SMS:CMS-Flow Coverages
The CMS-Flow model makes use of the simulation based modeling approach. This requires defining coverages in the Map module to build the components for use in the CMS-Flow simulation.
Boundary Conditions
All numeric models require boundary condition data. In CMS-Flow, boundary conditions are defined on feature arcs in a boundary conditions coverage.
The Create Feature Arc can be used to click out boundary conditions for the model or arcs can be converted from other coverages or modules. Arcs can also be imported.
One the boundary condition arcs have been created, right-click on the arc with the Select Feature Arc tool and select the Assign Boundary Conditions command to bring up the Arc Boundary Condition dialog. This command is unique to the CMS-Flow Boundary Condition coverage and is only accessible by right-clicking on a selected arc.
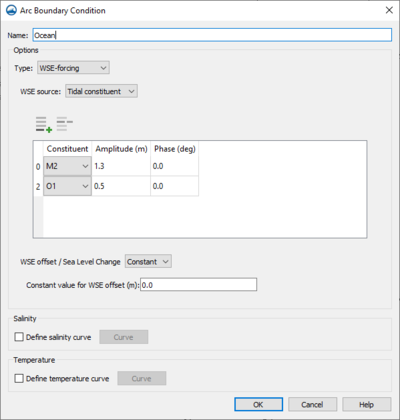
Arc Boundary Conditions Dialog
This dialog has the following options for boundary condition parameters.
- Name – Assign a name to the boundary arc.
- Type – Has the following options:
- "Unassigned" – The default option.
- "Flow rate forcing" – Specifies an inflow rate (flow in cubic meters/second at each cell). This can be used to represent a river flowing into the domain.
- Flow Source – Specifies a time series of water fluxes as either a constant value or as a curve.
- "Constant" – Allows entering a Constant flow value for the flow rate in m^3/s per cell.
- "Curve" – Clicking the Curve button will bring up an XY Series Editor dialog where a time series of water fluxes can be entered.
- Specify inflow direction – Measured clockwise from North (degrees). Positive values are directed into the domain and negative values are leaving the domain. Will be perpendicular to the cell face if no value is set.
- Conveyance coefficient – Distributes the total volume flux across the boundary to estimate depth-averaged velocities. Default is equal to approximately 2/3 for uniform flow.
- Flow Source – Specifies a time series of water fluxes as either a constant value or as a curve.
- "WSE forcing" – Specifies the water surface elevation as a function of time for the cellstring. Options include specifying a single curve (water level -vs- time) and all the cells will have the same water level at the specified time and extracting individual curves for each cell either from a regional tidal database (ADCIRC database) or from a regional (larger) circulation model.
- WSE Source – The following WSE sources can be selected:
- "Constant" – Allows setting a Constant WSE value for the water surface elevation.
- "Curve" – Clicking the Curve button will bring up an XY Series Editor dialog where a time series for the water surface elevation can be entered.
- "Parent CMS-Flow" – This option will extract multiple time series curves from a larger CMS-Flow grid. Clicking the Select button will allow choosing the CMS-Flow data file.
- "Parent ADCIRC" – This option will extract multiple time series curves from an ADCIRC model. This type provides an option to Use Velocity from the ADCIRC model. The Parent grid (fort.14) file, ADCIRC Solution File Type, Parent solution file, and Parent Starting Time will all need to be selected.
- "Extracted (SMS 13.4+)" – Option to pre-extract boundary forcing from a loaded parent grid or mesh. This type provides an option to Force Velocity from the parent.
- "Harmonic" – Option of forcing with a harmonic water surface elevation. With this option, the type of Speed, the Amplitude and the Phase can be entered in rows on the table.
- "Tidal Constituent" – Option of forcing with a tidal water surface elevation. With this option, the type of Constituent, the Amplitude and the Phase can be entered in rows on the table. Insert and delete rows to determine the constituents that will be used in the model run.
- "External Tidal" – This option tells the CMS to expect a "Tidal Constituents" simulation to be added and applied to the CMS-Flow solution. Guidance for this step is given on the page, Tidal_Components.
- WSE offset – An assumed spatially and temporally Constant or temporally varying Curve that may be used to correct the boundary water surface elevation for vertical data and sea level rise.
- WSE Source – The following WSE sources can be selected:
- Salinity – When this option is turned on, clicking the Curve button will bring up an XY Series Editor dialog where a time series of salinity values can be entered.
- Temperature – When this option is turned on, clicking the Curve button will bring up an XY Series Editor dialog where a time series of tempurature values can be entered.
Save Points
CMS-Flow includes save points which can be used to output calculations at specific locations.
Save points are created in the Save Points coverage using the Create Feature Point tool. When the coverage is linked to the CMS-Flow simulation data will be collected during the simulation model run.
The coverage has two unique commands. The coverage right-click menu in the Project Explorer has a Properties command that will bring up the Save Points Properties dialog. Right-clicking on a point in the graphics window and selecting the Assign Save Points... command bring up the Assign Save Points dialog.
