WMS:HEC-HMS Properties
For HMS, all of the parameters (properties) are edited from the same HMS Properties dialog. The dialog is reached through the Edit Parameters command in the HEC-HMS menu.
This dialog offers an option to edit the parameters in seven different types of elements: Sub-basins, Junctions, Reaches, Diversions, Reservoirs, Sources, and Sinks. By allowing the choice of which type is being used, the Properties dialog allows the definition of the parameters of a project accordingly.
Each of the elements listed above is further explained in it's designated section below.
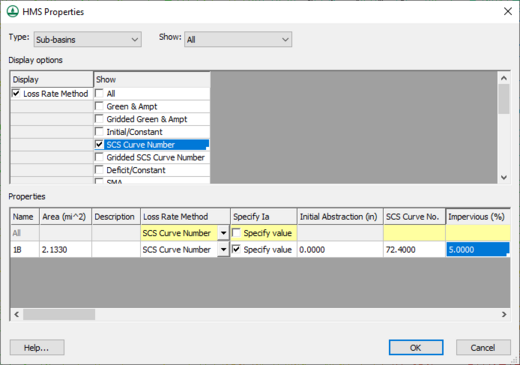
Displaying and showing options allow seeing only those variables for which to enter data. Toggling on Loss Rate Method in the Display column allows picking which method they want to use. Then toggle the display for the different parameters associated with a given methodology from the Show column.
The HMS Properties window is versatile in that it shows properties for all or selected basins, junctions, reaches, reservoirs, etc. The HMS documentation can be reviewed for detailed model formulation and behavior of the various properties, but different functions of the dialog are defined below:
- Type – Specifies which type of hydrologic unit parameters to view or edit. Options include:
- "Sub-basins" – An element/ hydraulic unit that can be defined in HMS.
- "Junctions" – An element with one or more inflows and only one outflow.
- "Reaches" – Reach routing will lag and attenuate the hydrograph computed (combined) at an outlet according to the reach properties defined.
- "Diversions" – An element of HMS that allows flow to be diverted from an outlet or drainage basin.
- "Reservoirs" – Reservoir routing is similar to the Modified-Puls reach routing method.
- "Sources" – An element that is used when wanting to run a model that is interior to a larger watershed and is defined at the headwaters of a stream within a model.
- "Sinks" – An element used when wanting to run a model that is interior to a larger watershed and is defined at the outlet of the model.
- Show – Choose to show or edit the parameters of the selected or all hydrologic units of the specified type.
- Display Options – The display options determine which properties (Display column) and which methods (Show column) are displayed/edited in the Properties spreadsheet.
- Display – Designated area for the defining the method and elements being used for the project.
- Show – The method used for showing the results.
- Properties – The properties of the selected (or all) hydrologic units are displayed as a spreadsheet for editing in this area. Only the properties and methods as determined in the display options are visible for reviewing and editing. While more than one method may have properties displayed, a method for simulation must be chosen as one of the properties. Property options are dependent on the methods chosen in the previous Display Options section.
HMS includes the following hydrologic units which can be used to define a model:
Type: Sub-Basins
Sub-basins are one of the basic hydrologic units that can be defined in an HMS model. To simulate runoff for a sub-basin, base flow, loss, and transform properties must be defined. This is done by first selecting the "Sub-basins" hydrologic unit Type from the HMS Properties dialog, and then turning on the display of the different properties and methods that to be defined. The properties are then edited in the properties table.
"Sub-basins" – An element/ hydraulic unit that can be defined in HMS and Represents surface runoff, and subsurface processes interacting with one another.
