SMS:1D Hyd Cross Section Coverage: Difference between revisions
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
; Assign centerline coverage : This command allows selecting which centerline coverage to associate the cross section coverage. Opens a ''Select Tree Item'' dialog to select the centerline coverage. | ; Assign centerline coverage : This command allows selecting which centerline coverage to associate the cross section coverage. Opens a ''Select Tree Item'' dialog to select the centerline coverage. | ||
; Generate centerline coverage : Creates a centerline coverage from the cross section point properties. Brings up the ''Generate Arcs'' dialog where the point properties can be defined. If adjacent cross sections both have the specified point property, an arc will be created in the centerline coverage connecting the two points. This arc will then be assigned to be the same type as the point property type. This command requires a cross section database and that the cross sections be in sequential order. | ; Generate centerline coverage : Creates a centerline coverage from the cross section point properties. Brings up the ''Generate Arcs'' dialog where the point properties can be defined. If adjacent cross sections both have the specified point property, an arc will be created in the centerline coverage connecting the two points. This arc will then be assigned to be the same type as the point property type. This command requires a cross section database and that the cross sections be in sequential order. | ||
; Remove invalid cross section segments : This command deletes cross sections that do not cross the centerline. Cross sections that are not "functional" with respect to the centerline are trimmed to include only the portion of the cross section that intersects the centerline and is functional. In this case, functional implies that the cross section is getting monotonically farther away from the centerline as you trace the cross section in either direction from the centerline. The functionality of the cross section is determined by the closest point on the centerline to each individual point on the cross section. This command requires that a centerline coverage be assigned to the cross section coverage. The cross section database (if one exists) will not be updated to match. | ; Remove invalid cross section segments : This command deletes cross sections that do not cross the centerline. Cross sections that are not "functional" with respect to the centerline are trimmed to include only the portion of the cross section that intersects the centerline and is functional. In this case, functional implies that the cross section is getting monotonically farther away from the centerline as you trace the cross section in either direction from the centerline. The functionality of the cross section is determined by the closest point on the centerline to each individual point on the cross section. This command requires that a centerline coverage be assigned to the cross section coverage. The cross section database (if one exists) will not be updated to match. | ||
; Reverse right → left cross sections : Checks the order of all cross section arcs that intersect the associated centerline. If the cross section arc intersects the centerline arc in a right to left direction (looking down stream), the arc direction is reversed. Only changes the feature data. The cross section database (if one exists) will not be updated to match. | ; Reverse right → left cross sections : Checks the order of all cross section arcs that intersect the associated centerline. If the cross section arc intersects the centerline arc in a right to left direction (looking down stream), the arc direction is reversed. Only changes the feature data. The cross section database (if one exists) will not be updated to match. | ||
; Remove unassigned cross section from database : Removes cross sections that have not been assigned from the cross section database. Requires a cross section database. | ; Remove unassigned cross section from database : Removes cross sections that have not been assigned from the cross section database. Requires a cross section database. | ||
; Reproject cross sections : Automatically runs the '''Reverse right → left cross sections''' command and the '''Remove invalid cross section segments''' command. Each cross section arcs is projected to a line that intersects the centerline arc perpendicular to that arc at the same location the cross section arc intersects the centerline arc. Each point on the cross section arc is projected to the perpendicular intersector in the direction of the centerline closest to that point. Note: this is not always the intersection point/direction. If a cross section database exists, it will be out of date after executing this command. A centerline coverage must be assigned to the cross section coverage for this feature. | ; Reproject cross sections : Automatically runs the '''Reverse right → left cross sections''' command and the '''Remove invalid cross section segments''' command. Each cross section arcs is projected to a line that intersects the centerline arc perpendicular to that arc at the same location the cross section arc intersects the centerline arc. Each point on the cross section arc is projected to the perpendicular intersector in the direction of the centerline closest to that point. Note: this is not always the intersection point/direction. If a cross section database exists, it will be out of date after executing this command. A centerline coverage must be assigned to the cross section coverage for this feature. | ||
