GIS Conversion and Editing: Difference between revisions
m (Jcreer moved page GIS Conversion to GIS Conversion and Editing) |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
===Feature Contours=== | ===Feature Contours=== | ||
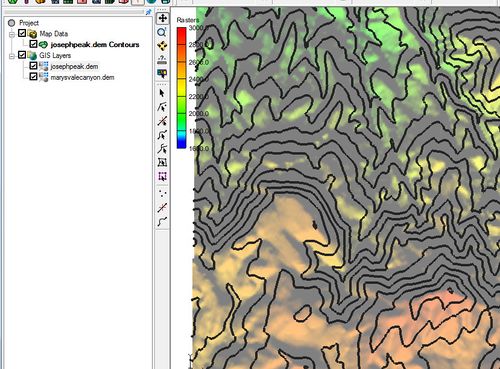
Activating this command will automatically generate contours which will appear as a new coverage under Map Data in the project explorer. By default, contour lines are shown in black unless the user changes the contour color in the ''Display Options'' dialog. | Activating this command will automatically generate contours which will appear as a new coverage under Map Data in the project explorer. By default, contour lines are shown in black unless the user changes the contour color in the ''Display Options'' dialog. The contour interval is found by creating 10 contours evenly spaced between the min and max dataset values. | ||
[[File:GIS FeatureContours.jpg|thumb|none|500 px| Generated feature contours appearing as black lines.]] | [[File:GIS FeatureContours.jpg|thumb|none|500 px| Generated feature contours appearing as black lines.]] | ||
Revision as of 16:03, 14 April 2015
GMS, SMS, and WMS can load GIS data such as digital elevation models (DEMs) and images. This GIS data will appear in the GIS Data section of the project explorer.
GIS Data Conversion
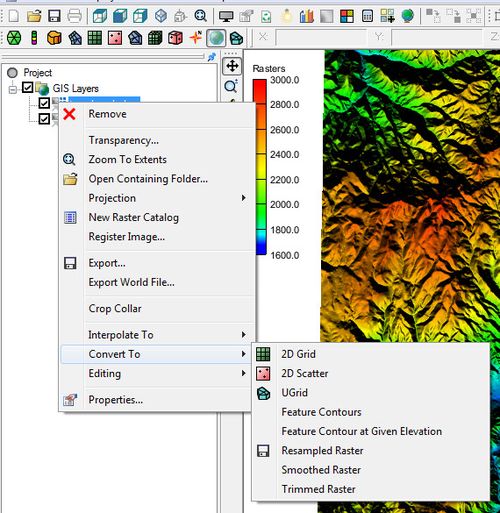
Both GMS and SMS offer methods to convert GIS data. Right-clicking on a GIS data item in the project explorer brings up a menu with a Convert To sub-menu. The commands in the Convert To sub-menu are:
Raster to 2D Scatter
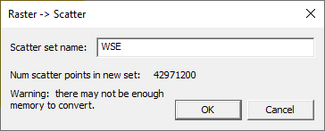
Selecting the command Convert To | 2D Scatter will bring up the Raster → Scatter dialog. The dialog shows the number of scatter point that will be generated in the new set and lets the user name the new scatter set. By default, the name of new scatter set will be the same as the raster set unless changed.
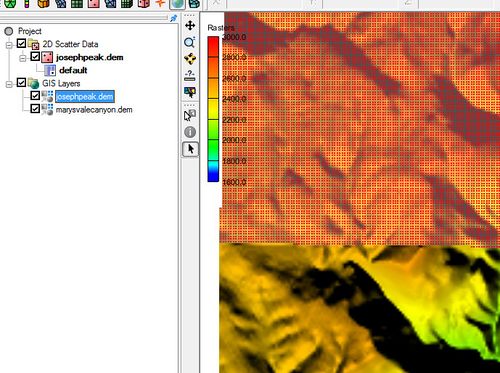
By default scatter points are shown in red unless changed in the Display Options dialog. Users may need to zoom in to see each point. Scatter points are visible in other views while the DEM is visible only in plan view.
Feature Contours
Activating this command will automatically generate contours which will appear as a new coverage under Map Data in the project explorer. By default, contour lines are shown in black unless the user changes the contour color in the Display Options dialog. The contour interval is found by creating 10 contours evenly spaced between the min and max dataset values.
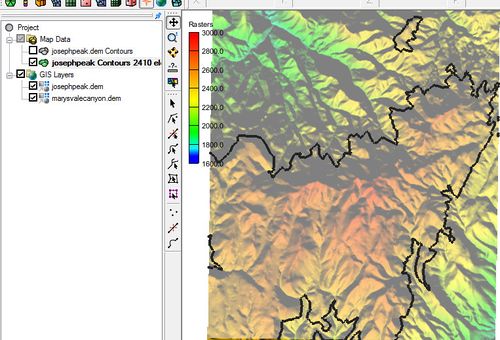
Feature Contours at Given Elevation
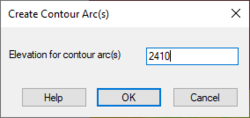
This command will bring up the Create Contour Arc dialog. In this dialog the user can specify an elevation to be used in generating the contours.
