WMS:Storage Capacity Curves: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
where: | where: | ||
: | :''Δ V 12'' – The volume between areas ''A<sub>1</sub>'' and ''A<sub>2</sub>''. | ||
:< | :''A<sub>i</sub>'' – Surface area ''i''. | ||
: | :''h'' – Vertical distance ''(E<sub>2</sub>-E<sub>1</sub>)'' between surface areas ''A<sub>1</sub>'' and ''A<sub>2</sub>''. | ||
:< | :''E<sub>i</sub>'' – Elevation of surface area ''i''. | ||
The same equation is used to compute the volume between each adjacent set of surface areas, with the bottom area assumed to be 0. A TIN can be used to automatically create and store for use in the detention basin calculator the elevation-volume relationship. | The same equation is used to compute the volume between each adjacent set of surface areas, with the bottom area assumed to be 0. A TIN can be used to automatically create and store for use in the detention basin calculator the elevation-volume relationship. | ||
Revision as of 16:15, 14 December 2016
There are three different methods for defining storage capacity: volume vs. elevation, area vs. elevation, and known geometry.
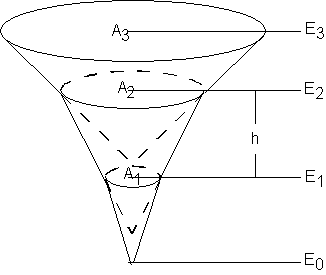
In all three cases a relationship between elevation and volume will be computed. For the volume vs. elevation option this is explicitly defined. If area vs. elevation is specified, then a corresponding volume for each elevation is computed using the conic method. The conic method is illustrated below.
The volume between incremental areas and is computed using the following equation:
where:
- Δ V 12 – The volume between areas A1 and A2.
- Ai – Surface area i.
- h – Vertical distance (E2-E1) between surface areas A1 and A2.
- Ei – Elevation of surface area i.
The same equation is used to compute the volume between each adjacent set of surface areas, with the bottom area assumed to be 0. A TIN can be used to automatically create and store for use in the detention basin calculator the elevation-volume relationship.
If the basin geometry option is chosen then an elevation vs. volume relationship is computed directly from the geometry defined for the basin.
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||