==Extracting Cross Sections== | ==Extracting Cross Sections== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 28: | ||
Line properties can be determined from an area property coverage by intersecting the cross section arcs with the area property polygons and marking them in the cross section database. | Line properties can be determined from an area property coverage by intersecting the cross section arcs with the area property polygons and marking them in the cross section database. | ||
Elevation for the cross sections can be extracted from the active scatter set or from arc nodes and vertices. After extracting cross sections using a scatter set, vertices are added to the cross section to match what is in the database. The z values are copied to all points. Use the arc nodes and vertices option if there are concerns about the triangulation of the scatter set. | Elevation for the cross sections can be extracted from the active scatter set, raster file, or from arc nodes and vertices. After extracting cross sections using a scatter set, vertices are added to the cross section to match what is in the database. The z values are copied to all points. Use the arc nodes and vertices option if there are concerns about the triangulation of the scatter set. | ||
=== Cross Section Database === | === Cross Section Database === | ||
<!--Obsolete: When extracting the cross sections, a prompt will appear asking for the name of a cross section database file.--> | <!--Obsolete: When extracting the cross sections, a prompt will appear asking for the name of a cross section database file.--> | ||
| Line 99: | Line 97: | ||
*When a trimming point type is selected, the point of that type closest to that end of the cross section will be used. | *When a trimming point type is selected, the point of that type closest to that end of the cross section will be used. | ||
*After interpolation is completed, a report dialog will appear. It includes information such as how many cross sections were created. | *After interpolation is completed, a report dialog will appear. It includes information such as how many cross sections were created. | ||
==Converting Cross Sections to a TIN== | |||
When converting cross sections to a TIN, please keep in mind the following: | |||
*Right-clicking on the coverage containing the cross sections and selecting ''Convert to'' | '''TIN''' brings up the ''Convert to TIN'' dialog.<!--need to verify name of dialog and menu options--> | |||
*This dialog allows selecting the ''Database'' option and specify any points or cross sections that should be excluded. | |||
*Any [[SMS:Breaklines|breaklines]] connecting similar classification points on adjacent cross sections will be honored and created. This includes breaklines for thalweg, channel toes, and so on. | |||
==Creating a Centerline Coverage from Annotated Cross Sections== | |||
When creating a centerline coverage from annotated cross sections, please keep in mind the following: | |||
*This tool is accessed by right-clicking on the cross section coverage and selecting '''Generate Centerline Coverage''' from the menu. | |||
*Using this tool creates a centerline and bank arcs interpolated from the thalweg and bank points on the cross sections. | |||
==Using HEC-RAS Cross Section Data== | |||
When using HEC-RAS cross section data, please keep in mind the following: | |||
*The HEC-RAS project used must be [[SMS:Images#Geo-Referencing|georeferenced]]. | |||
*The GIS data must be exported from the HEC-RAS project, creating a "**RASexport.sdf" file, where the "**" is the name of the project. | |||
*The exported data must include bank points to allow for trimming of the cross sections. | |||
*The exported data must include a centerline to facilitate interpolation. If a centerline is not included in the exported data, one can be created after the exported HEC-RAS data is imported into SMS. | |||
==Related Topics== | ==Related Topics== | ||
Latest revision as of 22:31, 15 August 2022
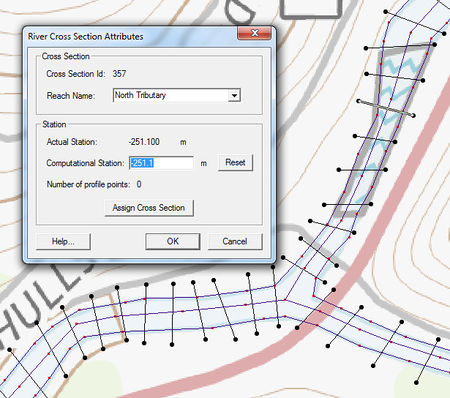
The 1D-Hydraulic Cross Section coverage is used to identify the cross section stations in the hydraulic model, and can also be used to automatically cut a cross section from an underlying digital terrain model. The attributes of a cross section feature arc is the cross section itself, along with the other parameters that define its topology in the model and include: a cross section ID (internally assigned), the reach name (inherited from the centerline arc it intersects), the station (inherited from the centerline), and any specific model attributes. The 1D-Hydraulic coverage is used in conjunction with the cross sections and digital terrain model in order to determine the thalweg position (from the centerline arc) and the left and right bank points (from the bank arcs).
A cross section is assigned automatically when cutting the cross sections, or can be assigned manually (imported from a file or entered directly) using the cross section editor.
See the help for Editing Cross Sections to learn more about how cross sections are managed and edited.
Coverage Specific Right-Click Commands
The 1D Hyd Cross Section Coverage contains all the standard commands in its right-click menu. The coverage also contains a couple specific commands unique to its right-click menu. These commands include:
- Add Arcs to Mesh
- Adds all cross section arcs to an existing mesh.
