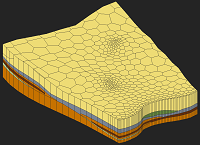
GMS:Creating and Editing UGrids: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
==Map → UGrid== | ==Map → UGrid== | ||
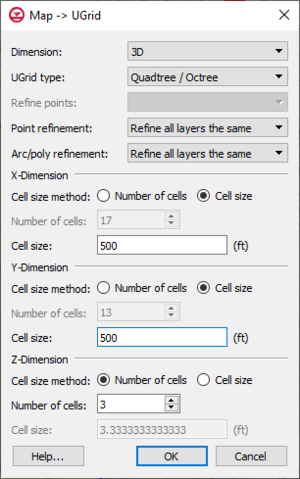
The ''Map → UGrid'' command creates a UGrid from feature objects. It can be found in the ''Feature Objects'' menu, in the Map toolbar, and in some pop-up menus when right-clicking on items in the [[GMS:Project Explorer|Project Explorer]] (Coverage, Grid Frame). The command opens the ''Create UGrid'' dialog. | The '''Map → UGrid''' command creates a UGrid from feature objects. It can be found in the ''Feature Objects'' menu, in the Map toolbar, and in some pop-up menus when right-clicking on items in the [[GMS:Project Explorer|Project Explorer]] (Coverage, Grid Frame). The command opens the ''Create UGrid'' dialog. | ||
[[Image:DialogCreateUGrid.png|thumb|right|Create UGrid dialog.]] | [[Image:DialogCreateUGrid.png|thumb|right|Create UGrid dialog.]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
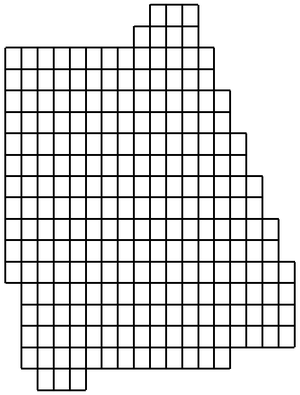
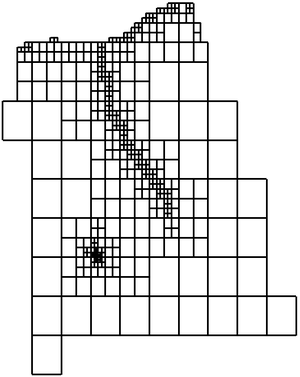
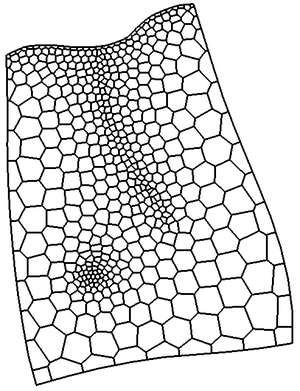
** If not using the Voronoi UGrid type, the size and number of cells in the X, Y and Z dimensions can be specified. For quad tree UGrids, the cell size represents the large, unrefined size. The small, refined size is determined by the refinement specified at points, arcs and polygons. Also for quad tree UGrids, if the cell size is specified, it represents a target cell size (large, unrefined size); the actual cell size will likely be somewhat different so that the cells fit within the grid boundaries. | ** If not using the Voronoi UGrid type, the size and number of cells in the X, Y and Z dimensions can be specified. For quad tree UGrids, the cell size represents the large, unrefined size. The small, refined size is determined by the refinement specified at points, arcs and polygons. Also for quad tree UGrids, if the cell size is specified, it represents a target cell size (large, unrefined size); the actual cell size will likely be somewhat different so that the cells fit within the grid boundaries. | ||
If a [[GMS:Grid_Frame|grid frame]] exists, it is used to determine the location of the grid boundaries. If polygons exist and the | If a [[GMS:Grid_Frame|grid frame]] exists, it is used to determine the location of the grid boundaries. If polygons exist and the ''Regular'' or ''Quad tree'' options are used, any cells that are not inside a polygon are not included in the UGrid. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||