| Show | Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| All – Select to turn on all property options for Loss Rate Method | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Loss Rate Method – Property area where you enter the loss rate method being used. Options include: "Green & Ampt," "Gridded Green & Ampt," "Initial/Constant," "SCS Curve Number," "Gridded SCS Curve Number," "Deficit/Constant," "SMA," "Gridded SMA," and "No Loss Rate." Initial Loss(in) – Represents the amount of precipitation received before surface runoff. Initial Content – Should be entered in specific terms of volume ratio and represents the initial water content. Saturated Content – Should be entered in specific terms of volume ratio and represents the maximum water capacity or the total porosity of the soil. Wet. Front Suct. (in) – Must be specified and represents the texture of the soil. Conductivity (in/hr) – Must be specified and represents the hydraulic conductivity according to the specified soil texture. Impervious (%) – The amount of the sub-basin that is connected directly. Specify Ia – Specify the area of vegetation below the water's surface. Initial Abstraction (in) – Factors in all losses prior to runoff. SCS Curve No. – A Number that represents all soil group and land use combinations within the sub-basin. Initial Abstraction Ratio – Used to compute the initial abstraction at each individual grid cell. Its default is 2.0. Potential Retention Scale Factor – Used to adjust the retention formulated from the curve number prior to being multiplied by the initial abstraction ratio. Its default is 1.0. Initial Deficit (in) – The amount of water required to fill the soil layer. Loss Rate (in/hr) – The rate at which water is lost. Max Deficit (in) – The maximum amount of water allowed within the soul layer before the start of infiltration. Init Canopy (%) – The initial canopy cover above the given area. Init Surface (%) – The percentage of surface area. Init Soil (%) – The initial percentage of soil. Init Groundwater 1 (%) – The initial percentage of water found in the first groundwater layer. Init Groundwater 2 (%) – The initial percentage of water found in the second groundwater layer. Canopy Storage (in) – The amount of storage available for water in the canopy. Surface Storage (in) – The amount of storage available for water on the surface. Max Infiltration (in/hr) – The amount of maximum infiltration allowed from the surface storage into the soil. Soil Storage (in) – The amount of storage available for water in the soil layer. Tension Storage (in) – The amount of storage for water in the soil that does not drain due to the pull of gravity. Soil Percolation (in/hr) – The amount of percolation allowed by the degree of storage in both the soil and the upper groundwater. Groundwater 1 Storage (in) – A representation of the amount of water storage in the upper groundwater layer. Groundwater 1 Percolation (in/hr) – Represents the rate of percolation from the top groundwater layer into the lower groundwater layer. Groundwater 1 Coeff (hr) – Represents the amount of time lag due to the transformation of stored water becoming lateral outflow. Groundwater 2 Storage (in) – Represents the amount of water storage in the lower level of groundwater. Groundwater 2 Percolation (in/hr) – Represents the rate of the function of current storage in the lower groundwater layer. Groundwater 2 Coeff (hr) – Represents the amount of time lag due to the transformation of stored water becoming lateral outflow (Generally a larger value than the groundwater 1 coefficient). | |
| Green & Ampt | Name – The name given to the specified element in the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Loss Rate Method – Property area where you enter the loss rate method being used. Options include: "Green & Ampt," "Gridded Green & Ampt," "Initial/Constant," "SCS Curve Number," "Gridded SCS Curve Number," "Deficit/Constant," "SMA," "Gridded SMA," and "No Loss Rate." Initial Loss(in) – Represents the amount of precipitation received before surface runoff. Initial Content – Should be entered in specific terms of volume ratio and represents the initial water content. Saturated Content – Should be entered in specific terms of volume ratio and represents the maximum water capacity or the total porosity of the soil. Wet. Front Suct. (in) – Must be specified and represents the texture of the soil. Conductivity (in/hr) – Must be specified and represents the hydraulic conductivity according to the specified soil texture. Impervious (%); The roughness of the plane the percentage of water not passing through. | |
| Gridded Green & Ampt | Name – The name given to the specified element in the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the module that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Loss Rate Method – Property area where you enter the loss rate method being used. Options include: "Green & Ampt," "Gridded Green & Ampt," "Initial/Constant," "SCS Curve Number," "Gridded SCS Curve Number," "Deficit/Constant," "SMA," "Gridded SMA," and "No Loss Rate." | |
