SMS:Scatter Triangles Menu: Difference between revisions
| (30 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The items unique to the Scatter module are listed below. The menu items operate on the active scatter set unless otherwise noted: | The items unique to the Scatter module are listed below. The menu items operate on the active scatter set unless otherwise noted: | ||
==Triangulate== | |||
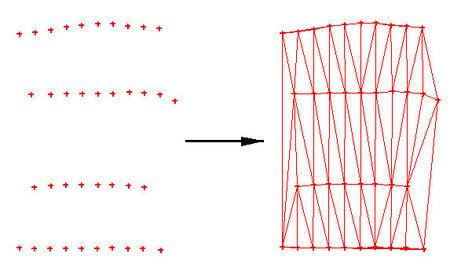
Scatter points or mesh nodes can be triangulated to form piecewise linear surfaces. For scattered data, these surfaces are also referred to as TINs (Triangular Irregular Networks). For mesh nodes, they form a finite element mesh. The points/nodes are connected into surfaces as scatter sets or meshes are created, but at times it may be necessary to reconnect the points (i.e. after deleting individual points/nodes or triangles/elements). New triangles are constructed in mass by triangulating a set of points when the '''Triangulate''' command from the ''Triangles'' menu is executed. The selected points are connected with a series of triangles. If points are not selected, then all points will be triangulated. | Scatter points or mesh nodes can be triangulated to form piecewise linear surfaces. For scattered data, these surfaces are also referred to as TINs (Triangular Irregular Networks). For mesh nodes, they form a finite element mesh. The points/nodes are connected into surfaces as scatter sets or meshes are created, but at times it may be necessary to reconnect the points (i.e. after deleting individual points/nodes or triangles/elements). New triangles are constructed in mass by triangulating a set of points when the '''Triangulate''' command from the ''Triangles'' menu is executed. The selected points are connected with a series of triangles. If points are not selected, then all points will be triangulated. | ||
[[File:Triangulate1.jpg|thumb|none|left|450 px]] | [[File:Triangulate1.jpg|thumb|none|left|450 px]] | ||
===Delaunay Criterion=== | |||
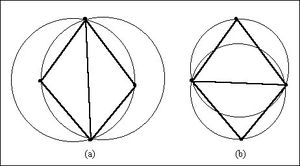
The resulting triangulation satisfies the | The resulting triangulation satisfies the Delaunay criterion. The Delaunay criterion ensures that no vertex lies within the interior of any of the circumcircles of the triangles in the network as shown below: | ||
[[File:Triangulate2.jpg|thumb|none|left|300 px]] | [[File:Triangulate2.jpg|thumb|none|left|300 px]] | ||
[[File:DelaunayCriterion.jpg|thumb|none|left|300 px]] | [[File:DelaunayCriterion.jpg|thumb|none|left|300 px|Two Adjacent Triangles Which (a) Violate and (b) Honor the Delaunay Criterion]] | ||
The result of enforcing the Delaunay criterion is that long thin triangles are avoided as much as possible. | |||
<!--===Triangulation=== | |||
The vertices associated with the active scatter set can be triangulated using the '''Triangulate''' command from the ''Triangles'' menu in the [[SMS:Scatter Module|Scatter module]]. Mesh nodes (either the selected nodes, or all nodes) can be triangulated using the '''Triangulate''' command from the [[SMS:2D Mesh Elements Menu|''Elements'' menu]] in the [[SMS:Mesh Module|2D Mesh module]].--> | |||
The | ==Optimize Triangulation== | ||
The Delaunay triangulation connects the points in the scatter set (TIN) to form triangles as close to equilateral triangles as possible. This does not mean that the resulting triangulation is the truest representation of the surface the scatter points were taken from. For example, two points on opposite banks of a channel could be close enough together to be connected by the Delaunay criterion, but connecting them creates a barrier in the surface which obstructs flow in the channel. | |||
Recognizing that the Delaunay triangulation may not be the most appropriate, SMS allows supports alternate triangulation methods as well as manual mesh editing which result in triangulations that are not Delaunay. | |||
Refer to the article on the *[[SMS:2D_Mesh_Module_Tools#Swap Edges|Swap Edges Tool]] and the [[SMS:Breaklines_Workflow|breakline workflow]] for information on manual edits to the surface. | |||
An alternate triangulation method can be selected in the [[SMS:Scatter_Options|Scatter Options]] command. | |||
==Select Thin Triangles== | |||
During the process of triangulation, a mesh of triangular elements is created around existing nodes. This usually creates triangular elements outside the desired scatter set boundary. Many of these exterior triangles are very skinny, and some are virtually invisible. The [[SMS:Boundary Triangles|'''Select Thin Triangles''']] command finds and selects skinny triangular elements which are on the scatter set boundary. | |||
During the process of triangulation, a mesh of triangular elements is created around existing nodes. This usually creates triangular elements outside the desired | |||
Thin triangles interior to the | Thin triangles interior to the scatter set will not be selected when this command is performed, since deletion of interior triangles would result in gaps in the mesh. After the thin triangles have been selected, they can be removed by selecting the [[SMS:Macros|'''Delete''']] [[File:Delete Macro Icon.svg|14 px]] macro. | ||
==Select/Delete Long Triangles== | |||
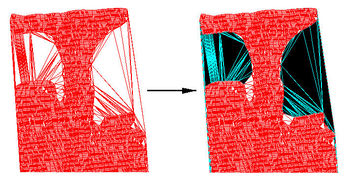
This option in the [[SMS:Scatter Module|Scatter Module]], ''Triangles'' Menu finds triangles longer than the length specified in the [[SMS:Scatter Options|''Scatter Options'']] dialog. The | This option in the [[SMS:Scatter Module|Scatter Module]], ''Triangles'' Menu finds triangles longer than the length specified in the [[SMS:Scatter Menu#Scatter Options|''Scatter Options'']] dialog. The ''Scatter Options'' also allows selecting the option to delete or select the long triangles. Selecting/deleting long triangles is useful for deleting triangles that span regions where interpolation is not desired, such as over regions of land (see figure below, the selected triangles are over land). | ||