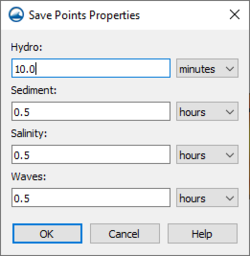
Save Points Properties Dialog
In the Save Points Properties dialog the output interval can be specified for data collected at each save point. The interval options can be specified for any of the following data types:
- Hydro
- Sediment
- Salinity
- Waves
All interval options can be specified in seconds, minutes, or hours.
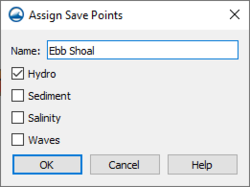
Assign Save Points
Each save point created in the coverage needs to be given parameters as to what type of data to collect during the simulation model run. Using the Select Feature Point tool, right-click on each save point and use the Assign Save Points... command. This will bring up the Assign Save Points dialog where the type of data to be gathered can be specified.
The dialog has the following options:
- Name – Each save point can be given a unique name. The given name will appear next to the point in the graphics window after being assigned.
- Hydro – Sets the save point to collect hydrologic data.
- Sediment – Sets the save point to collect sediment data.
- Salinity – Sets the save point to collect salinity data.
- Waves – Sets the save point to collect wave data.
Structures
CMS-Flow allows for 4 different structure types to be defined and used.
Rubble Mounds
CMS-Flow allows creating polygons to represent rubble mounds. After a polygon has been created on the CMS-Flow Structures coverage, attributes can be assigned to the polygon by right-clicking on the polygon and selecting the Assign Polygon Attributes... command.
When the Rubble Mound structure type is chosen, the dialog has the following options:
- Name – Each rubble mound can be given a unique name. The given name will appear next to the point in the graphics window after being assigned.
- The following options can be defined as either a Constant or Dataset:
- Rock diameter – The average diameter of the jetty rock or riprap.
- Porosity – The porosity value for the rubble mound jetty.
- Base depth – The starting elevation (bottom) of the rubble mound jetty.
- Calculation method – One of three different formulation equations can be used when including rubble mound jetties in the CMS-Flow simulation. They are as follows:
- "Sidropoulou et al. (2007)"
- "Kadlec and Knight (1996)"
- "Ward (1664)"
Weirs (13.4+)
CMS-Flow allows creating arcs to represent weirs. After a polygon has been created on the CMS-Flow Structures coverage, attributes can be assigned to the arc by right-clicking on the arc and selecting the Assign arc attributes... command.
When the Weir structure type is chosen, the dialog has the following options:
- Lateral distribution coefficient
- Orientation of weir (direction of sea side) - CMS needs to know the direction from which the dominant flow will be coming from. Select the direction of the sea side or strongest flow if not obviously the sea/ocean.
- Type of weir - One of two types can be selected. They are:
- Sharp-crested
- Broad-crested
- Flow coefficient - bayside to seaside
- Flow coefficient - seaside to bayside
- Crest elevation (mean water level) - This value is an elevation from the water surface to the crest of the weir. Generally this will be a negative value as they are typically submerged at mean and higher tides.
- Method to calculate flux over the weir - One of two formulation methods can be used when including weirs in the CMS-Flow simulation. They are:
- Approach 1
- Approach 2
Culverts (13.4+)
CMS-Flow allows creating arcs to represent culverts. After a polygon has been created on the CMS-Flow Structures coverage, attributes can be assigned to the arc by right-clicking on the arc and selecting the Assign arc attributes... command.
When the Culvert structure type is chosen, the dialog has the following options:
- Type of culvert - this can be one of two types:
- Box
- Circle
- With flap gate - check this box if a flap gate exists for this culvert.
- Width - available for Box culverts.
- Height - available for Box culverts.
- Radius - available for Circle culverts.
- Length - total length of the culvert between exposed ends.
- Darcy-weisbach friction coefficient - used when culvert is completely filled.
- Manning friction coefficient - used when culvert partially filled.
- Bay side entrance head loss
- Bay side exit head loss
- Sea side entrance head loss
- Sea side exit head loss
Tide Gates (13.4+)
CMS-Flow allows creating arcs to represent tide gates. After a polygon has been created on the CMS-Flow Structures coverage, attributes can be assigned to the arc by right-clicking on the arc and selecting the Assign arc attributes... command.
When the Tide Gate structure type is chosen, the dialog has the following options:
- Lateral distribution coefficient
- Orientation of gate (direction of sea side) - CMS needs to know the direction from which the dominant flow will be coming from. Select the direction of the sea side or strongest flow if not obviously the sea/ocean.
- Flow coefficient - bayside to seaside
- Flow coefficient - seaside to bayside
- Opening height of tide gate - This value is the distance of the tide gate opening to allow water through.
- Bottom elevation of tide gate - This value is an elevation from the water surface to the bottom of the tide gate. Generally this will be a negative value as it will typically be submerged at mean and higher tides.
- Method to calculate flux through tide gate - This will be one of two options:
- Approach 1
- Approach 2
- Schedule operation type - this will be one of four options:
- Uncontrolled
- Regular Time Interval - requires three additional values:
- Start time (hour)
- Opening frequency (hour)
- Open duration (hour)
- Designated Time Interval - requires the user to enter one or more rows in a table to two values associated with discrete opening times (elapsed time from start):
- Start time (hour)
- Open duration (hour)
- Open for ebb/Close for flood
Related Topics
| [hide] SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||