| Initial/Constant | Name – The name given to the specified element in the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the module that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Loss Rate Method – Property area where you enter the loss rate method being used. Options include: "Green & Ampt," "Gridded Green & Ampt," "Initial/Constant," "SCS Curve Number," "Gridded SCS Curve Number," "Deficit/Constant," "SMA," "Gridded SMA," and "No Loss Rate." Initial Loss(in) – Represents the amount of precipitation received before surface runoff. Constant Rate (in/hr) – Defines the infiltration rate when the soil is saturated. Impervious (%); The roughness of the plane the percentage of water not passing through. | |
| SCS Curve Number | Name – The name given to the specified element in the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the module that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Loss Rate Method – Property area where you enter the loss rate method being used. Options include: "Green & Ampt," "Gridded Green & Ampt," "Initial/Constant," "SCS Curve Number," "Gridded SCS Curve Number," "Deficit/Constant," "SMA," "Gridded SMA," and "No Loss Rate." Specify Ia – Specify the area of vegetation below the water's surface. Initial Abstraction (in) – Factors in all losses prior to runoff. SCS Curve No. – A Number that represents all soil group and land use combinations within the sub-basin. Impervious (%); The roughness of the plane the percentage of water not passing through. | |
| Gridded SCS Curve Number | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the module that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Loss Rate Method – Property area where you enter the loss rate method being used. Options include: "Green & Ampt," "Gridded Green & Ampt," "Initial/Constant," "SCS Curve Number," "Gridded SCS Curve Number," "Deficit/Constant," "SMA," "Gridded SMA," and "No Loss Rate." Initial Abstraction Ratio – Used to compute the initial abstraction at each individual grid cell. Its default is 2.0. Potential Retention Scale Factor – Used to adjust the retention formulated from the curve number prior to being multiplied by the initial abstraction ratio. Its default is 1.0. | |
| Deficit/Constant | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Loss Rate Method – Property area where you enter the loss rate method being used. Options include: "Green & Ampt," "Gridded Green & Ampt," "Initial/Constant," "SCS Curve Number," "Gridded SCS Curve Number," "Deficit/Constant," "SMA," "Gridded SMA," and "No Loss Rate." Initial Deficit (in) – The amount of water required to fill the soil layer. Loss Rate (in/hr) – The rate at which water is lost. Max Deficit (in) – The maximum amount of water allowed within the soul layer before the start of infiltration. Impervious (%) – Impervious (%); The roughness of the plane the percentage of water not passing through. | |
| SMA | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Loss Rate Method – Property area where you enter the loss rate method being used. Options include: "Green & Ampt," "Gridded Green & Ampt," "Initial/Constant," "SCS Curve Number," "Gridded SCS Curve Number," "Deficit/Constant," "SMA," "Gridded SMA," and "No Loss Rate." Init Canopy (%) – The initial canopy cover above the given area. Init Surface (%) – The percentage of surface area. Init Soil (%) – The initial percentage of soil. Init Groundwater 1 (%) – The initial percentage of water found in the first groundwater layer. Init Groundwater 2 (%) – The initial percentage of water found in the second groundwater layer. Canopy Storage (in) – The amount of storage available for water in the canopy. Surface Storage (in) – The amount of storage available for water on the surface. Max Infiltration (in/hr) – The amount of maximum infiltration allowed from the surface storage into the soil. Soil Storage (in) – The amount of storage available for water in the soil layer. Impervious (%) – Impervious (%); The roughness of the plane the percentage of water not passing through. Tension Storage (in) – The amount of storage for water in the soil that does not drain due to the pull of gravity. Soil Percolation (in/hr) – The amount of percolation allowed by the degree of storage in both the soil and the upper groundwater. Groundwater 1 Storage (in) – A representation of the amount of water storage in the upper groundwater layer. Groundwater 1 Percolation (in/hr) – Represents the rate of percolation from the top groundwater layer into the lower groundwater layer. Groundwater 1 Coeff (hr) – Represents the amount of time lag due to the transformation of stored water becoming lateral outflow. Groundwater 2 Storage (in) – Represents the amount of water storage in the lower level of groundwater. Groundwater 2 Percolation (in/hr) – Represents the rate of the function of current storage in the lower groundwater layer. Groundwater 2 Coeff (hr) – Represents the amount of time lag due to the transformation of stored water becoming lateral outflow (Generally a larger value than the groundwater 1 coefficient. | |
