GMS:2D Grid Module: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
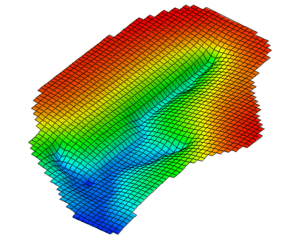
|[[Image:Sample_water_table.png|thumb|none|300 px|Watertable elevations from a MODFLOW simulation]] | |[[Image:Sample_water_table.png|thumb|none|300 px|Watertable elevations from a MODFLOW simulation]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
==2D Grid Types== | |||
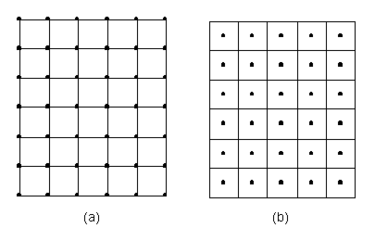
Two types of grids are supported in the 2D Grid module: mesh-centered grids and cell-centered grids. With a mesh-centered grid, the data values are stored at the corners of the grid cells. With a cell-centered grid, data values are stored at the cell centers. | |||
When a [[GMS:Datasets|dataset]] is imported to a cell-centered grid, there is one value in the dataset for each cell. The [[GMS:Contour Options|contouring]] and fringing functions use scalar values at the cell corners. Therefore, whenever contouring or fringing is performed, the values at the cell centers are interpolated to the cell corners. Interpolation to cell corners is only done for visualization purposes. All computations performed using the data calculator are performed on the original values at the cell centers. With mesh-centered grids, all visualization and computations are performed at the cell corners and no interpolation is necessary. | |||
Grids in GMS are Cartesian grids. That is, the row and column spacing in the grid can vary, but the row and column boundaries are straight. Each cell center or grid node can have a unique elevation. The grid can also be rotated about the Z axis if desired. | |||
[[Image:GridType1.png|thumb|none|375 px|Types of 2D grids supported in GMS. (a) Mesh-centered grid (b) Cell-centered grid.]] | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||