SMS:Generic Model: Difference between revisions
| (48 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
While SMS contains several custom interfaces for specific numerical models, it is not possible to build interfaces in SMS for every model in | While SMS contains several custom interfaces for specific numerical models, it is not possible to build interfaces in SMS for every model in existence. SMS has a generic interface whereby any two-dimensional finite element or finite difference model can be run using SMS as a pre- and post-processor. | ||
The generic model interface can be added to a [http://www.aquaveo.com/software/sms-pricing paid edition] of SMS. | |||
[[Category:Link to Store]] | |||
{{SMS_at_a_glance_generic_model_interface|Heading===Generic Model Overview==|Link=}} | |||
==Functionality== | ==Functionality== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 12: | ||
* Material Properties | * Material Properties | ||
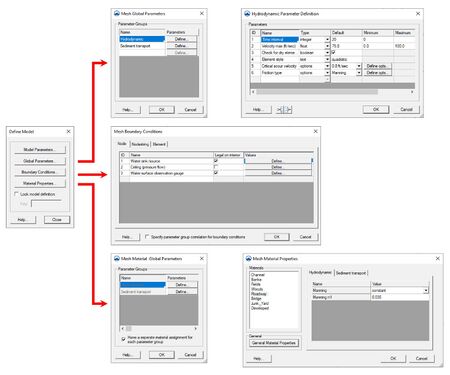
With the model attributes defined, | With the model attributes defined, generate a mesh or grid using the geometric tools in the map, mesh or Cartesian grid modules. Model parameters can then be set, boundary conditions specified, and material properties applied to the geometric data and saved out to a generic file format. | ||
==Using Multiple Meshes== | ==Using Multiple Meshes== | ||
Starting in SMS 11.2, multiple generic mesh model definitions can exist at the same time. When creating a new generic 2D mesh coverage, if multiple generic model definitions exist, a dialog will appear to | Starting in SMS 11.2, multiple generic mesh model definitions can exist at the same time. When creating a new generic 2D mesh coverage, if multiple generic model definitions exist, a dialog will appear to asking which model definition to use. When performing a map to 2D mesh operation, the definition and values will be copied from the coverage to the new mesh. | ||
The define model menu item will define the definition for the mesh, if the menu item is in the mesh module menu, or for the coverage, if in the feature objects menu. The generic model definition, or template, is stored in a *.2dm file with the SMS project. The *.2dm file will not contain a mesh or parameter values. This template will be used whenever a new mesh or coverage of that type is created. | The define model menu item will define the definition for the mesh, if the menu item is in the mesh module menu, or for the coverage, if in the feature objects menu. The generic model definition, or template, is stored in a *.2dm file with the SMS project. The *.2dm file will not contain a mesh or parameter values. This template will be used whenever a new mesh or coverage of that type is created. | ||
== Graphical Interface == | == Graphical Interface == | ||
SMS provides a graphical interface that is designed | SMS provides a graphical interface that is designed to visualize the projects being created, easily modify project parameters, and view the solutions produced by the Generic Model. See [[SMS:Generic Model Graphical Interface|Generic Model Graphical Interface]] for more information. | ||
The [[SMS:Generic Model Graphical Interface| | The [[SMS:Generic Model Graphical Interface|generic model graphical interface]] contains tools to create and edit a Generic Model simulation. The simulation consists of a geometric definition of the model domain (the mesh) and a set of numerical parameters. The parameters define the boundary conditions and options pertinent to the model. | ||
The interface is accessed by selecting the [[SMS:Mesh Module|2D Mesh | The interface is accessed by selecting the [[SMS:Mesh Module|2D Mesh module]] and setting the current model to ''Generic''. If a mesh has already been created for a Generic Model simulation or an existing simulation read, the mesh object will exist in the [[SMS:Project Explorer|Project Explorer]] and selecting that object will make the 2D Mesh module active and set the model to Generic. See the [[SMS:Mesh Module|Mesh module]] documentation for guidance on building and editing meshes as well as visualizing mesh results. | ||
The interface consists of the [[SMS:2D Mesh_Module_Menus|2D | The interface consists of the [[SMS:2D Mesh_Module_Menus|2D mesh module menus]] and [[SMS:2D Mesh Module Tools|tools]] augmented by the generic model ''Mesh'' menu. See [[SMS:Generic Model Graphical Interface|Generic Model Graphical Interface]] for more information. | ||
===Generic Model Menu=== | ===Generic Model Menu=== | ||
The following menu commands are available in the ''Mesh'' (generic model) menu: | The following menu commands are available in the ''Mesh'' (generic model) menu: | ||
;'''Check Mesh''' : This command will bring up the [[SMS:Model Checker|''Model Checker'']] dialog. The dialog will list all potential problems with a description of the problem and a recommend procedure to fix the problem. | |||
;'''Define Model''' : Opens the [[SMS:Generic Model Graphical Interface#Define Model|''Define Model'']] dialog. | |||
;'''Global Parameters...''' : Brings up the [[SMS:Generic Model Graphical Interface#Global Parameters|''Global Parameters'']] dialog. | |||
;'''Assign BC...''' : Opens the [[SMS:Generic Model Graphical Interface#Boundary Conditions|''Node Boundary Conditions'']], [[SMS:Generic Model Graphical Interface#Boundary Conditions|''Nodestring Boundary Conditions'']], or [[SMS:Generic Model Graphical Interface#Boundary Conditions|''Element Boundary Conditions'']] dialog depending on if a node, nodestring, or element is selected. | |||
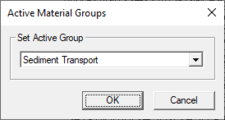
[[File:Mesh ActiveMaterialGroup.png|thumb|225 px|''Active Material Groups'' dialog.]] | |||
;'''Set Active Material Group''' : Opens the ''Active Material Group'' dialog. Here indicate which material group is active from the parameter groups created in the ''Global Parameters'' definition dialog. | |||