| Gridded SMA | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Loss Rate Method – Property area where you enter the loss rate method being used. Options include: "Green & Ampt," "Gridded Green & Ampt," "Initial/Constant," "SCS Curve Number," "Gridded SCS Curve Number," "Deficit/Constant," "SMA," "Gridded SMA," and "No Loss Rate." Init Canopy (%) – The initial canopy cover above the given area. Init Surface (%) – The percentage of surface area. Init Soil (%) – The initial percentage of soil. Init Groundwater 1 (%) – The initial percentage of water found in the first groundwater layer. Init Groundwater 2 (%) – The initial percentage of water found in the second groundwater layer. |
| Show | Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| All – Select to turn on all property options for Transform Method | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Transform Method – Allows the selection of methods to define the project. Options include: "Clark," "Kinematic Wave," "ModClark," "Snyder," "SCS," "User-Specified S-Graph," or "User-Specified UH." If none is chosen as the method then the sub-basin will change any excess precipitation as runoff in the end. Basin Data – Data pertaining to the specified basin. Map Data – Data pertaining to the specified map. Time of Concentration (hr) – Represents the maximum travel time within the sub-basin. Storage Coefficient (hr) – This accounts for the effects of storage within a linear reservoir. Overland Length (ft) – Length of a plane that contributes runoff to channels within the watershed. Slope (ft/ft) – The average slope from the area precipitation falls to the place runoff enters a channel. Roughness – The difference between the imperviousness and perviousness of a plane. % of Subbasin Area – The percentage of the subbasin area that is occupied by the given plane. Number of Steps – Communicates to the program to help it determine what the correct distance of steps is before calculating runoff. Channel Routing Method – The method used for the routing of the channel. Channel Parameters – Parameters of the channel. Second Record – Second case of recorded flow or precipitation. Time of Concentration (hr) – Represents the maximum travel time within the sub-basin. Storage Coefficient (hr) – This accounts for the effects of storage within a linear reservoir. Snyder (Standard) Lag, tp (hr) – The length of time between the centroid of precipitation mass and the peak flow of the resulting hydrograph. Snyder Peaking Coefficient, Cp – Measures the steepness of the hydrograph. SCS Lag – The amount of time recorded between each SCS time step. Time – Time of the recorded step. S-Graph – Is defined with the percentage of time lag(x) and cumulative runoff volume(y). Lag (hr) – The amount of time (in hours) between each step. | |
| Clark | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Transform Method – Allows the selection of methods to define the project. Options include: "Clark," "Kinematic Wave," "ModClark," "Snyder," "SCS," "User-Specified S-Graph," or "User-Specified UH." If none is chosen as the method then the sub-basin will change any excess precipitation as runoff in the end. Basin Data – Data pertaining to the specified basin. Map Data – Data pertaining to the specified map. Time of Concentration (hr) – Represents the maximum travel time within the sub-basin. Storage Coefficient (hr) – This accounts for the effects of storage within a linear reservoir. | |
| Kinetic Wave | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Transform Method – Allows the selection of methods to define the project. Options include: "Clark," "Kinematic Wave," "ModClark," "Snyder," "SCS," "User-Specified S-Graph," or "User-Specified UH." If none is chosen as the method then the sub-basin will change any excess precipitation as runoff in the end. Basin Data – Data pertaining to the specified basin. Map Data – Data pertaining to the specified map. Time of Concentration (hr) – Represents the maximum travel time within the sub-basin. Storage Coefficient (hr) – This accounts for the effects of storage within a linear reservoir. Overland Length (ft) – Length of a plane that contributes runoff to channels within the watershed. Slope (ft/ft) – The average slope from the area precipitation falls to the place runoff enters a channel. Roughness – The difference between the imperviousness and perviousness of a plane. % of Subbasin Area – The percentage of the subbasin area that is occupied by the given plane. Number of Steps – Communicates to the program to help it determine what the correct distance of steps is before calculating runoff. Channel Routing Method – Routing method specified for channels. Channel Parameters – Parameters of the channel. Second Record – Second case of recorded flow or precipitation. | |
