GMS:UGrid Display Options
From XMS Wiki
| UGrid Module | |
|---|---|
 | |
| UGrid | |
| Creating and Editing | |
| Viewing Modes | |
| Converting to Other Data Types | |
| Exporting UGrids | |
| UGrid Interpolation | |
| More | |
| Display Options | |
| Tool Palette | |
| Cell Properties | |
| UGrid Commands | |
The display options of UGrid data that GMS displays on the screen can be controlled through the UGrid Data tab of the Display Options dialog. This dialog is opened by right-clicking on the File:UGridFolder.png "UGrid Data" item in the Project Explorer and selecting the Display Options command. It can also be accessed from the from the Display menu or the Display Options ![]() macro. The following table describes the display options available for the UGrid module.
macro. The following table describes the display options available for the UGrid module.
| Display Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Cell edges | The Cell edges item is used to display the edges of cells. The cells are drawn using the specified color. |
| Cell faces | This option fills the cells with the material color. |
| Cell centers | This option displays a point at the center of every cell. |
| Points | Points are the corners of cells, or simply 3D points not attached to cells. A symbol can be displayed at these locations. If Point contours are on, the color of the symbol will be determined by the data and the contour options. |
| Inactive points | Show points that correspond with an inactive dataset value. |
| UGrid shell | The UGrid shell item is used to display an edge for each of the edges on the exterior of the set of all cells (visible or invisible) which corresponds to a discontinuity in the UGrid exterior. This display option provides a helpful spatial context when displaying isosurfaces or cross sections. |
| Feature angle | The UGrid shell feature angle is used only when the UGrid Shell option is selected. This angle represents a threshold angle at which an edge of the shell will be displayed. If for example, an angle of 45 degrees is defined, any edge of the UGrid which divides two cell faces that are at an angle greater than 45 degrees to each other will not be displayed. |
| Point numbers | The Point numbers item is used to display the ID associated with each point next to the point. |
| Cell numbers | The cell numbers item is used to display the ID associated with each cell at the centroid of the cell. |
| Scalar values | The Scalar Values item is used to display the scalar values of the active dataset for each node next to the node. |
| Face contours | Most of the objects supported by GMS can be contoured by turning on the Contour Options in the Display Options dialog. When an object is contoured, the values associated with the active dataset for the object are used to generate the contours. |
| Point contours | The same Contour Options but applied to points. |
| Vectors | Vector arrows are displayed using the active vector dataset. |
| Isosurfaces | Isosurfaces are the 3D equivalent of a contour line. An isosurface is a surface of constant value extracted from a 3D dataset. |
| Clip | Creates a clipping widget that can be used to hide part of the UGrid. Clicking the Options button will bring up the UGrid Clip Settings dialog. The options include setting the widget to be a plane, which can be manipulated with the mouse in the Graphics Window, or to be a scalar or scalar range, which work like isosurfaces. Whole cells or partial cells can be clipped. |
File:Display3DUGrid.jpg
The Display Options dialog showing the 3D UGrid tab.
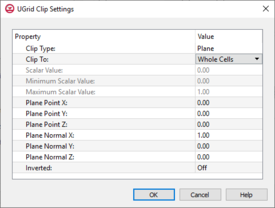
UGrid Clip Settings
| This contains information about functionality available starting at GMS version 10.2. The content may not apply to other versions. |
The Ugrid Clip Settings dialog allows setting parameters for clipping the UGrid display. The dialog has the following options:
- Clip Type – Can be set to "Plane", "Scalar", or "Scalar Range".
- "Plane" – Defines a clipping plane that cuts through the Ugrid. Allows the Edit Clip Plane tool to be used.
- "Scalar" – Defines the clipping area based on a single value.
- "Scalar Range" – Defines the clipping area based on a minimum and maximum value.
- Clip To – Set the clipping to use "Whole Cells" or "Partial Cells".
- Scalar Value – Creates a clipping region based on the set scalar value.
- Minimum Scalar Value – The lowers scalar value for the clipping range.
- Maximum Scalar Value – The highest scalar value for the clipping range.
- Plane Point X – Defines the location on the X axis of the the central clipping point.
- Plane Point Y – Defines the location on the Y axis of the the central clipping point.
- Plane Point Z – Defines the location on the Z axis of the the central clipping point.
- Plane Normal X – Determines the X value used in the plane calculation.
- Plane Normal Y – Determines the Y value used in the plane calculation.
- Plane Normal X – Determines the Z value used in the plane calculation.
- Inverted – The clipping area will be inverted when this option is set to "On".
| [hide]GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||