- Extract cross sections
- Brings up the Extract Cross Sections dialog where a cross section database can be created from the cross sections in the coverage.
- Summary table
- Brings up the Summary Table Options dialog which allows viewing calculations along cross section arcs.
- Convert To | Map → 2D Scatter
- This command functions similar to how it works with other coverages with one exception. The option to convert a cross section database is given in the Map → 2D Scatter dialog. Using this option will bring the Cross Section Features dialog where attributes of the cross section database and be selected for exclusion in the scatter set.
- Assign centerline coverage
- This command allows selecting which centerline coverage to associate the cross section coverage. Opens a Select Tree Item dialog to select the centerline coverage.
- Generate centerline coverage
- Creates a centerline coverage from the cross section point properties. Brings up the Generate Arcs dialog where the point properties can be defined. If adjacent cross sections both have the specified point property, an arc will be created in the centerline coverage connecting the two points. This arc will then be assigned to be the same type as the point property type. This command requires a cross section database and that the cross sections be in sequential order.
- Remove invalid cross section segments
- This command deletes cross sections that do not cross the centerline. Cross sections that are not "functional" with respect to the centerline are trimmed to include only the portion of the cross section that intersects the centerline and is functional. In this case, functional implies that the cross section is getting monotonically farther away from the centerline as you trace the cross section in either direction from the centerline. The functionality of the cross section is determined by the closest point on the centerline to each individual point on the cross section. This command requires that a centerline coverage be assigned to the cross section coverage. The cross section database (if one exists) will not be updated to match.
- Reverse right → left cross sections
- Checks the order of all cross section arcs that intersect the associated centerline. If the cross section arc intersects the centerline arc in a right to left direction (looking down stream), the arc direction is reversed. Only changes the feature data. The cross section database (if one exists) will not be updated to match.
- Remove unassigned cross section from database
- Removes cross sections that have not been assigned from the cross section database. Requires a cross section database.
- Reproject cross sections
- Automatically runs the Reverse right → left cross sections command and the Remove invalid cross section segments command. Each cross section arcs is projected to a line that intersects the centerline arc perpendicular to that arc at the same location the cross section arc intersects the centerline arc. Each point on the cross section arc is projected to the perpendicular intersector in the direction of the centerline closest to that point. Note: this is not always the intersection point/direction. If a cross section database exists, it will be out of date after executing this command. A centerline coverage must be assigned to the cross section coverage for this feature.
Extracting Cross Sections
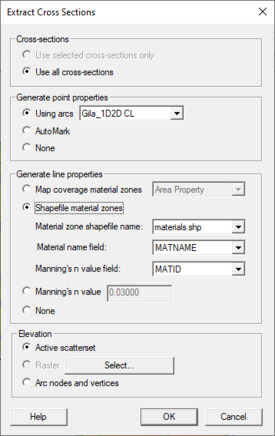
The Extract Cross sections command uses the cross section arcs and a digital terrain model (TINs are the only source that can currently be used) to extract the elevations at vertices of the feature arc cross sections, or at the intersection points with the triangles.
Cross sections for individual arcs may be extracted by selecting the arc(s) before choosing the Extract Cross Sections command. If not cross sections are selected then the Use All Cross Sections option is used.
Point properties (thalweg, left bank, right bank) can be defined from a 1D-Hydraulic Centerline coverage, or by AutoMark. The AutoMark option will examine the elevations of the extracted cross sections and try to infer the thalweg (low point) and the left and right bank points (change of slope) automatically.
Line properties can be determined from an area property coverage by intersecting the cross section arcs with the area property polygons and marking them in the cross section database.
Elevation for the cross sections can be extracted from the active scatter set, raster file, or from arc nodes and vertices. After extracting cross sections using a scatter set, vertices are added to the cross section to match what is in the database. The z values are copied to all points. Use the arc nodes and vertices option if there are concerns about the triangulation of the scatter set.
Cross Section Database
SMS stores all of the cross section information in the project file. The cross section database can also be edited independently using the Cross Section Editor tools. Extracting cross sections with feature arcs is only way to generate cross section information, they also can be imported from spreadsheet files (cut and paste), or entered manually.
Summary Table
The summary table is a tool that allows viewing calculations along cross section arcs in a project. To use the summary table, there must exist a cross section coverage, centerline coverage, and geometry (i.e. grid, mesh, scatter). To access the summary table, right-click on the 1D-Hydraulic Cross Section coverage and select Summary Table....
