SMS:FESWMS Point Attributes Dialog: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* ''None'' | * ''None'' | ||
* ''Boundary Conditions'' – Options button opens the ''FESWMS Nodal Boundary Conditions'' dialog. | * ''Boundary Conditions'' – Options button opens the ''FESWMS Nodal Boundary Conditions'' dialog. | ||
** ''FESWMS BC Nodes'' – FESWMS allows specifying boundary conditions on a nodal basis although it is generally preferable to use boundary conditions on [[SMS:FESWMS BC Nodestrings|nodestrings]]. Please refer to the FESWMS manual for information on the nodal boundary condition options. | |||
* ''FESWMS BC Nodes'' – FESWMS allows specifying boundary conditions on a nodal basis although it is generally preferable to use boundary conditions on [[SMS:FESWMS BC Nodestrings|nodestrings]]. Please refer to the FESWMS manual for information on the nodal boundary condition options. | |||
== Options Frame == | == Options Frame == | ||
Revision as of 15:30, 5 September 2017
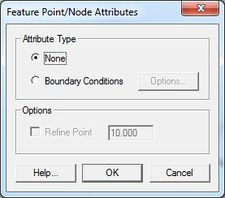
The FESWMS Feature Point/Node Attributes dialog is used to set the attributes for a feature point / refine point represented by a feature point in a 2D Mesh model coverage. Attributes that can be specified for each feature point / refine point include:
Attribute Type Frame
- None
- Boundary Conditions – Options button opens the FESWMS Nodal Boundary Conditions dialog.
- FESWMS BC Nodes – FESWMS allows specifying boundary conditions on a nodal basis although it is generally preferable to use boundary conditions on nodestrings. Please refer to the FESWMS manual for information on the nodal boundary condition options.
Options Frame
- Refine point (checked = on)
- Element size – Specify the nodal spacing, or element edge length in the vicinity of the refine point. Refine points are only used if the mesh is generated using the Paving or Scalar Paving Density mesh generation methods.
Related Topics
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||