| Modclark | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Transform Method – Allows the selection of methods to define the project. Options include: "Clark," "Kinematic Wave," "ModClark," "Snyder," "SCS," "User-Specified S-Graph," or "User-Specified UH." If none is chosen as the method then the sub-basin will change any excess precipitation as runoff in the end. Basin Data – Data pertaining to the specified basin. Map Data – Data pertaining to the specified map. Time of Concentration (hr) – Represents the maximum travel time within the sub-basin. Storage Coefficient (hr) – This accounts for the effects of storage within a linear reservoir. | |
| Snyder | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Transform Method – Allows the selection of methods to define the project. Options include: "Clark," "Kinematic Wave," "ModClark," "Snyder," "SCS," "User-Specified S-Graph," or "User-Specified UH." If none is chosen as the method then the sub-basin will change any excess precipitation as runoff in the end. Basin Data – Data pertaining to the specified basin. Map Data – Data pertaining to the specified map. Snyder (Standard) Lag, tp (hr) – The length of time between the centroid of precipitation mass and the peak flow of the resulting hydrograph. Snyder Peaking Coefficient, Cp – Measures the steepness of the hydrograph. | |
| SCS | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Transform Method – Allows the selection of methods to define the project. Options include: "Clark," "Kinematic Wave," "ModClark," "Snyder," "SCS," "User-Specified S-Graph," or "User-Specified UH." If none is chosen as the method then the sub-basin will change any excess precipitation as runoff in the end. Basin Data – Data pertaining to the specified basin. Map Data – Data pertaining to the specified map. SCS Lag – The amount of time recorded between each SCS time step. Time – Time of the recorded step. | |
| User-Specified S-Graph | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Transform Method – Allows the selection of methods to define the project. Options include: "Clark," "Kinematic Wave," "ModClark," "Snyder," "SCS," "User-Specified S-Graph," or "User-Specified UH." If none is chosen as the method then the sub-basin will change any excess precipitation as runoff in the end. Basin Data – Data pertaining to the specified basin. Map Data – Data pertaining to the specified map. S-Graph – Is defined with the percentage of time lag(x) and cumulative runoff volume(y). Lag (hr) – The amount of time (in hours) between each step. | |
| User-Specified UH | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Transform Method – Allows the selection of methods to define the project. Options include: "Clark," "Kinematic Wave," "ModClark," "Snyder," "SCS," "User-Specified S-Graph," or "User-Specified UH." If none is chosen as the method then the sub-basin will change any excess precipitation as runoff in the end. Basin Data – Data pertaining to the specified basin. Map Data – Data pertaining to the specified map. Unit Graph – A visual graph that uses time units paired with flow information. |
| Show | Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| All – Select to turn on all property options for Base Flow Method | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Baseflow Method – Options include all, recession, constant monthly, linear reservoir, bounded recession, no baseflow. Initial Q – The initial value of flow. Units – The factor for measurement. Recession Constant – The rate at that baseflow recedes between storms. Threshold Type – The type of threshold applicable to the model. Threshold Q – The threshold flow. Monthly Values – Represents the monthly values collected. Groundwater 1 Storage Coefficient – The time constant for the linear reservoir of the upper groundwater. Groundwater 2 Storage Coefficient – The time constant for the linear reservoir of the second groundwater layer. Groundwater 2 Number of Reservoirs – The time constant for the linear reservoir of the lower groundwater layer. | |
| Recession | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Baseflow Method – Options include all, recession, constant monthly, linear reservoir, bounded recession, no baseflow. Initial Q – The initial value of flow. Units – The factor for measurement. Recession Constant – The rate at that baseflow recedes between storms. Threshold Type – The type of threshold applicable to the model. Threshold Q – The threshold flow. | |
| Constant Monthly | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Baseflow Method – Options include all, recession, constant monthly, linear reservoir, bounded recession, no baseflow. Monthly Values – Represents the monthly values collected. | |
| Linear Reservoir | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Baseflow Method – Options include all, recession, constant monthly, linear reservoir, bounded recession, no baseflow. Groundwater 1 Storage Coefficient – The time constant for the linear reservoir of the upper groundwater. Groundwater 2 Storage Coefficient – The time constant for the linear reservoir of the second groundwater layer. Groundwater 2 Number of Reservoirs – The time constant for the linear reservoir of the lower groundwater layer. | |
| Bounded Recession | Name – The name given to the specified element of the project.