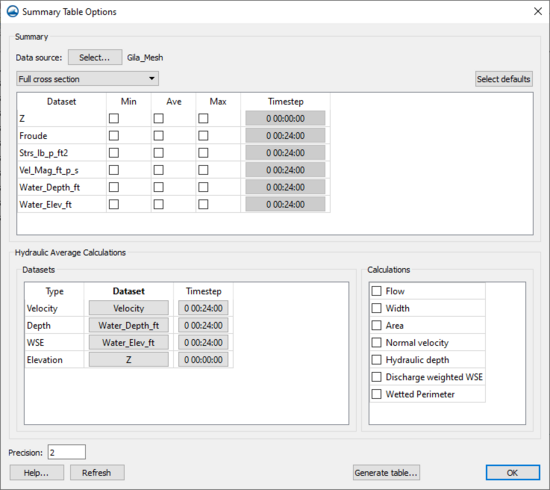
Summary Table Options
The Summary Table Options dialog is where which desired calculations are specified, as well as which geometry to use, and which portions of the cross section should be used.
- Data Source – The Data source Select button brings up a Select Tree Item dialog. This dialog is used to select the geometry that has the datasets for the calculations.
- Cross section options – There are three options for the cross sections: "Full cross section", "Main channel only", and "Overbanks and main channel".
- "Full cross section" – This option is used when there is no cross section database, overbanks have not been specified, or if the calculations should be done over the entire cross section.
- "Main channel only" – This option can only be used if there is a cross section database. The calculations will be performed only on the main channel portion of the cross section , defined as the space between the right and left overbanks.
- "Overbanks and main channel" – This option can only be used if there is a cross section database. The calculations will be performed on three separate portions of the cross section: the left overbank, main channel, and right overbank.
- Datasets – After selecting a data source, the spreadsheet will be populated with all of the scalar datasets that belong to the data source. For each dataset, toggle on minimum, average, and maximum to be calculated, as well as select the dataset time step to be used. To calculated the minimum, maximum, and average values for each cross section, SMS will interpolate the values from the dataset to the points along the cross section. These interpolated values will then be used to determine the minimum, maximum, and average value.
- Defaults – The Select defaults button will search for common dataset keywords in the list and automatically turn on the average calculation. The keywords are: "water_elev", "wse", "vel_mag", "vmag", and "froude".
- Calculations – Some other helpful calculations are available in the Calculations section.
- Flow – To calculate the flow over the cross sections, it is necessary to specify a velocity dataset (vector) and a depth dataset (scalar). SMS will then calculate the flow over the cross section at the specified time step.
- Width – To calculate the width of the cross sections, it is necessary to specify an elevation dataset and a water surface elevation dataset. SMS then compares the water surface elevation with the cross section elevation to determine the width.
- Area – Calculates the total area of each cross section. It is necessary to specify a depth dataset, an elevation dataset, and a watersurface elevation dataset.
- Normal Velocity – Determines the normal velocity for each cross section. It is necessary to specify a velocity dataset, a depth dataset, an elevation dataset, and a watersurface elevation dataset.
- Hydraulic Depth – Calculates the hydraulic depths of each cross section. It is necessary to specify a velocity dataset, a depth dataset, and a watersurface elevation dataset.
- Discharge Weighted WSE – Calculates the discharge weighted water surface elevation. It is necessary to specify a velocity dataset, a depth dataset, and a watersurface elevation dataset.
- Wetted Perimeter – Calucalates the wetted perimeter. It is necessary to specify an elevation dataset and a watersurface elevation dataset.
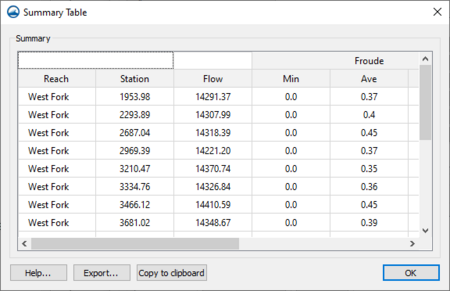
Summary Table
Once all of the options are set, click on Generate table... to have SMS compute the desired values and display them in a table.
Creating a Cross Section Database from Text
A Cross Section Database can be created by extracting data from feature arcs, manually entering cross section data within a project, importing the cross section data from a spreadsheet, or by importing the data from specially-formatted text file. When importing data from a text file, please keep in mind the following:
- Import the data as Feature Data
- Make sure the Cross section coverage option is turned on. A 1D Cross Section coverage must exist.
