WMS:Search Radius and Flow Distance: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:FloodedAreasDelineated.jpg|thumb|225 px|Flooded areas delineated using a 2,000 foot search radius]] | ||
The floodplain delineation process offers several options for selecting water levels that are used in the interpolation. As expected, these options and the values of the parameters used in the process affect the resulting floodplain delineation. Therefore, care must be taken in selecting these options and appropriate values. | The floodplain delineation process offers several options for selecting water levels that are used in the interpolation. As expected, these options and the values of the parameters used in the process affect the resulting floodplain delineation. Therefore, care must be taken in selecting these options and appropriate values. | ||
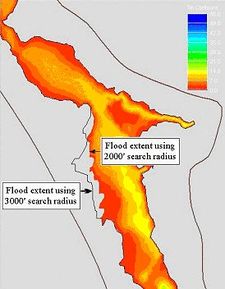
The effect of search radius and flow distance are demonstrated in the figure shown below. The figure shows the flooded areas delineated using a 2,000 foot search radius and flow distance in the shades of colors. The line represents the extent of flooding delineated using a 3,000 foot search radius and flow distance. For most places along the river these two flood extents coincide except in the west side of the middle portion. In that area a 3,000 foot search radius and flow distance resulted in more flooding than the 2,000 foot search radius and flow distance. This indicates the earlier the process could not compute flooding in that area because of the 2,000 foot limit. The water levels that could flood that area were discarded because they were outside of the 2,000 foot search radius or flow distance. To avoid this kind of problem, floodplains should be delineated by increasing the search radius and the flow distance until the flood extents stop changing. The final extent would then be the extent determined by the topography not by the search radius and flow distance. | The effect of search radius and flow distance are demonstrated in the figure shown below. The figure shows the flooded areas delineated using a 2,000 foot search radius and flow distance in the shades of colors. The line represents the extent of flooding delineated using a 3,000 foot search radius and flow distance. For most places along the river these two flood extents coincide except in the west side of the middle portion. In that area a 3,000 foot search radius and flow distance resulted in more flooding than the 2,000 foot search radius and flow distance. This indicates the earlier the process could not compute flooding in that area because of the 2,000 foot limit. The water levels that could flood that area were discarded because they were outside of the 2,000 foot search radius or flow distance. To avoid this kind of problem, floodplains should be delineated by increasing the search radius and the flow distance until the flood extents stop changing. The final extent would then be the extent determined by the topography not by the search radius and flow distance. | ||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
* [[WMS:Overview of | * [[WMS:Overview of Floodplain Delineation|Overview of Floodplain Delineation]] | ||
* [[WMS:Delineate | * [[WMS:Delineate Floodplain|Delineate Floodplain]] | ||
* [[WMS:Flow Paths and Barrier Coverages|Flow Paths and Barrier Coverages]] | * [[WMS:Flow Paths and Barrier Coverages|Flow Paths and Barrier Coverages]] | ||
{{WMSMain}} | {{WMSMain}} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:10, 8 December 2016
The floodplain delineation process offers several options for selecting water levels that are used in the interpolation. As expected, these options and the values of the parameters used in the process affect the resulting floodplain delineation. Therefore, care must be taken in selecting these options and appropriate values.
The effect of search radius and flow distance are demonstrated in the figure shown below. The figure shows the flooded areas delineated using a 2,000 foot search radius and flow distance in the shades of colors. The line represents the extent of flooding delineated using a 3,000 foot search radius and flow distance. For most places along the river these two flood extents coincide except in the west side of the middle portion. In that area a 3,000 foot search radius and flow distance resulted in more flooding than the 2,000 foot search radius and flow distance. This indicates the earlier the process could not compute flooding in that area because of the 2,000 foot limit. The water levels that could flood that area were discarded because they were outside of the 2,000 foot search radius or flow distance. To avoid this kind of problem, floodplains should be delineated by increasing the search radius and the flow distance until the flood extents stop changing. The final extent would then be the extent determined by the topography not by the search radius and flow distance.
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||