GMS:Cross Sections: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
{{Navbox GMS}} | {{Navbox GMS}} | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Solids|C]] | ||
Revision as of 19:55, 14 April 2014
Cross sections—also referred to as fence diagrams—are flat surfaces used to visualize the subsurface. GMS has different types of cross section objects:
- Solid Cross Sections
- Borehole Cross Sections
- 3D Grid Cross Sections
- 3D Mesh Cross Sections
Contents
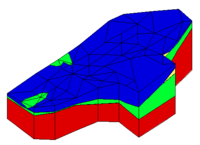
Solid Cross Sections
Solid cross sections can be created by "slicing" through a set of solids using the Create Cross Section tool. This can be done at any angle and the slicing can be done using a multi-segment polyline. Solid cross sections can be converted to a conceptual model. This is useful if you have a solid model of an embankment that you want to analyze using UTEXAS.
Borehole Cross Sections
Borehole cross sections are quite different than solid, 3D grid, and 3D mesh cross sections. See the page on Borehole Cross Sections.
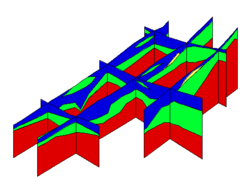
3D Grid Cross Sections
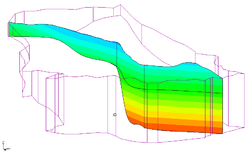
3D grid cross sections are created similar to solid cross sections. Data sets are automatically interpolated from the 3D grid to the cross sections and contours can be displayed on the cross sections.
3D Mesh Cross Sections
3D mesh cross sections are created similar to solid cross sections. Data sets are automatically interpolated from the 3D mesh to the cross sections and contours can be displayed on the cross sections.
Cross Section Options
When cross sections are created from a mesh or a grid, values of the active scalar and vector datasets are interpolated to the cross sections. Whenever a new dataset is chosen as the active dataset for the mesh, the data values are re-interpolated to the cross sections.
The properties of all cross section data that GMS displays on the screen can be controlled through the Cross Sections tab of the Display Options dialog. This dialog is opened by right-clicking on the File:CrossSectionFolder.GIF Cross Sections entry in the Project Explorer and selecting the Display Options command. It can also be accessed from the from the Display menu or the File:Dispopts.gif Display Options macro. The following table describes the display options available for the cross sections.
| Display Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Interior edge removal | By default, the lines representing the intersection of the cross section with the faces of the cells or elements are displayed on the cross section. These lines can be hidden by selecting the Interior edge removal option. |
| Cross section edges | If this option is on, the lines that make up the cross section are displayed. |
| Cross section faces | If this option is on, then the cross section will be displayed as a set of filled polygons. |
| Contours | If the Contours item is selected, contours are displayed on the cross sections using the active scalar dataset. |
| Vectors | If the Vectors item is selected, vectors are displayed on the cross sections using the active vector dataset when the cross sections are displayed. |
| Flow trace | If the Flow trace item is selected, a flow trace image is texture mapped to each cross section using the active vector dataset when flow trace option is used with the Animation wizard. |
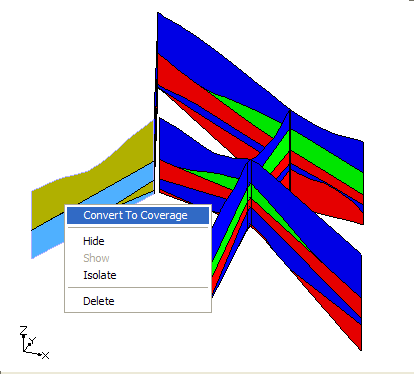
Convert Cross Section to Coverage
Cross sections can be converted to coverages by right clicking on the coverage and selecting the Convert To Coverage command. The outer boundary of each material zone is converted into arcs and polygons are automatically built.
When this command is executed the user is prompted to select where the new coverage(s) should be created in the project explorer. If the user wishes to have the materials from the cross section assigned to the appropriate polygons in the coverage then the user should select an appropriate conceptual model. The conceptual model must support the assignment of materials to polygons (MODFLOW, SEEP2D/UTEXAS, FEMWATER).
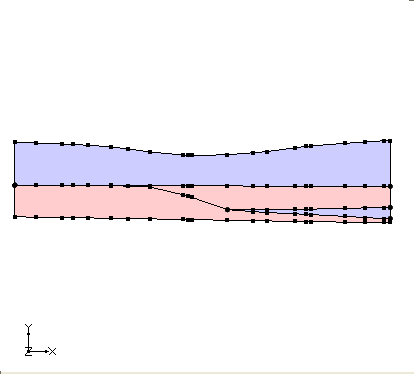
Coordinate Transformation
The coordinates of points from the cross section are transformed into the XY plane. The x coordinates are calculated relative to zero where zero is defined as one end of the cross section. Currently the end of the cross section that is designated as zero is the end with the minimum Y coordinate. If the cross section is horizontal then the end of the cross section with the minimum X is used.
The x coordinates are calculated by finding the distance of the point from the end of the cross section that was set as zero. The Y coordinates are calculated by subtracting the minimum z value of the cross section from the z value of the point (y = z - z_min).
Limitations
- The cross section must be vertical.
- The cross section must be a single panel (when viewing the cross section in plan view it appears as a single line segment).
| GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||