- The text file must have an XS ID or Station ID column. This defines the points found in each cross section.
- The cross section points in the text file must be in sequential order unless there is a distance column in the text data file.
- A PT column can be used to assign special points. These are used to annotate features such as thalweg, left bank, right bank, left toe, right toe, abutment, pier, and so on.
- It is not recommended that the PT column be the final/last column in the text data file.
- Content should be included in the PT column in the first few rows to make sure the import wizard recognizes the column.
- If the data on the first few rows does not contain a PT type, a dummy PT type can be used to make sure the import wizard recognizes the column.
Interpolating Cross Sections Along a Centerline
When interpolating cross sections along a centerline, please keep in mind the following:
- Both a 1D Cross Section coverage and a 1D Centerline coverage (including a centerline arc) are required.
- All of the cross sections must intersect the centerline arc.
- When interpolating, SMS uses the centerline arc to orient the interpolated cross sections. Keep in mind that interpolated cross sections:
- Are created from two bounding cross sections in the cross section database.
- Have an interpolated skew angle to the centerline.
- Have interpolated bends for each bend in the bounding cross section.
- Orientation is based on the centerline, so it is recommended that the centerline be smoother than the desired cross section spacing.
- At least two adjacent cross sections must be selected before initiating interpolation by right-clicking in the Graphics Window and selecting Interpolate Cross Sections.
- When specifying the spacing option, it can be either a specific distance or a specific number of cross sections between each pair of bounding cross sections.
- If points should be excluded from the interpolation, be sure to specify them in the Excluded Features dialog.
- Examples of points that might be excluded include pier locations or water surface points.
- Examples of cross sections that might be excluded include those with specific point types (such as bridge cross sections).
- After interpolation is completed, a report dialog will appear. It includes information such as how many cross sections were created.
Trimming Cross Sections to Annotation Type
When trimming cross section to annotation type, please keep in mind the following:
- A 1D Cross Section coverage must exist, and it should have feature points identified (such as bank arcs).
- Right-clicking after selecting the desired cross section and selecting Trim to bring up the Trim dialog. This dialog allows selection of the trimming points for each end (left and/or right) of the cross section.
- When a trimming point type is selected, the point of that type closest to that end of the cross section will be used.
- After interpolation is completed, a report dialog will appear. It includes information such as how many cross sections were created.
Converting Cross Sections to a TIN
When converting cross sections to a TIN, please keep in mind the following:
- Right-clicking on the coverage containing the cross sections and selecting Convert to | TIN brings up the Convert to TIN dialog.
- This dialog allows selecting the Database option and specify any points or cross sections that should be excluded.
- Any breaklines connecting similar classification points on adjacent cross sections will be honored and created. This includes breaklines for thalweg, channel toes, and so on.
Creating a Centerline Coverage from Annotated Cross Sections
When creating a centerline coverage from annotated cross sections, please keep in mind the following:
- This tool is accessed by right-clicking on the cross section coverage and selecting Generate Centerline Coverage from the menu.
- Using this tool creates a centerline and bank arcs interpolated from the thalweg and bank points on the cross sections.
Using HEC-RAS Cross Section Data
When using HEC-RAS cross section data, please keep in mind the following:
- The HEC-RAS project used must be georeferenced.
- The GIS data must be exported from the HEC-RAS project, creating a "**RASexport.sdf" file, where the "**" is the name of the project.
- The exported data must include bank points to allow for trimming of the cross sections.
- The exported data must include a centerline to facilitate interpolation. If a centerline is not included in the exported data, one can be created after the exported HEC-RAS data is imported into SMS.
Related Topics
SMS – Surface-water Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | 1D Grid • Cartesian Grid • Curvilinear Grid • GIS • Map • Mesh • Particle • Quadtree • Raster • Scatter • UGrid |  |
| General Models: | 3D Structure • FVCOM • Generic • PTM | |
| Coastal Models: | ADCIRC • BOUSS-2D • CGWAVE • CMS-Flow • CMS-Wave • GenCade • STWAVE • WAM | |
| Riverine/Estuarine Models: | AdH • HEC-RAS • HYDRO AS-2D • RMA2 • RMA4 • SRH-2D • TUFLOW • TUFLOW FV | |
| Aquaveo • SMS Tutorials • SMS Workflows | ||