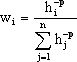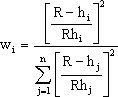WMS:Shepard's Method: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The simplest form of inverse distance weighted interpolation is sometimes called "Shepard's method" (Shepard 1968). The equation used is as follows: | The simplest form of inverse distance weighted interpolation is sometimes called "Shepard's method" (Shepard 1968). The equation used is as follows: | ||
:[[Image:WMSidw_eq1.jpg]] | |||
where n is the number of scatter points in the set, fi are the prescribed function values at the scatter points (e.g. the dataset values), and wi are the weight functions assigned to each scatter point. The classical form of the weight function is: | |||
:[[Image:WMSidw_eq2.jpg]] | |||
where p is an arbitrary positive real number called the power parameter (typically, p=2) and h<sub>i</sub> is the distance from the scatter point to the interpolation point or | |||
where p is an arbitrary positive real number called the power parameter (typically, p=2) and | |||
:[[Image:WMSidw_eq3.jpg]] | |||
where (x,y) are the coordinates of the interpolation point and ( | where (x,y) are the coordinates of the interpolation point and (x<sub>i</sub>,y<sub>i</sub>) are the coordinates of each scatter point. The weight function varies from a value of unity at the scatter point to a value approaching zero as the distance from the scatter point increases. The weight functions are normalized so that the weights sum to unity. | ||
Although the weight function shown above is the classical form of the weight function in inverse distance weighted interpolation, the following equation is used in WMS: | Although the weight function shown above is the classical form of the weight function in inverse distance weighted interpolation, the following equation is used in WMS: | ||
:[[Image:WMSidw_eq4.jpg]] | |||
where h<sub>i</sub> is the distance from the interpolation point to scatter point i, R is the distance from the interpolation point to the most distant scatter point, and n is the total number of scatter points. This equation has been found to give superior results to the classical equation (Franke & Nielson, 1980). | |||
where | |||
The weight function is a function of Euclidean distance and is radially symmetric about each scatter point. As a result, the interpolating surface is somewhat symmetric about each point and tends toward the mean value of the scatter points between the scatter points. Shepard's method has been used extensively because of its simplicity. | The weight function is a function of Euclidean distance and is radially symmetric about each scatter point. As a result, the interpolating surface is somewhat symmetric about each point and tends toward the mean value of the scatter points between the scatter points. Shepard's method has been used extensively because of its simplicity. | ||
3D Interpolation | ==3D Interpolation== | ||
The 3D equations for Shepard's method are identical to the 2D equations except that the distances are computed using: | The 3D equations for Shepard's method are identical to the 2D equations except that the distances are computed using: | ||
:[[Image:WMSIdw_eq1.jpg]] | |||
where (x,y,z) are the coordinates of the interpolation point and (x<sub>i</sub>,y<sub>i</sub>,z<sub>i</sub>) are the coordinates of each scatter point. | |||
where (x,y,z) are the coordinates of the interpolation point and ( | |||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
| Line 46: | Line 36: | ||
[[Category:Interpolation]] | [[Category:Interpolation]] | ||
[[Category:Equations| | [[Category:Equations|ShepardsM]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:07, 31 May 2018
The simplest form of inverse distance weighted interpolation is sometimes called "Shepard's method" (Shepard 1968). The equation used is as follows:
where n is the number of scatter points in the set, fi are the prescribed function values at the scatter points (e.g. the dataset values), and wi are the weight functions assigned to each scatter point. The classical form of the weight function is:
where p is an arbitrary positive real number called the power parameter (typically, p=2) and hi is the distance from the scatter point to the interpolation point or
where (x,y) are the coordinates of the interpolation point and (xi,yi) are the coordinates of each scatter point. The weight function varies from a value of unity at the scatter point to a value approaching zero as the distance from the scatter point increases. The weight functions are normalized so that the weights sum to unity.
Although the weight function shown above is the classical form of the weight function in inverse distance weighted interpolation, the following equation is used in WMS:
where hi is the distance from the interpolation point to scatter point i, R is the distance from the interpolation point to the most distant scatter point, and n is the total number of scatter points. This equation has been found to give superior results to the classical equation (Franke & Nielson, 1980).
The weight function is a function of Euclidean distance and is radially symmetric about each scatter point. As a result, the interpolating surface is somewhat symmetric about each point and tends toward the mean value of the scatter points between the scatter points. Shepard's method has been used extensively because of its simplicity.
3D Interpolation
The 3D equations for Shepard's method are identical to the 2D equations except that the distances are computed using:
where (x,y,z) are the coordinates of the interpolation point and (xi,yi,zi) are the coordinates of each scatter point.
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||