GMS:Display Menu: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
; [[GMS:Display Options|Display Options]] : Opens the ''Display Options'' dialog. | ; [[GMS:Display Options|Display Options]] : Opens the ''Display Options'' dialog. | ||
; [[GMS:Contour Options|Contour Options]] : Opens the ''Contour Options'' dialog. | ; [[GMS:Contour Options|Contour Options]] : Opens the ''Contour Options'' dialog. | ||
; Refresh Display : Clears and redraws the Graphics Window. | ; <!--Refresh Display : Clears and redraws the Graphics Window.--> | ||
; Redraw Display : | ; Redraw Display : Clears and redraws the Graphics Window. | ||
; Frame Image : Adjusts the view so that all currently visible objects fit in the [[GMS:The_GMS_Window#Graphics_Window|Graphics Window]]. | ; Frame Image : Adjusts the view so that all currently visible objects fit in the [[GMS:The_GMS_Window#Graphics_Window|Graphics Window]]. | ||
; {{hide in print|Zoom To Selections}} : {{hide in print|Frames the window around whatever objects are currently selected.}} | ; {{hide in print|Zoom To Selections}} : {{hide in print|Frames the window around whatever objects are currently selected.}} | ||
; Map Locator : Used to navigate to any place on Earth. The Graphics Window is positioned to the location shown in the Map Locator and the display projection is set to a global projection if not already in one. | ; Map Locator : Used to navigate to any place on Earth. The Graphics Window is positioned to the location shown in the ''Map Locator'' and the display projection is set to a global projection if not already in one. | ||
{{Anchor|Projection}} | {{Anchor|Projection}} | ||
; [[Projections|Display Projection...]] : Sets the projection used for the display. | ; [[Projections|Display Projection...]] : Sets the projection used for the display. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
<blockquote style="margin-top:0px; margin-bottom:0px;"> | <blockquote style="margin-top:0px; margin-bottom:0px;"> | ||
; Hide [[File:GMS Hide Macro.svg|16 px]] : Causes the selected objects to become invisible. | ; Hide [[File:GMS Hide Macro.svg|16 px]] : Causes the selected objects to become invisible. | ||
; Show [[File:GMS Show | ; Show [[File:GMS Show Macro.svg|16 px]] : Causes hidden objects to become visible. | ||
; Isolate [[File:GMS Isolate | ; Isolate [[File:GMS Isolate Macro.svg|16 px]] : Hides all but the selected objects. | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
; {{anchor|view|views}}''View'' : A submenu with commands for altering the view in the Graphics Window. | ; {{anchor|view|views}}''View'' : A submenu with commands for altering the view in the Graphics Window. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
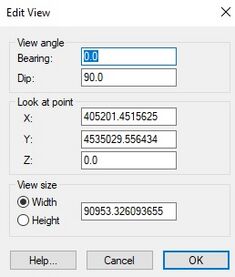
; View Angle : Opens the ''Edit View'' dialog. In this dialog the bearing and dip angles can be explicitly defined. The objects in the [[GMS:The GMS Window|Graphics Window]] can be rotated and viewed in three dimensions. Two angles, bearing and dip, are used to rotate the view. The bearing and dip values correspond to a rotation about the z and x axes. The bearing affects the horizontal angle (rotating the object in the xy plane), and the dip changes the vertical angle (shifting the viewing angle on the object to a higher or lower perspective). The object cannot be tilted sideways. Using only two viewing angles rather than three limits the viewing angles, but it is simpler. Alternatively, the viewing angles can be manipulated interactively with the [[GMS:Toolbars|'''Rotate''']] tool. | ; View Angle : Opens the ''Edit View'' dialog. In this dialog the bearing and dip angles can be explicitly defined. The objects in the [[GMS:The GMS Window|Graphics Window]] can be rotated and viewed in three dimensions. Two angles, bearing and dip, are used to rotate the view. The bearing and dip values correspond to a rotation about the z and x axes. The bearing affects the horizontal angle (rotating the object in the xy plane), and the dip changes the vertical angle (shifting the viewing angle on the object to a higher or lower perspective). The object cannot be tilted sideways. Using only two viewing angles rather than three limits the viewing angles, but it is simpler. Alternatively, the viewing angles can be manipulated interactively with the [[GMS:Toolbars|'''Rotate''']] tool. | ||
