WMS:HEC-HMS Frequency Storm: Difference between revisions
From XMS Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
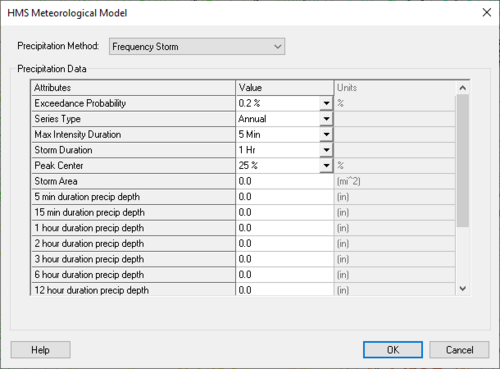
"The frequency storm method can be used to create a balanced, synthetic storm with a known exceedance probability. Automatic adjustments for storm area and series type are based on the exceedance probability. Depth-duration data are usually obtained from publications such as TP-40 (National Weather Service, 1961)." (HEC-HMS User's Manual) The options for defining a frequency storm are shown below: | "The frequency storm method can be used to create a balanced, synthetic storm with a known exceedance probability. Automatic adjustments for storm area and series type are based on the exceedance probability. Depth-duration data are usually obtained from publications such as TP-40 (National Weather Service, 1961)." (HEC-HMS User's Manual) The options for defining a frequency storm are shown below: | ||
[[Image:HMSFrequencyStorm1.jpg|thumb|none|left|500 px|''HMS Meteorological Model'' dialog]] | [[Image:HMSFrequencyStorm1.jpg|thumb|none|left|500 px|''HMS Meteorological Model'' dialog for the "Frequency Storm" method.]] | ||
Follow the following steps (from the HEC-HMS User's Manual) to set up a frequency storm: | Follow the following steps (from the HEC-HMS User's Manual) to set up a frequency storm: | ||
Revision as of 17:29, 4 September 2014
"The frequency storm method can be used to create a balanced, synthetic storm with a known exceedance probability. Automatic adjustments for storm area and series type are based on the exceedance probability. Depth-duration data are usually obtained from publications such as TP-40 (National Weather Service, 1961)." (HEC-HMS User's Manual) The options for defining a frequency storm are shown below:
Follow the following steps (from the HEC-HMS User's Manual) to set up a frequency storm:
- Select a storm exceedance probability from the list (Exceedance probability = (1 / Return Period) * 100%).
- Set the series type for the desired output.
- Select the maximum intensity duration and the total storm duration.
- Enter the precipitation depths corresponding to the selected exceedance probability for the durations between the maximum intensity and storm durations.
- Select the percentage of the storm duration that occurs before the peak intensity.
- Enter the storm area. This is equal to the total drainage area at the point where the exceedance probability will be inferred for the computed flow.
Related Topics:
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||