Area (mi^2) – Area of the project that is being defined. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Baseflow Method – Options include all, recession, constant monthly, linear reservoir, bounded recession, no baseflow. Initial Q – Initial Q – The initial value of flow. Units – The factor used for measurement. Recession Ratio – Is calculated by the recession constant and the average of ratios of ordinates spaced one day apart. Monthly Values – Represents the monthly values collected. |
Unlike HEC-1, meteorological data are not defined as a sub-basin property, but rather as part of the meteorological parameters of the HMS simulation.
Type: Junctions
"A junction is an element with one or more inflows and only one outflow. All inflow is added together to produce the outflow by assuming zero storage at the junction. It is usually used to represent a river or stream confluence." (HEC, 2002)
WMS treats outlets as junctions. This means that when creating an outlet, WMS is actually creating a junction. WMS is also creating a reach when creating an outlet. The only data associated with junctions is a description. This description is exported to the HMS file when saving the file. A reach is also associated with each outlet.
Type: Reaches
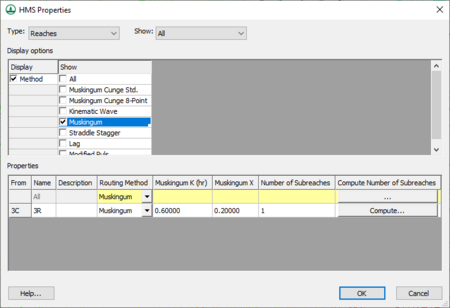
Reach routing will lag and attenuate the hydrograph computed (combined) at an outlet according to the reach properties defined. To define reach parameters, open the HMS Properties dialog, shown below, and then select the HMS Property type to be Reaches. Show or edit properties for only the selected reach(es), or for all reaches in the model. Select a reach in WMS by selecting the upstream outlet of the reach since it is from this point hydrographs are routed.
Choose to Display properties of the reach and then show one or more methods in the properties table. The method that HMS will use and the associated parameters are all edited from the properties table.
"Reaches" – The reach element represents a segment of stream or river
| Show | Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| All – Select this if multiple methods are needed. | From –
Name – The name given to the specified element of the project Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Routing Method &ndash: Options include: None, Muskingum Cunge, Muskingum Cunge 8-Point, Kinematic Wave, Muskingum, Straddle Stagger, Lag, and Modified Puls. Time Step Method – Options include: Automatic Fixed Interval and Automatic Adaption. Cross Section Shape – When kinematic wave routing method is selected the options include: circle, rectangle, trapezoid, and triangle. When the Muskingum-Cunge routing method is selected, the options include circle, rectangle, trapezoid, and triangle. Reach Length (ft) – The length of the reach in feet. Allow WMS to Update Slope – Checking this box will allow WMS to update the slope when the factors change. Energy Slope (ft/ft) – The average slope from the area precipitation falls to the place runoff enters a channel. Bottom Width/Diameter (ft) – The measurement in feet of the bottom width and diameter of the channel. Side Slope (xH:1V) – Is described as the amount of horizontal distance for each unit of vertical distance. Mannings n – A coefficient that represents the roughness that applies to the flow due to the material of the channel. Mannings Left Overbank – A coefficient that represents the roughness of the left river bank. Mannings Channel – A coefficient that represents the roughness of the channel. Mannings Right Overbank – A coefficient that represents the roughness of the right river bank. Min Number of Routing Increments – Muskingum K (hr) – Coefficient in hours for entire reach. Muskingum X – Weighting coefficient. Number of Subreaches – This is used to hint to the program about when to determine the proper distance step to use during routing calculations. Lag (min) – The amount of time (in minutes) between each step. Straddle Duration (min) – The duration of attenuation. Time – Time of the recorded step. Options include hours and minutes. Storage-Outflow – The degree of storage given by the outflow. Initial Condition – Outflow=Inflow and Outflow. Outflow Value – The coefficient assigned to the outflow of water | |
| Muskingum Cunge Std. – Defined by the channel's length, shape, and slope. | From –
