GMS:Creating and Editing 3D Grids: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{3D Grid links}} | {{3D Grid links}} | ||
== Creating 3D Grids == | |||
Two techniques are available for creating 3D grids: the '''Create Grid''' command in the 3D Grid Module and the '''Map → 3D Grid''' command in the Map Module. When a 3D Cell Centered Grid is created two different viewing modes are available. | Two techniques are available for creating 3D grids: the '''Create Grid''' command in the 3D Grid Module and the '''Map → 3D Grid''' command in the Map Module. When a 3D Cell Centered Grid is created two different viewing modes are available. | ||
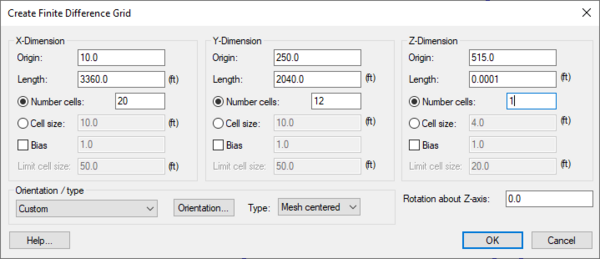
===Create Grid=== | |||
{{for|how to create 2D Grids|GMS:2D Grid Creation and Editing#Create Grid}} | {{for|how to create 2D Grids|GMS:2D Grid Creation and Editing#Create Grid}} | ||
{{Create Finite Difference Grid dialog}} | {{Create Finite Difference Grid dialog}} | ||
===Map → 3D Grid=== | |||
:Once the feature object coverages defining a conceptual model have been completely defined, the conceptual model is ready to be converted to a numerical model. The first step in this conversion process is to create a grid using the '''Map → 3D Grid''' command. Typically, the [[GMS:Grid Frame|'''Grid Frame''']] command is used prior to this command to define the location and dimensions of the grid. | :Once the feature object coverages defining a conceptual model have been completely defined, the conceptual model is ready to be converted to a numerical model. The first step in this conversion process is to create a grid using the '''Map → 3D Grid''' command. Typically, the [[GMS:Grid Frame|'''Grid Frame''']] command is used prior to this command to define the location and dimensions of the grid. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
:When refine points are specified the user must enter the ''Base size'', ''Bias'' and ''Max size''. The ''base size'' is the size the user wants the cell to be right at the refine point. The ''Max size'' is the largest size that the user would like the cells to be in the entire grid. The ''bias'' determines how quickly the cell size will vary as they move away from the refine point. If using a bias of 1.1 then the row next to the refine point will be 1.1 times the ''base size''. The next row will be 1.1 size the previous row. | :When refine points are specified the user must enter the ''Base size'', ''Bias'' and ''Max size''. The ''base size'' is the size the user wants the cell to be right at the refine point. The ''Max size'' is the largest size that the user would like the cells to be in the entire grid. The ''bias'' determines how quickly the cell size will vary as they move away from the refine point. If using a bias of 1.1 then the row next to the refine point will be 1.1 times the ''base size''. The next row will be 1.1 size the previous row. | ||
== Editing 3D Grids == | |||
Each cell in a 3D grid has attributes associated with it. Each grid cell can be specified as [[GMS:Active/Inactive Cells|active/inactive]] and each cell has a [[GMS:Materials|material]] associated with it. To edit the cell attributes associated with a numerical model see [[GMS:Cell Properties|Cell Properties]]. | Each cell in a 3D grid has attributes associated with it. Each grid cell can be specified as [[GMS:Active/Inactive Cells|active/inactive]] and each cell has a [[GMS:Materials|material]] associated with it. To edit the cell attributes associated with a numerical model see [[GMS:Cell Properties|Cell Properties]]. | ||