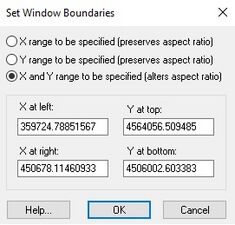
; Window Bounds : The region of the real world coordinate system that is mapped to the [[GMS:The GMS Window|Graphics Window]] can be altered using the [[GMS:Toolbars|'''Pan''']] and [[GMS:Toolbars|'''Zoom''']] tools. It is also possible to precisely control the visible region by selecting the '''Set Window Bounds''' command from the ''View'' menu. This command brings up the ''Set Window Boundaries'' dialog. If the ''X range to be specified (preserves aspect ratio)'' option is selected, the x coordinate at the left and right and the y coordinate at the bottom of the Graphics Window are specified. The y coordinate at the top of the Graphics Window is not specified in order to maintain the aspect ratio. If the ''Y range to be specified (preserves aspect ratio)'' option is selected, the y coordinate at the top and bottom and the x coordinate at the left of the Graphics Window are specified. The x coordinate at the right of the Graphics Window is not specified in order to maintain the aspect ratio. If the ''X and Y range to be specified (alters aspect ratio)'' option is selected, the x coordinate at the right and left and y coordinate at the top and bottom of the Graphics Window are specified. Since all four coordinates are specified, the aspect ratio of the scene may be altered. | ; Window Bounds : The region of the real world coordinate system that is mapped to the [[GMS:The GMS Window|Graphics Window]] can be altered using the [[GMS:Toolbars|'''Pan''']] and [[GMS:Toolbars|'''Zoom''']] tools. It is also possible to precisely control the visible region by selecting the '''Set Window Bounds''' command from the ''View'' menu. This command brings up the ''Set Window Boundaries'' dialog. If the ''X range to be specified (preserves aspect ratio)'' option is selected, the x coordinate at the left and right and the y coordinate at the bottom of the Graphics Window are specified. The y coordinate at the top of the Graphics Window is not specified in order to maintain the aspect ratio. If the ''Y range to be specified (preserves aspect ratio)'' option is selected, the y coordinate at the top and bottom and the x coordinate at the left of the Graphics Window are specified. The x coordinate at the right of the Graphics Window is not specified in order to maintain the aspect ratio. If the ''X and Y range to be specified (alters aspect ratio)'' option is selected, the x coordinate at the right and left and y coordinate at the top and bottom of the Graphics Window are specified. Since all four coordinates are specified, the aspect ratio of the scene may be altered. | ||
; Plan View [[ | ; Plan View [[File:Plan View Macro.svg|16 px]] : Changes the viewing angle to look down the z-axis with the x-axis horizontal and the y-axis vertical. | ||
; Front View [[ | ; Front View [[File:Front View Macro.svg|16 px]] : Changes the viewing angle to look down the y-axis with the x-axis horizontal and the z-axis vertical. | ||
; Side View [[ | ; Side View [[File:Side View Macro.svg|16 px]] : Changes the viewing angle to look down the x-axis with the y-axis horizontal and the z-axis vertical. | ||
; Oblique View [[ | ; Oblique View [[File:Oblique View Macro.svg|16 px]] : Changes the viewing angle to look at the model at an angle of 45<sup>o</sup> to each axis. | ||
; Previous : Restores the [[GMS:The GMS Window|Graphics Window]] viewing parameters as they were before the last viewing command was issued (rotate, zoom, pan, etc.). Views are automatically saved in a list so continued use of this command will continue to restore previous views. | ; Previous : Restores the [[GMS:The GMS Window|Graphics Window]] viewing parameters as they were before the last viewing command was issued (rotate, zoom, pan, etc.). Views are automatically saved in a list so continued use of this command will continue to restore previous views. | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:21, 25 March 2022
The Display menu is one of the standard menus and is available in all of the modules. The commands in the Display menu are as follows:
- Display Options
- Opens the Display Options dialog.