Name – The name given to the specified element of the project Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Routing Method – Options include: None, Muskingum Cunge, Muskingum Cunge 8-Point, Kinematic Wave, Muskingum, Straddle Stagger, Lag, and Modified Puls. Time Step Method – Options include: Automatic Fixed Interval and Automatic Adaption. Cross Section Shape – When kinematic wave routing method is selected the options include: circle, rectangle, trapezoid, and triangle. When the Muskingum-Cunge routing method is selected, the options include circle, rectangle, trapezoid, and triangle. Reach Length (ft) – The length of the reach in feet. Allow WMS to Update Slope – Checking this box will allow WMS to update the slope when the factors change. Energy Slope (ft/ft) – The average slope from the area precipitation falls to the place runoff enters a channel. Bottom Width/Diameter (ft) – The measurement in feet of the bottom width and diameter of the channel. Side Slope (xH:1V) – Is described as the amount of horizontal distance for each unit of vertical distance. Mannings n – A coefficient that represents the roughness that applies to the flow due to the material of the channel. | |
| Muskingum Cunge 8-Point – Defined by the channel's length, shape, and slope. | From –
Name – The name given to the specified element of the project. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Routing Method – Options include: None, Muskingum Cunge, Muskingum Cunge 8-Point, Kinematic Wave, Muskingum, Straddle Stagger, Lag, and Modified Puls. Time Step Method – Options include: Automatic Fixed Interval and Automatic Adaption. Reach Length (ft) – The length of the reach in feet. Energy Slope (ft/ft) – The average slope from the area precipitation falls to the place runoff enters a channel. Mannings Left Overbank – A coefficient that represents the roughness of the left river bank. Mannings Channel – A coefficient that represents the roughness of the channel. Mannings Right Overbank – A coefficient that represents the roughness of the right river bank. Cross Section – The cross-section of the reach. | |
| Kinematic Wave – Defined by the channel's length, shape, and slope – Ignores inertial and pressure forces to estimate the full unsteady flow equations. | From –
Name – The name given to the specified element of the project. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Routing Method – Options include: None, Muskingum Cunge, Muskingum Cunge 8-Point, Kinematic Wave, Muskingum, Straddle Stagger, Lag, and Modified Puls. Cross Section Shape – When kinematic wave routing method is selected the options include: circle, rectangle, trapezoid, and triangle. When the Muskingum-Cunge routing method is selected, the options include circle, rectangle, trapezoid, and triangle. Reach Length (ft) – The length of the reach in feet. Allow WMS to Update Slope – Checking this box will allow WMS to update the slope when the factors change. Energy Slope (ft/ft) – The average slope from the area precipitation falls to the place runoff enters a channel. Bottom Width/Diameter (ft) – The measurement in feet of the bottom width and diameter of the channel. Side Slope (xH:1V) – Is described as the amount of horizontal distance for each unit of vertical distance. Mannings n – A coefficient that represents the roughness that applies to the flow due to the material of the channel. Min Number of Routing Increments – | |
| Muskingum – Dependent primarily upon an input weighting factor for the reach. | From –
Name – The name given to the specified element of the project. Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Routing Method – Options include: None, Muskingum Cunge, Muskingum Cunge 8-Point, Kinematic Wave, Muskingum, Straddle Stagger, Lag, and Modified Puls. Muskingum K (hr) – Coefficient in hours for entire reach. Muskingum X – Weighting coefficient. Number of Subreaches – This is used to hint to the program about when to determine the proper distance step to use during routing calculations. Compute Number of Subreaches – The step used to calculate the number of reaches. | |
| Straddle Stagger – This requires the number of ordinates to lag and the duration. | From –
Name – The name given to the specified element of the project Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Routing Method – Options include: None, Muskingum Cunge, Muskingum Cunge 8-Point, Kinematic Wave, Muskingum, Straddle Stagger, Lag, and Modified Puls. Lag (min) – The amount of time (in minutes) between each step. Straddle Duration (min) – Duration of attenuation. | |
| Lag – Lags the hydrograph without any attenuation. The only parameter for this method is the lag time with its accompanying units (minutes or hours). | From –
