GMS:Cross Sections: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 20:22, 9 June 2011
Cross sections - also referred to as fence diagrams - are flat surfaces used to visualize the subsurface. GMS has different types of cross section objects:
- Solid Cross Sections
- Borehole Cross Sections
- 3D Grid Cross Sections
- 3D Mesh Cross Sections
Contents
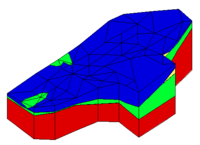
Solid Cross Sections
Solid cross sections can be created by "slicing" through a set of solids using the Create Cross Section tool. This can be done at any angle and the slicing can be done using a multi-segment polyline. Solid cross sections can be converted to a conceptual model. This is useful if you have a solid model of an embankment that you want to analyze using UTEXAS.
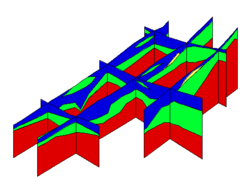
Borehole Cross Sections
Borehole cross sections are quite different than solid, 3D grid, and 3D mesh cross sections. See the page on Borehole Cross Sections.
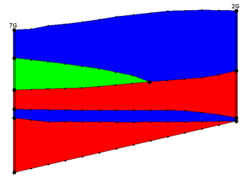
3D Grid Cross Sections
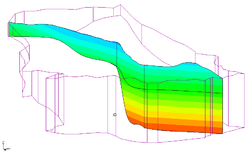
3D grid cross sections are created similar to solid cross sections. Data sets are automatically interpolated from the 3D grid to the cross sections and contours can be displayed on the cross sections.
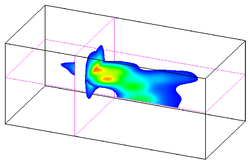
3D Mesh Cross Sections
3D mesh cross sections are created similar to solid cross sections. Data sets are automatically interpolated from the 3D mesh to the cross sections and contours can be displayed on the cross sections.
| GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||