After entering an elevation and clicking OK, contours will be generated similar to those created with the Feature Contours command but using the specified elevation. Only contours at the specified elevation will be generated.
GIS Data Editing
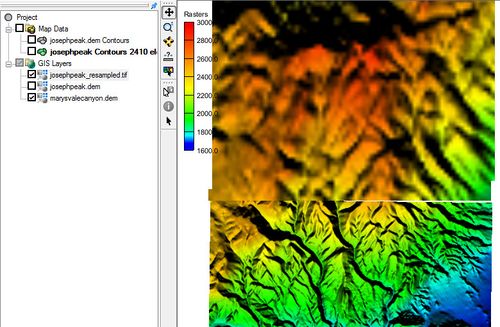
Resampled Raster
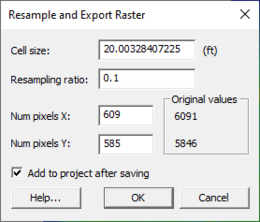
This command will bring up the Resample and Export Raster dialog. The dialog has the following options:
- Cell size – specify the size of each cell based on the Resampling ratio.
- Resampling ratio – specifies the resampling ratio. This is required for processing. Changing this field will change the other fields in the dialog automatically.
- Num pixels X – the number of pixels on the x axis that will be generated. The original number will be displayed to the right.
- Num pixels Y – the number of pixels on the y axis. The original number will be displayed to the right.
- Add to project after saving – toggling this option on will load the resampled file into GMS/SMS upon completion.
After completing the Resample and Export Raster dialog and clicking OK the Save As dialog will appear allowing the user to save a file with the resampled data.
Smoothed Raster
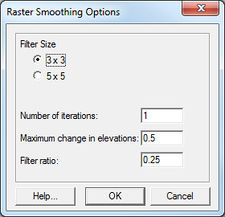
This command will bring up the Raster Smoothing Options dialog. The dialog has the following options:
- Filter Size – to smooth the raster, an N x N filter matrix is placed over each elevation point and a new elevation is computed by taking an inverse-distance weighted average of all elevations within the filter. The dimension of N can be specified as either 3x3 or 5x5, meaning that new elevations are computed from either the nearest 8 or 24 neighboring points.
- Number of iterations – specify the number of smoothing iterations. By default only one iteration is done, but sometimes several smoothing iterations are required to propagate a change in elevations across a large flat area.
- Maximum change in elevation – can be used to ensure that the integrity of the original elevations are maintained.
- Filter ratio – should be between 0-1, and is used to specify the weight of the central cell of the filtering matrix.
After completing th Raster Smoothing Options dialog and clicking OK the Save As dialog will appear allowing the user to save a file with the smoothed data.
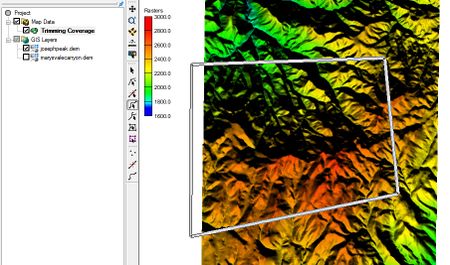
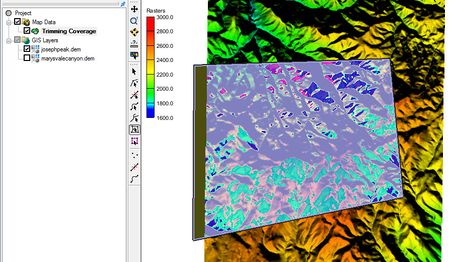
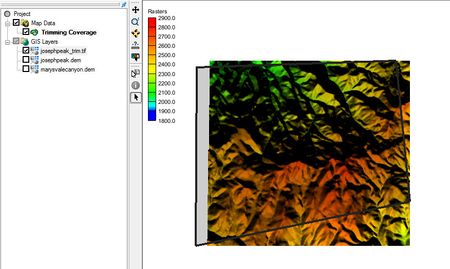
Trimmed Raster
Coverage polygons must be selected to define the trimming rectangle. If this is not done, then a warning dialog will appear as a reminder.
To create a trimmed raster:
- Select a coverage (or create a new coverage) in the Map module.
- Select the Create Arc tool and draw a closed set of arcs.
- While the arcs are selected, go to Feature Objects |Build Polygons.
- Use the Select Polygon tool to select the polygon just created.
- Right-click a DEM in the GIS data and select Convert To | Trimmed Raster.
- The Save As dialog will appear allowing the user to save a file with the trimmed data.
The final raster is trimmed along the rectangle enclosing the polygon. Trimmed rasters will also trim to the rectangle enclosing multiple selected polygons.
Merged Raster
Two or more DEM datasets can be merged together by doing the following:
- Select two or more DEM items in the project explorer by holding down the Shift key while selecting each item.
- Right-click on one of the selected DEMs and select Convert To | Merged Raster. This command is only available when multiple raster items have been selected.
- The Save As dialog will appear to save a file with the merged data.
The new merged DEM will be visible in the project explorer. When merging, the smallest cell size among the merging rasters is used.
Saving Raster Data
Raster data being converted can be save in any of the following formats:
|
|
Related Topics
GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||