Name – The name given to the specified element of the project Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Routing Method – Options include: None, Muskingum Cunge, Muskingum Cunge 8-Point, Kinematic Wave, Muskingum, Straddle Stagger, Lag, and Modified Puls. Lag – The amount of time (in minutes) between each step. Time – Time of the recorded step. Options include: Hours and Minutes. | |
| Modified Puls – Uses a storage routing technique or level-pool routing. | From –
Name – The name given to the specified element of the project Description – A description of the element to which properties will be assigned. Routing Method – Options include: None, Muskingum Cunge, Muskingum Cunge 8-Point, Kinematic Wave, Muskingum, Straddle Stagger, Lag, and Modified Puls. Number of Subreaches – This is used to hint to the program about when to determine the proper distance step to use during routing calculations. Storage-Outflow – The degree of storage given by the outflow. Initial Condition – The initial condition of the reach. Outflow Value – The coefficient assigned to the outflow of water. |
Using the basin data computed by WMS when a TIN or DEM is used to delineate the watershed, the K coefficient and the number of sub reaches can easily be estimated. K is essentially the travel time for the reach, which can be estimated by noting the length of the stream segment (see this by displaying in the Muskingum Cunge method) and multiplying by an assumed channel velocity (1-5 ft/s would be appropriate for most natural channels). Convert the estimated travel times from seconds to hours before entering it into the K property field. The sub-reaches value is the number of time steps the flood wave is in the channel and can be determined by dividing K by the computational time step found in the Job Control dialog (again be sure that units are consistent). A button exists in the Muskingum K property field so that these computations can be done directly within WMS.
Type: Diversions
HMS allows the flow to be diverted from an outlet or drainage basin. This flow can be thought of as leaving the normal drainage system at that point. It can be retrieved at a downstream outlet where the diverted flow then contributes to the flow at that outlet. If no downstream retrieval outlet point is specified, the flow simply leaves the system at the diverted outlet point and never returns (similar to a sink).
Diversion Data
Diversions are created using a combination of the Add Diversions and Retrieve Diversion commands found in the Tree menu. Once created, data for the diversion can be defined and/or edited by using the HEC-HMS Properties dialog.
The following data should be defined for a diversion:
- Name – The name identification string of the diversion as used on the DT record. It is important to assign a unique name to each diversion in a given model because this name is used by WMS and by HEC-1 to identify the diversion.
- Max Volume – Maximum volume of diverted flow in acre-feet (1000 cu m).
- Peak Flow – Peak flow that can be diverted in any computation period in cfs (cms).
- The flow capacity of a stream flow diversion is specified using an inflow and outflow table. This table is defined with the XY Series Editor.
Type: Reservoirs
Reservoir routing is similar to the Modified-Puls reach routing method. The difference is that relationships between elevation-storage and elevation-outflow can be used to determine the storage-outflow curve. This input can either be in the form of:
- Storage-Outflow (same as reach routing)
- Elevation-Storage-Outflow
- Elevation-Area-Outflow
Also, establish the initial conditions (whether there is storage), and the number of sub-reaches.
Type: Sources
If wanting to run a model that is interior to a larger watershed then define a source at the headwaters of a stream within a model. A source can be defined either as a hydrograph or a constant flow rate. Sources can only be defined at outlet points that do not have upstream reaches or basins defined, i.e. the stream headwaters.
Before defining a source in the HMS properties dialog, first add the source to the outlet. This is done using the Add | Source command from the Tree menu.
Type: Sinks
If wanting to run a model that is interior to a larger watershed then define a sink at the outlet of the model. A sink can be defined either as a hydrograph or a constant flow rate. Sinks can only be defined at outlet points that do not have downstream reaches.
Before defining a sink the HMS properties dialog, first add the sink to the outlet. This is done using the Add | Sink command from the Tree menu.
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||