SMS:Synthetic Storm Coverage
Background
When simulating an actual storm (hindcast), the storm information such as the track locations, central pressures, radius information, speeds, and Holland B values can come from an analysis on data collected during the storm. However, if the simulation is intended for design analysis, it may be better to not choose a storm that has happened but a storm which may happen. Often several configurations for storms would be analyzed to see the results of each. The synthetic storm coverage and associated generator executable provide a mechanism for creating a PBL coverage (trop file) based upon user specified parameters.
The first step is to decide upon a track path or multiple paths to simulate. For multiple paths, one option is to create a single track and use the perturbation tools in SMS to generate similar tracks by using offsets and modifications of central pressures, etc.
Once the track locations have been defined, define the associated data for the track (central pressures, Holland B, storm radius, etc.). The US Army Engineer Research and Development Center has developed a utility that creates a full PBL input trop file from a small set of user defined parameters.
Inputs
The following parameters are used to fill in the track data:
- Storm name
- Storm number
- Starting date/time (nearest hour)
- Forward speed in knots
- Far field atmospheric pressure in millibars
- Initial central pressure in millibars
- Minimum central pressure in millibars
- Landfall central pressure in millibars
- Initial storm radius in miles
- Landfall storm radius in miles
- Initial Holland B value
In addition to these parameters the locations where minimum central pressure exists along the track and the landfall location are specified.
Methodology
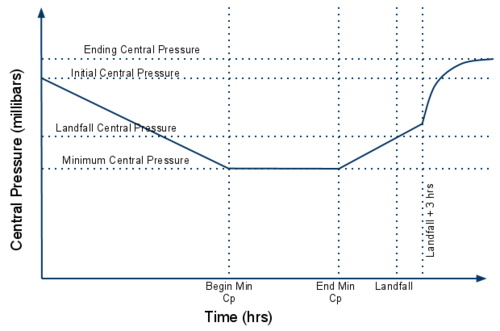
ERDC has developed curves to represent general behavior of storms. These curves are a simplistic approach and should be used with caution. When in doubt if providing appropriate wind fields, consult a meteorologist.
Sample curves for central pressure, Holland B, and storm radius can be seen below. Some of the values shown are user supplied and others are determined by the synthetic storm generator (like ending radius).
User Interface
Synthetic storms are created in SMS using the "synthetic storm coverage." This coverage is in the folder "\Models\Wind" when accessing it from the New Coverage dialog or changing the type of an existing coverage.
The coverage must contain a single track made up of multiple arcs. The locations of starting minimum central pressure, ending minimum central pressure, and landfall are specified on arc end nodes. Change the type of an arc node by selecting the node, right-clicking, and choosing the desired type from the Type submenu. When changing a node to any type except for generic and a node of that type already exists, the existing node will be changed to a generic node. There can only be one node of each "non-generic" type.
The parameters for the storm generator are stored with the coverage and can be accessed by right-clicking on the coverage and choosing Properties to open the Synthetic storm coverage attributes dialog.
When the track has been defined, the node types specified, and the properties assigned to the coverage the PBL coverage can be created. To create the PBL coverage, right-click on the coverage and choose Create PBL coverage. This will run the ERDC storm generator utility and read the resulting data into a new PBL coverage.
Related Topics
| [hide] SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||