SMS:FESWMS Spindown: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
This replaces the need to perform incremental loading by hand in [[SMS:FESWMS|FESWMS]]. | This replaces the need to perform incremental loading by hand in [[SMS:FESWMS|FESWMS]]. | ||
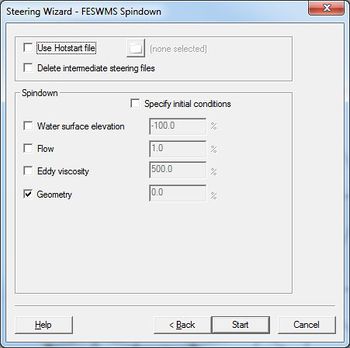
==FESWMS Spindown Dialog== | |||
[[File:FESWMS Spin-down.png|thumb|none|475 px|The ''FESWMS Spindown'' dialog]] | [[File:FESWMS Spin-down.png|thumb|none|475 px|The ''FESWMS Spindown'' dialog]] | ||
Revision as of 18:51, 28 June 2016
For cold start simulations, the initial velocities are zero and the water surface elevation is constant. This is often referred to as the "bathtub condition." Often FESWMS will not directly converge using these initial conditions.
Incremental Loading Strategy
The flow equations are nonlinear and thus require an iterative solution, starting from some initial guessed value. Convergence of the iterative solution is not guaranteed. Since the desired boundary conditions may be vastly different from a cold start condition, it may be impossible to get convergence starting from this bathtub type condition. However, a solution can be obtained using a series of “Runs” that generate solutions progressively closer to the desired answer. Intermediate boundary conditions that are closer to the final desired boundary conditions are specified to generate a set of flow conditions. These conditions do not represent the final desired flow conditions, but are closer to the final desired flow conditions than the original cold start, and can be used as initial conditions for a subsequent run. Starting the model from a previous solution is called “Hot Starting”. In the incremental loading strategy, “loads” consisting of applied flow rates and water surface elevations along the boundary increment from a cold start condition to the final condition. By choosing a suitably small increment in the boundary conditions, convergence can be attained.
FESWMS Spindown refers to the process of using the Steering Module to automate the process of incremental loading. The Steering Module can vary the following:
- Boundary Conditions
- Water surface elevation
- Flow rate
- Model Parameters
- Eddy viscosity
- Finite Element Network
- Geometry (nodal elevations)
This replaces the need to perform incremental loading by hand in FESWMS.
FESWMS Spindown Dialog
Related Topics
- FESWMS
- FESWMS Files
- FESWMS Graphical Interface
- FESWMS Hydraulic Structures
- FESWMS Model Control Dialog
- Steering
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||