GMS:Horizon Conceptual Model: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
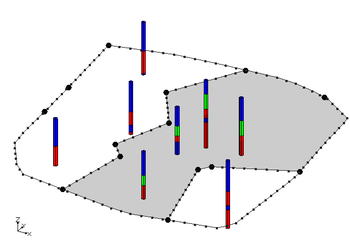
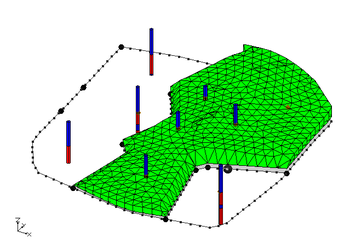
If the user wishes to explicitly control the areal extent of a solid created from horizons, this can be done using horizon coverages. GMS has a conceptual model type for horizons. Coverages that are inside of a horizons conceptual model can be associated with a horizon ID. The polygons in a horizon coverage determine the areal extent of the solid for the associated horizon. The first figure below shows a horizon coverage for the green material. The solid associated with this horizon will not extend beyond the boundary of the polygon. The second figure shows the solid resulting from the boreholes and the horizon coverage. When the Horizons->Solids command is executed the user may include a Horizons conceptual model as part of the input to the command. | If the user wishes to explicitly control the areal extent of a solid created from horizons, this can be done using horizon coverages. GMS has a conceptual model type for horizons. Coverages that are inside of a horizons conceptual model can be associated with a horizon ID. The polygons in a horizon coverage determine the areal extent of the solid for the associated horizon. The first figure below shows a horizon coverage for the green material. The solid associated with this horizon will not extend beyond the boundary of the polygon. The second figure shows the solid resulting from the boreholes and the horizon coverage. When the Horizons->Solids command is executed the user may include a Horizons conceptual model as part of the input to the command. | ||
[[Image:HorCoverage.png| | [[Image:HorCoverage.png|350px]] | ||
[[Image:HorCoverageSolid.png| | [[Image:HorCoverageSolid.png|350px]] | ||
Revision as of 17:45, 23 June 2011
If the user wishes to explicitly control the areal extent of a solid created from horizons, this can be done using horizon coverages. GMS has a conceptual model type for horizons. Coverages that are inside of a horizons conceptual model can be associated with a horizon ID. The polygons in a horizon coverage determine the areal extent of the solid for the associated horizon. The first figure below shows a horizon coverage for the green material. The solid associated with this horizon will not extend beyond the boundary of the polygon. The second figure shows the solid resulting from the boreholes and the horizon coverage. When the Horizons->Solids command is executed the user may include a Horizons conceptual model as part of the input to the command.
The Horizons algorithm is used to create either solids, HUF units, or 3D Meshes from Borehole and TIN data. How to use the three Horizon commands are explained in more detail below:
GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||