strings. The extent and position of the wave maker can be modified using I,J indices in the dialog. BOUSS-2D generates waves emanating from this cell string. The properties of the waves are defined using the Wave Generator Properties dialog (described below) that is accessed through the Options button. The edit fields are used to position and size the wave maker in the computational domain. The first two values are the Start and End cells of the wave maker along the column or row that is specified by the third value, which is the Offset value. The Start and End values are limited to the number of cells in either the I- or J-direction, and the Offset value is limited to the number of rows or columns | # ''Wave-maker BC'' – [[File:BOUSS WaveGeneratorProp.jpg|thumb|450 px|The ''BOUSS-2D Wave Generator Properties'' dialog.]] The wave-maker option is only available when a single cell string is selected and that cell string lies in a single column or row (straight line). Legal cell strings can be created using the ''SHIFT'' key when creating cell strings, using automatically created cell strings along a grid boundary, or by creating short cell strings. The extent and position of the wave maker can be modified using I,J indices in the dialog. BOUSS-2D generates waves emanating from this cell string. The properties of the waves are defined using the ''Wave Generator Properties'' dialog (described below) that is accessed through the '''Options''' button. The edit fields are used to position and size the wave maker in the computational domain. The first two values are the Start and End cells of the wave maker along the column or row that is specified by the third value, which is the Offset value. The Start and End values are limited to the number of cells in either the I- or J-direction, and the Offset value is limited to the number of rows or columns. | ||
When the '''OK''' button is clicked, a check is done to see if the wave maker cell string is at a constant depth. If the depth varies by more than 20% and the wave maker is on the edge of the grid (not internal),SMS will ask whether to force constant depth along the wave maker cell string or not. If so, the grid is extended to allow the wave maker to be at the deepest elevation along the string, with a maximum slope of 1:10 from the existing grid to the new wave-maker position. A ''Wave Calculator'' is provided as part of BOUSS-2D interface in SMS (see Appendix B) to assist in the preparation of wave input parameters required by the model. Note that the ''BOUSS-2D'' | '''Assign BC''' menu item is disabled any time multiple wave makers are selected or if a wave maker and one or more other cell strings are selected. | |||
--> | |||
== Running the Model == | == Running the Model == | ||
The [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] files are written automatically with the SMS project file or can be saved separately using the ''File'' | '''Save BOUSS-2D''' or [[SMS:BOUSS-2D#Saving BOUSS-2D|''File'' | '''Save As''']] menu commands. See [[SMS:BOUSS-2D Files|BOUSS-2D Files]] for more information on the files used for the [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] run. | The [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] files are written automatically with the SMS project file or can be saved separately using the ''File'' | '''Save BOUSS-2D''' or [[SMS:BOUSS-2D#Saving BOUSS-2D|''File'' | '''Save As''']] menu commands. See [[SMS:BOUSS-2D Files|BOUSS-2D Files]] for more information on the files used for the [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] run. | ||
[[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] can be launched from SMS using the | [[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] can be launched from SMS using the '''Run BOUSS-2D''' right-click menu command. A check of some of the common problems called the ''Model Checker'' is done each time the model is launched, or by selecting the '''Model Check''' right-click menu command. | ||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
*[[SMS:BOUSS-2D|BOUSS-2D]] | |||
*[[SMS:Cartesian Grid Module#Creating 2D Grids|Create a 2D Cartesian grid]] | *[[SMS:Cartesian Grid Module#Creating 2D Grids|Create a 2D Cartesian grid]] | ||
| Line 117: | Line 130: | ||
[[Category:BOUSS-2D|G]] | [[Category:BOUSS-2D|G]] | ||
[[Category:SMS Menus|B]] | [[Category:SMS Menus|B]] | ||
[[Category:BOUSS-2D Dialogs|Graph]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:46, 19 July 2019
The BOUSS-2D graphical interface includes tools to assit with creating, editing, and debugging a BOUSS-2D model.
BOUSS-2D Menu
The following menu commands are available in the BOUSS-2D simulation ![]() right-click menu:
right-click menu:
- Generating Arcs along land boundary
- Opens a dialog that will create arcs in a damping or porosity coverage from an existing grid or scatterset.
- Generating Arcs along open boundary
- Opens a dialog that will create arcs in a damping or porosity coverage from an existing grid or scatterset.
- Calculators
- Brings up a pop up menu to access theWave Conditions Calculator (see appendix A) as well as the Run-up/Overtopping Estimator.
- Probe Manager
- Brings up the Probe Manager to control time series output from the model.
- Model Control…
Brings up the Model Control dialog to specificy model parameters.
- Model Check …
- Launches the Model Check to search for common problems.
- Export BOUSS-2D
- When the BOUSS-2D files are exported a new directory under the project called “BOUSS-2D” is created. In this directory, the grids will be written to. Also a new directory under the “BOUSS-2D” will be created and it will be the name of the simulation. In this directory, the *.par file(link to Parameter file) can be found.
