WMS:HEC-HMS Defining the Meteorological Model
Define meteorologic data for the model by selecting the Meteorologic Parameters menu item from the HEC-HMS menu.
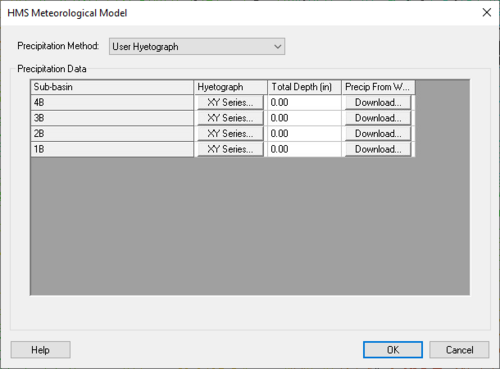
Selecting this menu item will bring up the HMS Meteorological Model dialog. This dialog is used to assign precipitation data to all the basins in the model.
The same precipitation method must be assigned to all the basins in the HMS model. The precipitation method choosen should be based on the type of analysis to be run. If having rainfall gage data for the watershed, use the user hyetograph or the user gage weighting method. If wanting to create a synthetic storm with a known exceedance probability, select the frequency storm method. If wanting to model a standard project storm, select the standard project storm or the SCS hypothetical storm method. Only use the No Precipitation option if the HMS model does not have any basins. See the topics below for more detailed information about the HMS Meteorological Model dialog.
HEC-HMS User Hyetograph
The User Hyetograph method can be used if a hyetograph is known for each sub-basin of the watershed being modeled. Get this hyetograph from recorded data or from any other method. Enter the same or different hyetographs for each basin, but each basin can only have a single hyetograph. Define the hyetograph by clicking on the XY Series button in the HMS Meteorological Model dialog shown below, and define the hyetograph in the XY series editor:
Standard Project Storm
Frequency Storm
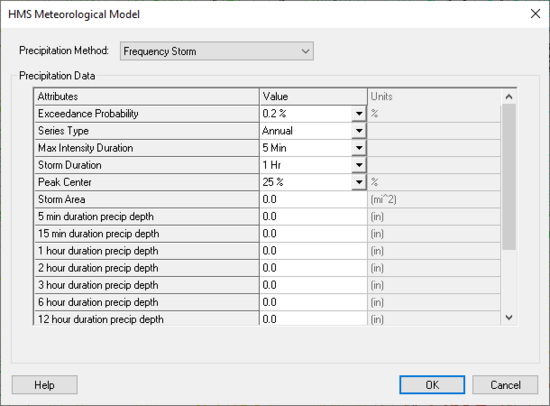
"The frequency storm method can be used to create a balanced, synthetic storm with a known exceedance probability. Automatic adjustments for storm area and series type are based on the exceedance probability. Depth-duration data are usually obtained from publications such as TP-40 (National Weather Service, 1961)." (HEC-HMS User's Manual) The options for defining a frequency storm are shown below:
Follow the following steps (from the HEC-HMS User's Manual) to set up a frequency storm:
- Select a storm exceedance probability from the list (Exceedance probability = (1 / Return Period) * 100%).
- Set the series type for the desired output.
- Select the maximum intensity duration and the total storm duration.
- Enter the precipitation depths corresponding to the selected exceedance probability for the durations between the maximum intensity and storm durations.
- Select the percentage of the storm duration that occurs before the peak intensity.
- Enter the storm area. This is equal to the total drainage area at the point where the exceedance probability will be inferred for the computed flow.
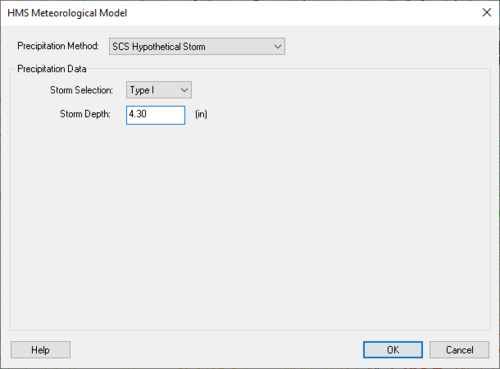
SCS Hypothetical Storm
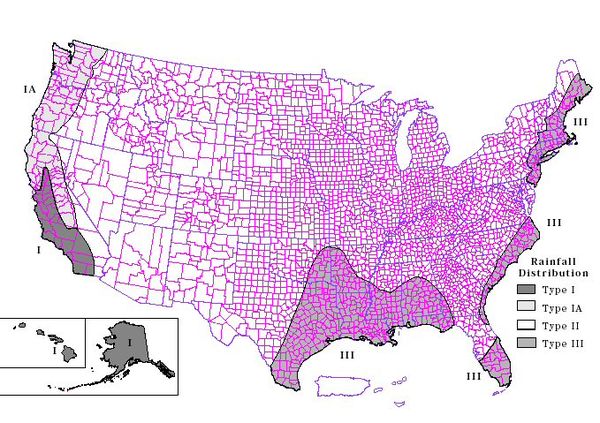
"The SCS hypothetical storm method implements the four synthetic rainfall distributions developed by the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) from observed precipitation events. Each distribution contains rainfall intensities arranged to maximize the peak runoff for a given total storm depth. The four distributions correspond to different geographic regions (Soil Conservation Service, 1986)." (HEC-HMS User's Manual)
The only data requirements for this method are the storm type and the storm depth. The storm depth can be determined for different areas of the United States by looking at the following map (Figure B-2 from Appendix B of the TR-55 manual).
This method does not perform any depth-area reductions. The HMS Meteorological Model dialog for this method is shown below:
Related Topics:
- Frequency Storm
- Gages
- Convert Grids (NEXRAD Radar rainfall grids)
- SCS Hypothetical Storm
- Standard Project Storm
- Meteorological Options
- HMS Overview
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||