- Contour Options
- Opens the Contour Options dialog.
- Redraw Display
- Clears and redraws the Graphics Window.
- Frame Image
- Adjusts the view so that all currently visible objects fit in the Graphics Window.
- Map Locator
- Used to navigate to any place on Earth. The Graphics Window is positioned to the location shown in the Map Locator and the display projection is set to a global projection if not already in one.
- Display Projection...
- Sets the projection used for the display.
- Visibility
- A submenu for the Hide, Show and Isolate commands. These commands only act on the graphics objects associated with the current selection tool. If the current tool is not a selection tool, these commands are not available.
- View
- A submenu with commands for altering the view in the Graphics Window.
- View Angle
- Opens the Edit View dialog. In this dialog the bearing and dip angles can be explicitly defined. The objects in the Graphics Window can be rotated and viewed in three dimensions. Two angles, bearing and dip, are used to rotate the view. The bearing and dip values correspond to a rotation about the z and x axes. The bearing affects the horizontal angle (rotating the object in the xy plane), and the dip changes the vertical angle (shifting the viewing angle on the object to a higher or lower perspective). The object cannot be tilted sideways. Using only two viewing angles rather than three limits the viewing angles, but it is simpler. Alternatively, the viewing angles can be manipulated interactively with the Rotate tool.
- Window Bounds
- The region of the real world coordinate system that is mapped to the Graphics Window can be altered using the Pan and Zoom tools. It is also possible to precisely control the visible region by selecting the Set Window Bounds command from the View menu. This command brings up the Set Window Boundaries dialog. If the X range to be specified (preserves aspect ratio) option is selected, the x coordinate at the left and right and the y coordinate at the bottom of the Graphics Window are specified. The y coordinate at the top of the Graphics Window is not specified in order to maintain the aspect ratio. If the Y range to be specified (preserves aspect ratio) option is selected, the y coordinate at the top and bottom and the x coordinate at the left of the Graphics Window are specified. The x coordinate at the right of the Graphics Window is not specified in order to maintain the aspect ratio. If the X and Y range to be specified (alters aspect ratio) option is selected, the x coordinate at the right and left and y coordinate at the top and bottom of the Graphics Window are specified. Since all four coordinates are specified, the aspect ratio of the scene may be altered.
- Plan View
- Changes the viewing angle to look down the z-axis with the x-axis horizontal and the y-axis vertical.
- Front View
- Changes the viewing angle to look down the y-axis with the x-axis horizontal and the z-axis vertical.
- Side View
- Changes the viewing angle to look down the x-axis with the y-axis horizontal and the z-axis vertical.
- Oblique View
- Changes the viewing angle to look at the model at an angle of 45o to each axis.
- Previous
- Restores the Graphics Window viewing parameters as they were before the last viewing command was issued (rotate, zoom, pan, etc.). Views are automatically saved in a list so continued use of this command will continue to restore previous views.
- General/Ortho Mode
- A command is provided in the Display menu for switching between the orthogonal and general viewing modes. The orthogonal mode is only available with 3D grids.
- Convert To Cad
- Exports any visible geometric data to a CAD file. This command can also be found by right-clicking in the empty space in the Project Explorer.
- Toolbars
- The Toolbars submenu allows hiding and showing the listed toolbars.
- Plot Wizard
- Brings up the Plot Wizard dialog.
- Animate
- The Animate command launches the Animation Wizard.
- Play Animation
- The Play Animation command launches an AVI player that allows browsing for an AVI file and play the animation.
Related Topics
GMS – Groundwater Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 2D Grid • 2D Mesh • 2D Scatter Point • 3D Grid • 3D Mesh • 3D Scatter Point • Boreholes • GIS • Map • Solid • TINs • UGrids | |
| Models: | FEFLOW • FEMWATER • HydroGeoSphere • MODAEM • MODFLOW • MODPATH • mod-PATH3DU • MT3DMS • MT3D-USGS • PEST • PHT3D • RT3D • SEAM3D • SEAWAT • SEEP2D • T-PROGS • ZONEBUDGET | |
| Aquaveo | ||