User:Jcreer/CMS-Wave 13.2: Difference between revisions
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
==Output control== | ==Output control== | ||
The Output Control tab contains additional options for outputting results from the CMSWave model run. | |||
* Radiation stresses | |||
* | *''Limit observation output'' – | ||
* Wave | *''Radiation Stresses'' – Turns on wave radiation stresses calculations for the simulation. (Results in a [[SMS:CMS-Wave Radiation Stress File|wave radiation stress file]] with spatially varied data (a value for each cell)???). | ||
*''Breaking type'' – Option to turn on (production of wave breaking data???) (wave breaking file creation???) and define data type (results in a [[SMS:CMS-Wave Wave Breaking File|wave breaking file]] with spatially varied data (a value for each cell)). | |||
**"None" – (Wave breaking file type will not be produced???). | |||
**"Write indices" – (Select for output of wave breaking indices???) | |||
**"Calculate energy dissipation" – (Select for output of dataset of energy dissipation fluxes???) | |||
==Options== | ==Options== | ||
Revision as of 22:02, 7 February 2022
Graphical Interface
The CMS-Wave graphical interface includes tools to assist with creating, editing, and debugging a CMS-Wave model. The CMS-Wave interface exists in the Cartesian Grid Module.
Map Coverages
Model Control
The CMS-Wave Model Control dialog is used to setup the options that apply to the simulation as a whole. These options include time controls, run types, output options, global parameters, print options and other global settings.
Running the Model
The CMS-Wave files are written automatically with the SMS project file or can be saved separately using the File | Save CMS-Wave or Save As menu commands. See CMS-Wave Files for more information on the files used for the CMS-Wave run.
CMS-Wave can be launched from SMS using the CMS-Wave | Run CMS-Wave menu command. A check of some of the common problems, called the Model Checker, is done each time the model is launched, or by selecting the CMS-Wave | Model Check menu command.
Visualizing Results
Select the spectral grid as the grid to use in the Spectral Energy dialog. This will open the spectral grid for viewing in the Spectral Energy dialog. Make sure to set the original grid back before leaving the dialog to ensure the model does not change.
CMS-Wave Menu
See CMS-Wave Menu for more information.
Related Topics
| [hide] SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||
Model Control
The Model Control… command in the CMS-Wave Menu opens the CMS-Wave Model Control dialog. This dialog is divided into sections for different types of parameters which are used by the model as it runs. These include:
Parameters
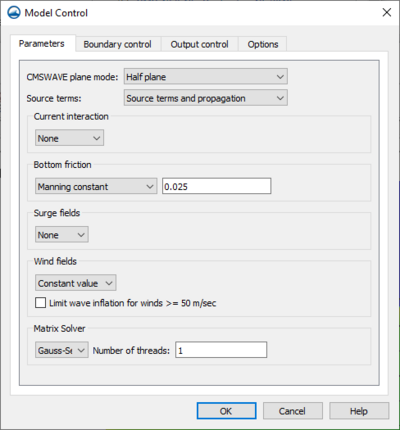
The Parameters tab of the CMS-Wave Model Control dialog contains the following options:
- CMSWAVE plane mode – Select the plane mode for the project.
- "Half plane" – Appropriate for nearshore coastal applications allowing wave input and generation on two boundaries resulting in a faster run-time.
- "Full plane" – Used with enclosed or semi-enclosed bays, estuaries, and lakes where there is no clear “offshore” direction and seas and swells may oppose each other. Allows wave input and generation on all four boundaries.
- "Full plane with input reverse spectra" – This option allows spectral input to be used on two opposite boundaries.
- Source terms – (This option defines whether CMS-Wave should generate waves using wind input or not.???)
- "Source terms and propagation" – Uses wind input if provided.
- "Propagation only" – Neglects wind input in calculation.
- Current interaction – Option to define currents for the simulation.
- "None" – No current interaction will be in the simulation.
- "Use dataset" – A vector dataset can be used to define the currents for the simulation. Click Select to select from the dataset options in a dialog.
- Current interaction – Option to define currents for the simulation.
- "None" – No current interaction will be in the simulation.
- "Use dataset" – A vector dataset can be used to define the currents for the simulation.
- Bottom friction – This option allows defining friction for the ocean bottom.
- "None" – No bottom friction is applied to the simulation.
- "Darcy-Weisbach constant" – Set a constant value to use the Darcy-Weisbach method for bottom friction.
- "Darcy-Weisbach dataset" – Select a dataset in the project to use the Darcy-Weisbach method for bottom friction.
- "Manning constant" – Set a constant value to use as the Manning's n value.
- "Manning dataset" – Select a dataset in the project to use the Darcy-Weisbach method for bottom friction.
- Surge fields – Option to set surge field values.
- "None" – No surge field values will be used in the simulation.
- "Constant Value" – Set a constant value for surge fields used in the simulation.
- "Use dataset" – Select a dataset in the project to define surge fields in the simulation.
- Wind fields – This option requires the Source terms" be set to use "Source terms and propagation".
- "Constant value" – Use a constant value for wind fields included in the simulation.
- "Use dataset" – Use a dataset in the project to define wind fields in the simulation.
- Limit wave inflation for wind >= 50 m/sec – When turned on, the wave inflation for wind will be limited.
- Matrix Solver – Select the matrix solver used in the simulation.
- "Gauss-Seidel" – Sets matrix solver to Gauss-Seidel solver with multi-processor capability.
- Number of threads –
- "ADI" – Sets matrix solver to Alternative Direction Iterative solver.
- "Gauss-Seidel" – Sets matrix solver to Gauss-Seidel solver with multi-processor capability.