- Run BOUSS-2D
- Brings up a dialog that allows checking what executable of BOUSS-2D should be run and then runs the model with the currently loaded simulation. As the model runs, a dialog monitors progress of the model and gives the status messages. When the run is complete, the spatial solutions are read in for analysis and visualization.
- Save Project, Export, and Run BOUSS-2D
- Performs the processes of saving the project, exporting BOUSS-2D files, and launching the BOUSS-2D model run.
Obsolete Commands
The following commands are no long in use in current versions of SMS but may appear in older versions.
- Spectral Energy
- Brings up the Spectral Energy dialog to define/view wave energy spectra. Generally, BOUSS-2D will generate wave conditions internally, but a spectrum may be input. This command also allows visualizing wave spectra that are generated inside of the model.
- Assign BC
- Used to assign damping, porosity, or wave maker conditions along a selected cell string(s). Using this command will open the BOUSS-2D Boundary Conditions dialog.
- Assign Cell Attributes
- Selected cells can be defined as land or water
Polygon Attributes
The Polygon Attributes dialog in BOUSS-2D is used to set the attributes for feature polygons before converting to a grid. It is reached by double-clicking on a polygon in an BOUSS-2D coverage. Attributes that can be specified for each polygon include:
- Polygon Type
- Land – Specifies the area as being land cells when the coverage is used to create a grid.
- Ocean – Specifies the area as being ocean cells when the coverage is used to create a grid.
2D Grid Helps
When creating a Cartesian grid from a BOUSS-2D map coverage, the Map → 2D Grid dialog contains and addition option: the Grid Helps button at the bottom of the dialog. Clicking the Grid Helps button will open the BOUSS-2D Map → 2D Grid Helps dialog. An appropriate cell size depends on the wavelength of the waves being modeled. Use the BOUSS-2D Map → 2D Grid Helps dialog to get help with determining a cell size.
Model Control
The BOUSS-2D Model Control dialog is used to setup the options that apply to the simulation as a whole. These options include time controls, run types, output options, global parameters, print options and other global settings.
Wave Maker
A wave maker is created be position a point in a wave maker coverage in the Map module. BOUSS-2D generates waves emanating from this point. Right-clicking on the point and selecting the Attributes will open the BOUSS-2D Wave Generator Properties dialog where the properties of the wave are defined. The dialog contains the following three sections:
Wave Simulation Parameters
- Type – Options include "Regular", "Irregular Unidirectional", and "Irregular Multidimensional". Selecting "Irregular Multidimensional" will activate the Spread option, Standard dev., and Maximum cutoff fields under Directional Parameters.
- Surface Elev. Time Series – Can be "Synthesize" or "From File".
- Spectrum source – Can be "From Parameters" or "From File".
- Random number seed –
- Series Duration –
Spectral Parameters
- Type – Available when the "Irregular Unidirectional" or "Irregular Multidimensional" type has been selected. Options include:
- "TMA Spectrum (Shallow Water)"
- "JONSWAP Spectrum"
- "Bretschneider (ITTC) Spectrum"
- "Pierson-Moskowitz Spectrum"
- "Ochi-Hubble Double Peak Spectrum"
- Option – Contains specific options for the "JONSWAP Spectrum" and "Pierson-Moskowitz Spectrum" types.
- "Specify hs and Tp"
- "Specify wind speed and fetch distance"
- "Specify wind speed 19.5 m above sea level"
- "Specify significant wave height"
- "Specify spectral peak period"
- Wave parameters – This spreadsheet allows setting parameters for each wave run. Available parameters depend on the selected type. These options can include:
- Wave Height
- Wave Period
- Number of Wave Cycles
- Sig. Wave Height
- Peak Wave Period
- hs. Low/High Freq.
- Tp. Low/High Freq.
- Gamma
- Wind Speed @ 19.5 m
- Spectral Peak Period
- Min. Wave Period
- Max. Wave Period
- Tidal Offset
- Storm Duration
- Rescale Spectrum
- Add – Create an additional wave column in the spreadsheet.
- Delete – Remove a selected wave column from the spreadsheet.
- Calculate Min Period – Opens a data selection window where a dataset can be specified.
Directional Parameters
- Projection – Can be set to "Oceanographic", "Meteorologic", "Shore Normal", or "Cartesian".
- Spread option – Options include "Wrapped Normal Distributions" and "Cosine Power Function". This field is only active when the wave simulation Type is set for "Irregular Multidirectional".
- Standard dev. – Active when the wave simulation Type is set for "Irregular Multidirectional".
- Maximum cutoff – Active when the wave simulation Type is set for "Irregular Multidirectional".
- Wave angle – This is the angle the wave will move from the wave point.
Running the Model
The BOUSS-2D files are written automatically with the SMS project file or can be saved separately using the File | Save BOUSS-2D or File | Save As menu commands. See BOUSS-2D Files for more information on the files used for the BOUSS-2D run.
BOUSS-2D can be launched from SMS using the Run BOUSS-2D right-click menu command. A check of some of the common problems called the Model Checker is done each time the model is launched, or by selecting the Model Check right-click menu command.
Related Topics
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||