; '''Material Properties...''' : Opens the [[SMS:Generic Model Graphical Interface#Material Properties|''Material Properties'']] dialog. | |||
; '''Run Mesh''' : Launches the generic mesh model executable. The model executable must be specified in the ''Preferences'' dialog for this command to function. By default, a model executable is not specified for the generic model. | |||
==Case Studies / Sample Problems== | ==Case Studies / Sample Problems== | ||
The following [[SMS:Tutorials|tutorials]] may be helpful for learning to use the Generic Model Interface in SMS: | The following [[SMS:Tutorials|tutorials]] may be helpful for learning to use the Generic Model Interface in SMS: | ||
* General Section | * General Section | ||
** ''Mesh Editing'' [http://smstutorials-13.2.aquaveo.com/SMS_MeshEditing.pdf] | |||
* Mesh Editing | ** ''Observation'' [http://smstutorials-13.2.aquaveo.com/SMS_Observation.pdf] | ||
* Observation | |||
* Models Section | * Models Section | ||
** ''Generic Mesh Model'' [http://smstutorials-13.2.aquaveo.com/SMS_Gen2DM.pdf] | |||
* Generic Mesh Model | |||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
* [[SMS:BASEMENT|BASEMENT]] | * [[SMS:BASEMENT|BASEMENT]] | ||
* [[SMS:HYDRO AS-2D|HYDRO AS-2D]] | * [[SMS:HYDRO AS-2D|HYDRO AS-2D]] | ||
* [[SMS:ELCIRC|ELCIRC]] | * [[SMS:ELCIRC|ELCIRC]] | ||
* [[SMS:FVCOM|FVCOM]] | * [[SMS:FVCOM|FVCOM]] | ||
* [[SMS:TUFLOW FV|TUFLOW FV]] | |||
| Line 62: | Line 60: | ||
[[Category:SMS 2D Mesh|G]] | [[Category:SMS 2D Mesh|G]] | ||
[[Category:Generic Model|M]] | [[Category:Generic Model|M]] | ||
[[Category:External Links]] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:24, 2 May 2023
While SMS contains several custom interfaces for specific numerical models, it is not possible to build interfaces in SMS for every model in existence. SMS has a generic interface whereby any two-dimensional finite element or finite difference model can be run using SMS as a pre- and post-processor.
The generic model interface can be added to a paid edition of SMS.
Generic Model Overview
- Allows creation of a user defined mesh module interface to use SMS with a model not natively supported
- User defines available model parameters and boundary condition options
- User defined interface can be used to build models
- User data is exported into ASCII data that can be read as input for a numeric model
Functionality
The following can be defined for a generic model:
- Global Model Parameters
- Boundary Conditions
- Material Properties
With the model attributes defined, generate a mesh or grid using the geometric tools in the map, mesh or Cartesian grid modules. Model parameters can then be set, boundary conditions specified, and material properties applied to the geometric data and saved out to a generic file format.
Using Multiple Meshes
Starting in SMS 11.2, multiple generic mesh model definitions can exist at the same time. When creating a new generic 2D mesh coverage, if multiple generic model definitions exist, a dialog will appear to asking which model definition to use. When performing a map to 2D mesh operation, the definition and values will be copied from the coverage to the new mesh.
The define model menu item will define the definition for the mesh, if the menu item is in the mesh module menu, or for the coverage, if in the feature objects menu. The generic model definition, or template, is stored in a *.2dm file with the SMS project. The *.2dm file will not contain a mesh or parameter values. This template will be used whenever a new mesh or coverage of that type is created.
Graphical Interface
SMS provides a graphical interface that is designed to visualize the projects being created, easily modify project parameters, and view the solutions produced by the Generic Model. See Generic Model Graphical Interface for more information.
The generic model graphical interface contains tools to create and edit a Generic Model simulation. The simulation consists of a geometric definition of the model domain (the mesh) and a set of numerical parameters. The parameters define the boundary conditions and options pertinent to the model.
The interface is accessed by selecting the 2D Mesh module and setting the current model to Generic. If a mesh has already been created for a Generic Model simulation or an existing simulation read, the mesh object will exist in the Project Explorer and selecting that object will make the 2D Mesh module active and set the model to Generic. See the Mesh module documentation for guidance on building and editing meshes as well as visualizing mesh results.
The interface consists of the 2D mesh module menus and tools augmented by the generic model Mesh menu. See Generic Model Graphical Interface for more information.
Generic Model Menu
The following menu commands are available in the Mesh (generic model) menu:
- Check Mesh
- This command will bring up the Model Checker dialog. The dialog will list all potential problems with a description of the problem and a recommend procedure to fix the problem.
- Define Model
- Opens the Define Model dialog.
- Global Parameters...
- Brings up the Global Parameters dialog.
- Assign BC...
- Opens the Node Boundary Conditions, Nodestring Boundary Conditions, or Element Boundary Conditions dialog depending on if a node, nodestring, or element is selected.
- Set Active Material Group
- Opens the Active Material Group dialog. Here indicate which material group is active from the parameter groups created in the Global Parameters definition dialog.
- Material Properties...
- Opens the Material Properties dialog.
- Run Mesh
- Launches the generic mesh model executable. The model executable must be specified in the Preferences dialog for this command to function. By default, a model executable is not specified for the generic model.
Case Studies / Sample Problems
The following tutorials may be helpful for learning to use the Generic Model Interface in SMS:
Related Topics
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||