[[Image:Check_long_triangles.jpg|thumb|none|left|350 px]] | [[Image:Check_long_triangles.jpg|thumb|none|left|350 px]] | ||
==Process Boundary Triangles== | |||
[ | When scatter points are triangulated, the resulting [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convex_hull convex hull] often contains triangles outside the desired mesh boundary. The ''Process Boundary Triangles'' dialog was developed to help remove invalid boundary triangles. To open the ''Process Boundary Triangles'' dialog: | ||
* In the [[SMS:Scatter Module|Scatter Module]], make the [[SMS:Scatter_Module_Tools|'''Select Triangle''']] [[File:SMS Select Mesh Element Tool.svg|16 px]] tool active | |||
* Select '''Process Boundary Triangles...''' from the right-click menu | |||
OR | |||
* In the [[SMS:Scatter Module|Scatter Module]], select '''Process Boundary Triangles...''' from the [[SMS:Scatter Triangles Menu|''Triangles'' menu]] | |||
See the article [[SMS:Process Boundary Triangles|Process Boundary Triangles]] for more information. | |||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
* [[SMS:Scatter Module|Scatter Module]] | * [[SMS:Scatter Module|Scatter Module]] | ||
* [[SMS: | * [[SMS:Scatter_Module#Scatter_Module_Menus|Scatter Module Menus]] | ||
| Line 44: | Line 49: | ||
{{Template:Navbox SMS}} | {{Template:Navbox SMS}} | ||
[[Category:SMS Scatter]] | [[Category:SMS Scatter|T]] | ||
[[Category:SMS Menus|S]] | |||
[[Category:External Links]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:26, 24 May 2022
The items unique to the Scatter module are listed below. The menu items operate on the active scatter set unless otherwise noted:
Triangulate
Scatter points or mesh nodes can be triangulated to form piecewise linear surfaces. For scattered data, these surfaces are also referred to as TINs (Triangular Irregular Networks). For mesh nodes, they form a finite element mesh. The points/nodes are connected into surfaces as scatter sets or meshes are created, but at times it may be necessary to reconnect the points (i.e. after deleting individual points/nodes or triangles/elements). New triangles are constructed in mass by triangulating a set of points when the Triangulate command from the Triangles menu is executed. The selected points are connected with a series of triangles. If points are not selected, then all points will be triangulated.
Delaunay Criterion
The resulting triangulation satisfies the Delaunay criterion. The Delaunay criterion ensures that no vertex lies within the interior of any of the circumcircles of the triangles in the network as shown below:
The result of enforcing the Delaunay criterion is that long thin triangles are avoided as much as possible.
Optimize Triangulation
The Delaunay triangulation connects the points in the scatter set (TIN) to form triangles as close to equilateral triangles as possible. This does not mean that the resulting triangulation is the truest representation of the surface the scatter points were taken from. For example, two points on opposite banks of a channel could be close enough together to be connected by the Delaunay criterion, but connecting them creates a barrier in the surface which obstructs flow in the channel. Recognizing that the Delaunay triangulation may not be the most appropriate, SMS allows supports alternate triangulation methods as well as manual mesh editing which result in triangulations that are not Delaunay. Refer to the article on the *Swap Edges Tool and the breakline workflow for information on manual edits to the surface. An alternate triangulation method can be selected in the Scatter Options command.
Select Thin Triangles
During the process of triangulation, a mesh of triangular elements is created around existing nodes. This usually creates triangular elements outside the desired scatter set boundary. Many of these exterior triangles are very skinny, and some are virtually invisible. The Select Thin Triangles command finds and selects skinny triangular elements which are on the scatter set boundary.
Thin triangles interior to the scatter set will not be selected when this command is performed, since deletion of interior triangles would result in gaps in the mesh. After the thin triangles have been selected, they can be removed by selecting the Delete ![]() macro.
macro.
Select/Delete Long Triangles
This option in the Scatter Module, Triangles Menu finds triangles longer than the length specified in the Scatter Options dialog. The Scatter Options also allows selecting the option to delete or select the long triangles. Selecting/deleting long triangles is useful for deleting triangles that span regions where interpolation is not desired, such as over regions of land (see figure below, the selected triangles are over land).
Process Boundary Triangles
When scatter points are triangulated, the resulting convex hull often contains triangles outside the desired mesh boundary. The Process Boundary Triangles dialog was developed to help remove invalid boundary triangles. To open the Process Boundary Triangles dialog:
- In the Scatter Module, make the Select Triangle
 tool active
tool active - Select Process Boundary Triangles... from the right-click menu
OR
- In the Scatter Module, select Process Boundary Triangles... from the Triangles menu
See the article Process Boundary Triangles for more information.
Related Topics
SMS Menu Bars | |
|---|---|
| Standard Menus: | File • Edit • Display • Window • Help |
| Module Menus: | 2D Mesh • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter |
| Model Menus: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • FESWMS • Generic Model • GenCade • PTM • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • STWAVE • TUFLOW |
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||