- Water Level – A constant value or a scalar dataset can be used to define the water level for the simulation. If “constant” is selected, the constant value will be defined in the CMS-Wave Case Definition dialog for each case.
Boundary control
The Boundary control tab contains options for assigning spectral data for the model run.
- Source – Select the source for the external boundary conditions
- "Spectral Coverage" – Uses the spectral coverage in the simulation for all boundary conditions.
- "None" – Requires that energy spectra be entered.
- Interpolation Type – Sets the method for (CMS-Wave??) to use when interpolating between spectra.
- "Average spectra" –
- "IDW interpolation" – Sets the type of data interpolation to Inverse Distance Weighting.
- Computational Spectral Grid – Adjust and view data related to the computational spectral grid.
- Frequency Distribution – Adjust the Frequency Distribution settings for the computational spectral grid.
- Number – Adjust the number of frequency bands.
- Delta – Adjust the step size in Hz.
- Minimum – Adjust the minimum frequency in Hz.
- Angle Distribution – View the Angle Distribution settings for the computational spectral grid.
- Number – View the number of angle bands.
- Delta – View the step size in degrees.
- Minimum – View the minimum angle in degrees.
- Frequency Distribution – Adjust the Frequency Distribution settings for the computational spectral grid.
- Sides – Specified when using a spectral coverage source. The types of boundary conditions include:
- "Specified spectrum" – Click Select to the right to open a dialog box to assign the spectral coverage to the boundary.
- "Zero spectrum" – The boundary doesn't have any spectral energy applied.
- "Open lateral boundary" –
- Case data – Defines the time step or cases that will be used and the input boundary conditions for each.
- Wind direction angle convention – Set the convention for the wind direction field for the model.
- "Cartesian" – The direction FROM. The origin (0.0) indicates the direction is coming from North. It increases clockwise from North (viewed from above). This is most commonly used for wind direction.
- "Meterologic" – The direction TO. The origin (0.0) indicates the direction is going to the North. It increases clockwise (like a bearing) so 45 degrees indicates a direction heading towards the North East.
- "Oceanographic" – The Cartesian coordinate axes as a direction TO. East, or the positive X axis, defines the zero direction. It increases in a counter clockwise direction or righthand rule. 45 degrees indicates a direction heading to the North East and 90 degrees indicates a direction heading to the North.
- "Shore normal" – "TO" convention based on a Theta(grid) which defines the grid orientation relative to the positive X axis (CCW direction).
- Populate from Spectra – Click the Populate button to import data from the (Spectral coverage???).
- Set Reference Time – Click this button to open the CMS-Wave Simulation Reference Time dialog and adjust the reference time and time units.
- Reference time – Set the desired Reference time for the simulation.
- Time units – Sets time units for case data to "days", "hours", or "minutes".
- Graphic icons???
- Time – The time offset value representing how much later the time is than the specified reference time. Hence, if 5 is entered for the time offset, and the time units is hours, then it is the case of 5 hours later. When nesting is used, the case ids, and the number of cases, will be determined by the parent simulation.
- Wind Direction – Available if "Constant value" has been selected on the Parameters" tab.
- Wind Magnitude – Available if "Constant value" has been selected on the Parameters" tab.
- Water Level – Available if "Constant value" has been selected on the Parameters" tab.
- Wind direction angle convention – Set the convention for the wind direction field for the model.
Output control
The Output Control tab contains additional options for outputting results from the CMSWave model run.
- Limit observation output –
- Radiation Stresses – Turns on wave radiation stresses calculations for the simulation. (Results in a wave radiation stress file with spatially varied data (a value for each cell)???).
- Breaking type – Option to turn on (production of wave breaking data???) (wave breaking file creation???) and define data type (results in a wave breaking file with spatially varied data (a value for each cell)).
- "None" – (Wave breaking file type will not be produced???).
- "Write indices" – (Select for output of wave breaking indices???)
- "Calculate energy dissipation" – (Select for output of dataset of energy dissipation fluxes???)
Options
Here specify the format for SMS to write out the input datasets. They can be written in either ASCII or XMDF format.
- Bed friction
- Allow wetting and drying
- Infragravity wave effect
- Diffraction intensity
- Forward reflection – A constant value for the entire simulation or spatially varying data using a scalar dataset can be used to define the forward reflection for the model.
- Backward reflection – A constant value for the entire simulation or spatially varying data using a scalar dataset can be used to define the backward reflection for the model.
- Muddy bed – Spatially varying data using a scalar dataset can be used to define the muddy bed (values??) for the model.
- Non-linear wave effect
- Run up
- Quick mode
Related Topics
| [hide] SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||
Menu
The simulation right-click menu includes the general simulation commands Delete, Duplicate, and Rename along with the following model specific commands:
- Model Control
- Brings up the CMS-Wave Model Control dialog. The dialog allows viewing and editing the current parameters that affect how CMS-Wave runs and what options are to be included in the current simulation.
- Model Check
- Check for common problems. If problems are found, the Model Checker dialog will open.
- Save Simulation
- Tells SMS that it is time to write out the files that CMS-Wave needs to run. Note that the project must be saved before the files may be exported. The user will not see anything happen, but SMS uses the input information from the model control, the boundary conditions, and quadtree data to create the files in preparation for CMS-Flow to work.
- Run Simulation
- When the model is ready and has been exported, it may be launched. Launching CMS-Wave initiates the model run for the simulation. Upon successful completion of the launch, the analysis is complete and results are ready to be read and displayed by SMS.
- Save Project, Simulation, and Run
- This is a combination of the previous steps put together into one.
Related Topics
| [show] SMS Menu Bars |
|---|
| [hide] SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||