WMS:Storage Capacity Curves: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
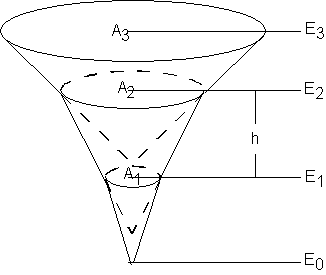
In all three cases a relationship between elevation and volume will be computed. For the volume vs. elevation option this is explicitly defined. If area vs. elevation is specified, then a corresponding volume for each elevation is computed using the conic method. The conic method is illustrated below. | In all three cases a relationship between elevation and volume will be computed. For the volume vs. elevation option this is explicitly defined. If area vs. elevation is specified, then a corresponding volume for each elevation is computed using the conic method. The conic method is illustrated below. | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Storage Capacity Curves.png]] | ||
The volume between incremental areas < | The volume between incremental areas ''A<sub>1</sub>'' and ''A<sub>2</sub>'' is computed using the following equation: | ||
:<math>\Delta V 12 = \frac {h}{3}(A_1 + A_2 + \sqrt {A_1 A_2}) </math> | :<math>\Delta V 12 = \frac {h}{3}(A_1 + A_2 + \sqrt {A_1 A_2}) </math> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
where: | where: | ||
:''Δ V 12'' – The volume between areas ''A<sub>1</sub>'' and ''A<sub>2</sub>''. | |||
< | :''A<sub>i</sub>'' – Surface area ''i''. | ||
:''h'' – Vertical distance ''(E<sub>2</sub>-E<sub>1</sub>)'' between surface areas ''A<sub>1</sub>'' and ''A<sub>2</sub>''. | |||
< | :''E<sub>i</sub>'' – Elevation of surface area ''i''. | ||
The same equation is used to compute the volume between each adjacent set of surface areas, with the bottom area assumed to be 0. A TIN can be used to automatically create and store for use in the detention basin calculator the elevation-volume relationship. | The same equation is used to compute the volume between each adjacent set of surface areas, with the bottom area assumed to be 0. A TIN can be used to automatically create and store for use in the detention basin calculator the elevation-volume relationship. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{WMSMain}} | {{WMSMain}} | ||
[[Category:Hydrologic Modeling|S]] | |||
[[Category:Equations|Storage]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:15, 14 December 2016
There are three different methods for defining storage capacity: volume vs. elevation, area vs. elevation, and known geometry.
In all three cases a relationship between elevation and volume will be computed. For the volume vs. elevation option this is explicitly defined. If area vs. elevation is specified, then a corresponding volume for each elevation is computed using the conic method. The conic method is illustrated below.
The volume between incremental areas A1 and A2 is computed using the following equation:
where:
- Δ V 12 – The volume between areas A1 and A2.
- Ai – Surface area i.
- h – Vertical distance (E2-E1) between surface areas A1 and A2.
- Ei – Elevation of surface area i.
The same equation is used to compute the volume between each adjacent set of surface areas, with the bottom area assumed to be 0. A TIN can be used to automatically create and store for use in the detention basin calculator the elevation-volume relationship.
If the basin geometry option is chosen then an elevation vs. volume relationship is computed directly from the geometry defined for the basin.
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||