WMS:Feature Objects to Geodatabase: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
If choosing to map the WMS coverage attributes manually, the user will be prompted for each feature class created in the new geodatabase, which can take a while. If choosing to let WMS map the attributes, the user will not be prompted and WMS will build the geodatabase automatically. | If choosing to map the WMS coverage attributes manually, the user will be prompted for each feature class created in the new geodatabase, which can take a while. If choosing to let WMS map the attributes, the user will not be prompted and WMS will build the geodatabase automatically. | ||
[[Image:GIS FeatureToGeodatabase.png|thumb|none|left|400 px|''Feature Objects to Geodatabase Mapping'' dialog]] | [[Image:GIS FeatureToGeodatabase.png|thumb|none|left|400 px|''Feature Objects to Geodatabase Mapping'' dialog]] | ||
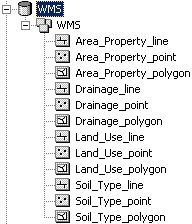
Once WMS has finished building the geodatabase, users can view the results in ArcCatalog or ArcMap. WMS will have created a new geodatabase with a single feature dataset, with feature classes for the points, lines, and polygons of each WMS coverage. | Once WMS has finished building the geodatabase, users can view the results in ArcCatalog or ArcMap. WMS will have created a new geodatabase with a single feature dataset, with feature classes for the points, lines, and polygons of each WMS coverage. | ||
[[Image:WMSGeodatabase001.png]] | [[Image:WMSGeodatabase001.png]] | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 2 February 2016
A geodatabase is a geographic database used to store GIS information, such as features and rasters. In addition to storing data, a geodatabase allows users to set up relationships between data and create rules to validate data. Geodatabases are used in ArcGIS products.
In order to create a geodatabase from WMS, the user must first switch to the GIS module and enable ArcObjects. WMS uses the feature objects stored in each coverage to build the geodatabase.
Set up and build feature objects to add to the geodatabase and define a coordinate system for the project. Vector data are stored in feature datasets and feature classes in the geodatabase which require a common spatial reference. The spatial reference in the geodatabase is defined from the current coordinate system in WMS.
Once the data and spatial reference are defined, select Feature Objects → Geodatabase from the Mapping menu in the GIS module. At this point, the user will be prompted whether to specify which coverage attributes will be mapped to the geodatabase. Users have the option to specify which WMS coverage attributes to map over, or to let WMS map all of the appropriate attributes for the user.
If choosing to map the WMS coverage attributes manually, the user will be prompted for each feature class created in the new geodatabase, which can take a while. If choosing to let WMS map the attributes, the user will not be prompted and WMS will build the geodatabase automatically.
Once WMS has finished building the geodatabase, users can view the results in ArcCatalog or ArcMap. WMS will have created a new geodatabase with a single feature dataset, with feature classes for the points, lines, and polygons of each WMS coverage.
Related Topics
WMS – Watershed Modeling System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Modules: | Terrain Data • Drainage • Map • Hydrologic Modeling • River • GIS • 2D Grid • 2D Scatter |  |
| Models: | CE-QUAL-W2 • GSSHA • HEC-1 • HEC-HMS • HEC-RAS • HSPF • MODRAT • NSS • OC Hydrograph • OC Rational • Rational • River Tools • Storm Drain • SMPDBK • SWMM • TR-20 • TR-55 | |
| Toolbars: | Modules • Macros • Units • Digitize • Static Tools • Dynamic Tools • Drawing • Get Data Tools | |
| Aquaveo | ||