WMS:Stochastic Simulation Parameters: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[WMS:Floodplain | [[WMS:Delineate Floodplain|Previous Step in Stochastic Modeling]] | ||
[[WMS:Linking Models|Next Step in Stochastic Modeling]] | [[WMS:Linking Models|Next Step in Stochastic Modeling]] | ||
Revision as of 16:15, 8 December 2016
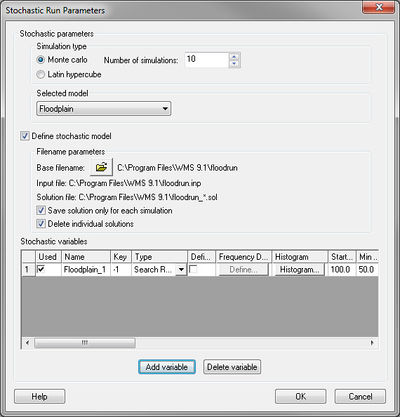
There are several simulation parameters that control a stochastic simulation. They are defined in the Stochastic Run Parameters dialog shown below. Each section of this dialog is discussed below.
Simulation Type
The simulation type and number of simulations can be set. In a Monte Carlo simulation, each specified input variable is randomly varied within a specified minimum and maximum value a given number of times. If only a few simulations are run it may not be guaranteed to fully explore the parameter space. A Latin Hypercube simulation, on the other hand, divides the range into intervals and insures that parameters are chosen from each interval. With this kind of simulation it's more likely to explore the parameter space with fewer simulations.
Stochastic Models
HEC-1 or TR-20 for hydrologic modeling, HEC-RAS for hydraulic modeling, and Floodplain Delineation are the only currently available models for stochastic modeling. For each model included, a basin input file and solution files directory needs to be defined. For HEC-1, TR-20, or HEC-RAS select the input file of the already created model. These models will have key values (negative numbers) for the input parameters that will be defined as stochastic variables. The current floodplain delineation options will be saved in the flood run file.
Add stochastic variables for any of the models. Each stochastic variable requires a key value (a negative number that has been entered in place of a parameter such as precipitation), a type, a starting value, a minimum value, a maximum value, a standard deviation, and a distribution. The distribution can be either normal or uniform and optionally defined as log.
Previous Step in Stochastic Modeling
Next Step in Stochastic Modeling
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||